An Overview of Key Security Concepts
CIA Triad
CIA Triad – Confidentiality
“To prevent any disclosure of data without prior authorization by the owner.”
- We can force Confidentiality with encryption
- Elements such as authentication, access controls, physical security and permissions are normally used to enforce Confidentiality.
CIA Triad – Integrity
- Normally implemented to verify and validate if the information that we sent or received has not been modified by an unauthorized person of the system.
- We can implement technical controls such as algorithms or hashes (MD5, SHA1, etc.)
CIA Triad – Availability
- The basic principle of this term is to be sure that the information and data is always available when needed.
- Technical Implementations
- RAIDs
- Clusters (Different set of servers working as one)
- ISP Redundancy
- Back-Ups
Non-Repudiation – How does it apply to CIA?
“Valid proof of the identity of the data sender or receiver”
- Technical Implementations:
- Digital signatures
- Logs
Access Management
- Access criteria
- Groups
- Time frame and specific dates
- Physical location
- Transaction type
- “Needed to Know” Just access information needed for the role
- Single Sign-on (SSO)
Incident Response
“Computer security incident management involves the monitoring and detection of security events on a computer or a computer network and the execution of proper resources to those events. Means the information security or the incident management team will regularly check and monitor the security events occurring on a computer or in our network.”
Incident Management
- Events
- Incident
- Response team: Computer Security Incident Response Team (CSIRT)
- Investigation
Key Concepts – Incident Response
E-Discovery
Data inventory, helps to understand the current tech status, data classification, data management, we could use automated systems. Understand how you control data retention and backup.
Automated Systems
Using SIEM, SOA, UBA, Big data analysis, honeypots/honey-tokens. Artificial Intelligence or other technologies, we could enhance the mechanism to detect and control incidents that could compromise the tech environment.
BCP (Business Continuity Plan) & Disaster Recovery
Understand the company in order to prepare the BCP. A BIA, it’s good to have a clear understanding of the critical business areas. Also indicate if a security incident will trigger the BCP or the Disaster Recovery.
Post Incident
Root-Cause analysis, understand the difference between error, problem and isolated incident. Lessons learned and reports are a key.
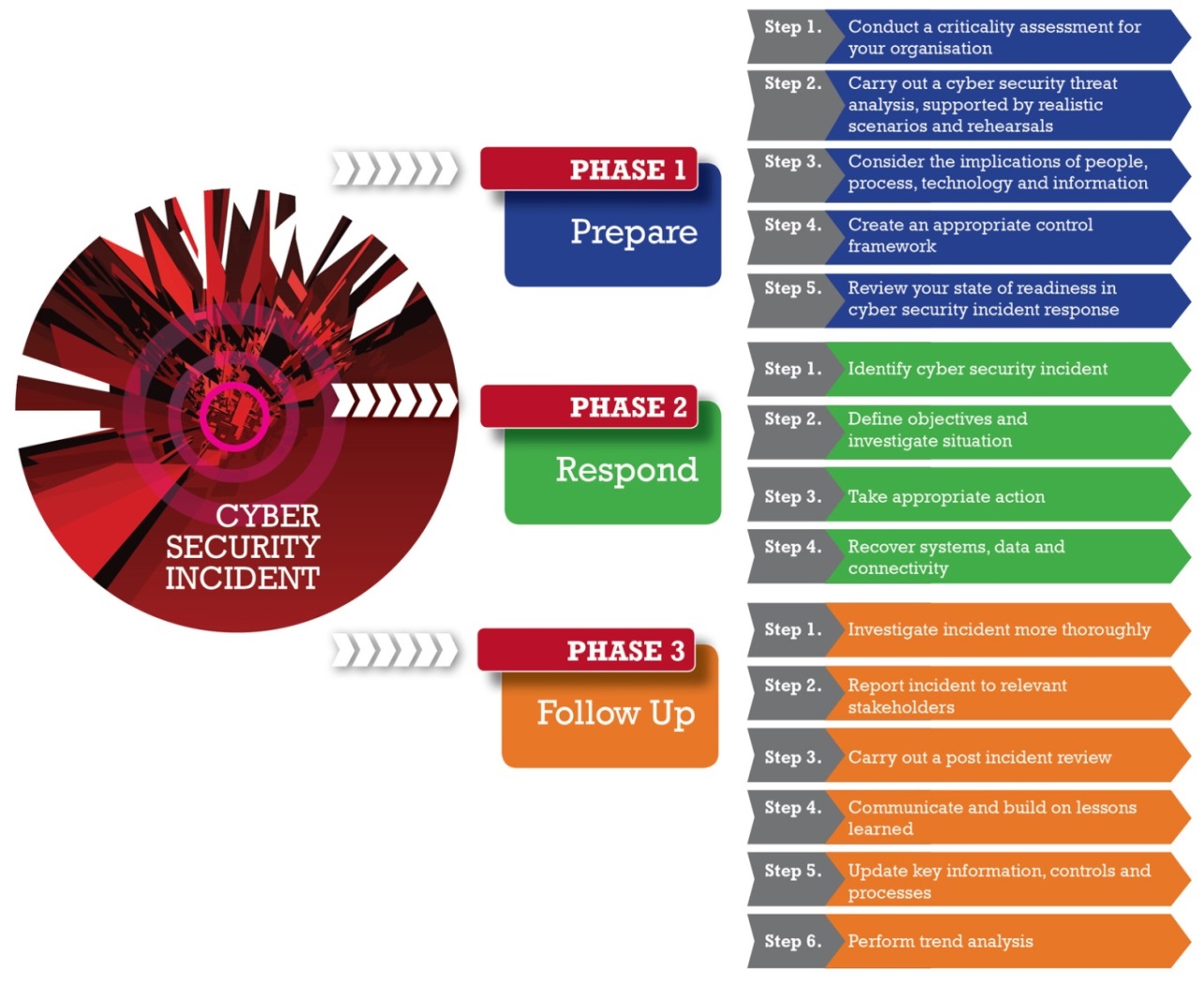
Incident Response Process
- Prepare
- Respond
- Follow up
Introduction to Frameworks and Best Practices
Best Practices, baseline, and frameworks
- Used to improve the controls, methodologies, and governance for the IT departments or the global behavior of the organization.
- Seeks to improve performance, controls, and metrics.
- Helps to translate the business needs into technical or operational needs.
Normative and compliance
- Rules to follow for a specific industry.
- Enforcement for the government, industry, or clients.
- Event if the company or the organization do not want to implement those controls, for compliance.
Best practices, frameworks, and others
- COBIT
- ITIL
- ISOs
- COSO
- Project manager methodologies
- Industry best practices
- Developer recommendations
- others
IT Governance Process
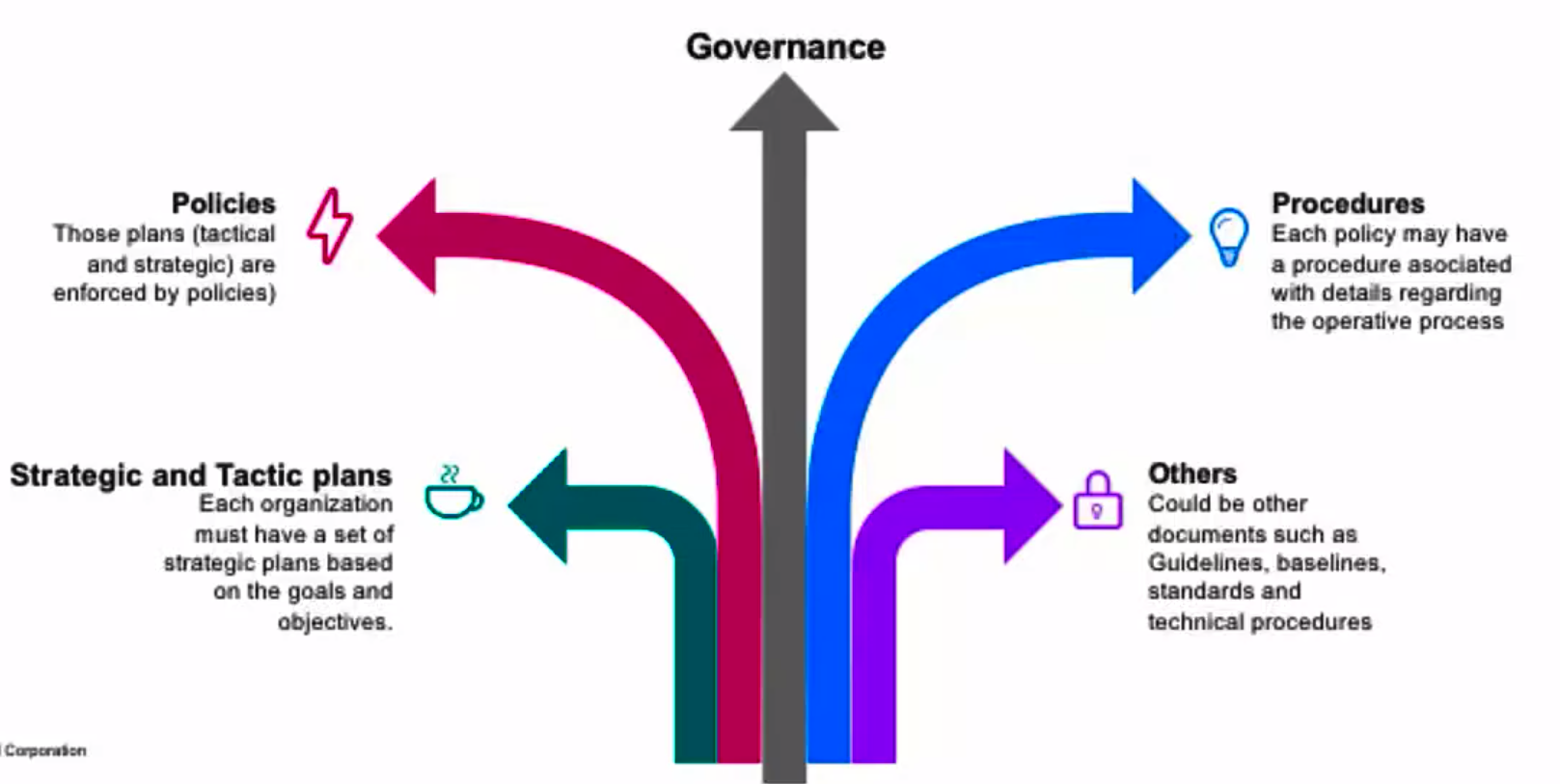
Security Policies, procedures, and other
- Strategic and Tactic plans
- Procedures
- Policies
- Governance
- Others
Cybersecurity Compliance and Audit Overview
Compliance;
- SOX
- HIPAA
- GLBA
PCI/DSS
- Audit
- Define audit scope and limitations
- Look for information, gathering information
- Do the audit (different methods)
- Feedback based on the findings
- Deliver a report
- Discuss the results
Pentest Process and Mile 2 CPTE Training
Pentest – Ethical Hacking
A method of evaluating computer and network security by simulating an attack on a computer system or network from external and internal threats.