Fundamentals of Human-Computer Interaction: users, usability, tasks, and cognitive models
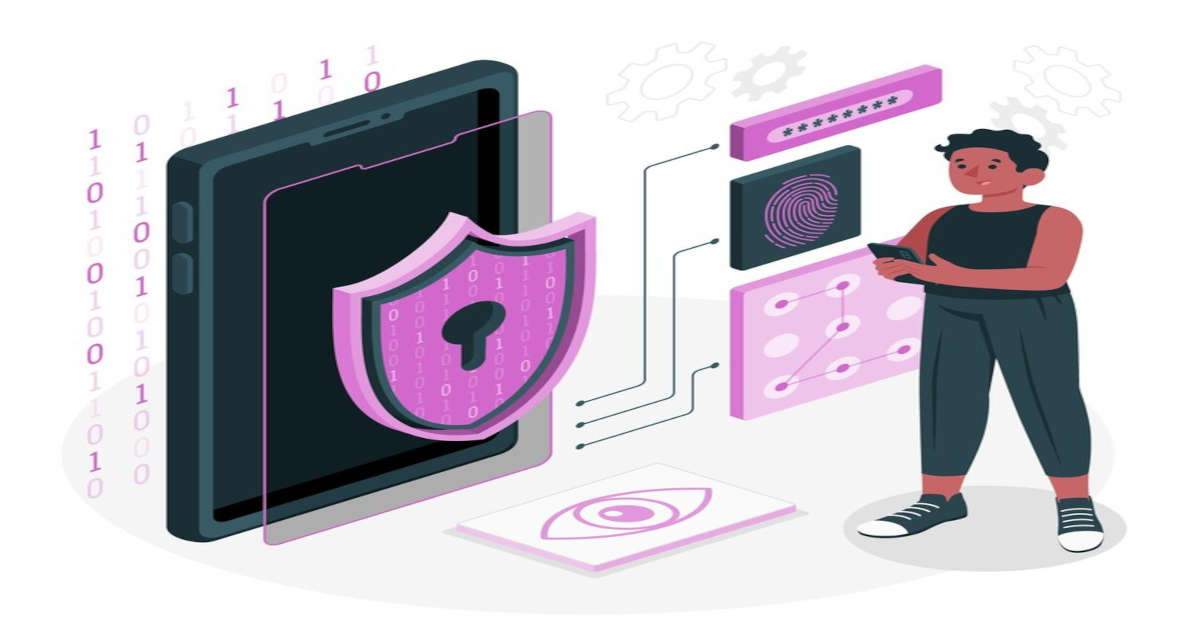
What is Human Computer Interaction?
“HCI is a study of how humans interact with the computers.”
- It is important to keep in mind how humans interact with the machines.
- Cybersecurity experts, designers etc. should always consider HCI element as the major proponent for design and security infrastructure.
- HCI involves knowing the users, tasks, context of the tasks.
- Evaluation of how easy/difficult it is to use the system.
Usability
“It is a measure of how easy it is to use a system for a user.”
Measuring Usability
- Speed
- How quickly can the task be accomplished.
- Efficiency
- How many mistakes are made in accomplishing the task.
- Learnability
- How easy is it to learn to use the system.
- Memorability
- Once learned, how easy is it to remember how to use the system.
- User Preference
- What do users like?
How do we measure Usability?
- Speed – timing
- Efficiency – counting error
- Learnability, Memorability and User Preference don’t have straight forward measurement tools.
Tasks and Task analysis
“Tasks are goals that users have when interacting with the system.”
Common errors in task creation
- Leading or too descriptive
Click on the username box at the upper right of the screen and enter your username, then click on the password box underneath and enter your password. Click submit…
- Specific questions?
What is the third headline on CNN.com?
- Directing users towards things you want to tell them, not what they want to know.
What are the names of the members of the website security team?
Chunking Information
“Breaking a long list of pieces of information into smaller groups.” “Aggregating several pieces of information into coherent groups to make them easier to remember.”
- When designing systems, the most important thing to consider is human memory, as it is very volatile.
- Working memory’s limitations should be kept in mind.
- For design technology products, we should not expect user to remember more than 3 things at a time in his/her working memory.
Mental Models
Number of factors affecting mental models;
- Affordance
- Mapping
- Visibility
Feedback
The user sees some visual change when they click a button.
Constraints
A user should not be allowed to perform a task until certain conditions are met.
Conventions
There are some conventions in place, for cross culture usability.