Computing Platforms and Software Application
Computing Platforms and Compatibility
A computing platform is the environment where the hardware and the software work together to run applications.
- Hardware is the type of computer or device, such as a desktop computer, a laptop, or a smartphone.
- Software refers to the type of operating system (OS), such as Windows, macOS, iOS, Android and Linux, and the programs and applications that run on the OS.
Types of computing platforms
Desktop platform
Includes personal computers and laptops that run operating system like Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Web-based platform
Includes modern browsers like Firefox, and Chrome that function the same in various operating system, regardless of the hardware.
Mobile platform
Includes devices like Pixel and the iPhone that run operating systems like Android OS and iOS.
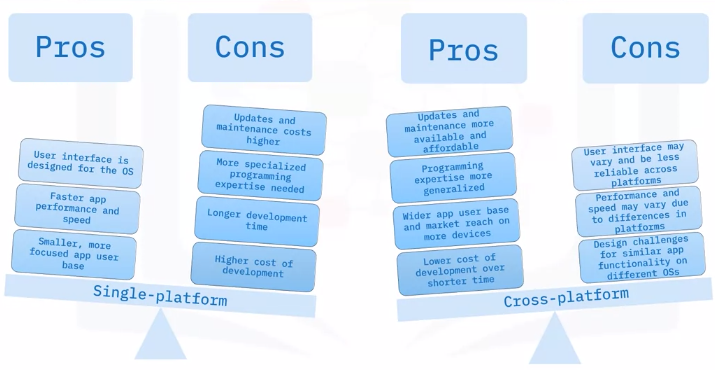
Single-platform vs. cross-platform
Compatibility concerns
- Cross-platform software acts differently or may have limited usability across devices and platforms.
- Software is created by different developers, and programs may interpret the code differently in each application.
- Functionality and results differ across platforms, which might mean undesired results or a difference in appearance.
Commercial and Open Source Software
Commercial Software
- Commercial Proprietary Closed source
- Copyrighted software, which is identified in the End User License Agreement (EULA).
- Private source code, which users are not allowed to copy, modify, or redistribute.
- Developed for commercial profit and can include open source code bundled with private source code.
- Commercial software usually requires a product key or serial number to certify that software is original.
- Some commercial software is free, but upgrades and updates may cost extra, or the software contains ads.
- Examples: Microsoft Office, Adobe Photoshop, and Intuit QuickBooks.
Open source software
- Open source: Free and open source (FOSS)
- Free software, which can be downloaded, installed, and used without limits or restrictions
- Free source code, which can be freely copied, modified, and redistributed.
- Open access to the software functions and software code without cost or restrictions.
- Developers and users can contribute to the source code to improve the software.
- Open source software requires users to agree to an End User License Agreement (EULA) to use the software.
- Examples: Linux, Mozilla Firefox, and Apache OpenOffice.
Software Licenses
What is a software license?
A software license states the terms and conditions for software providers and users.
- It is a contract between the developer of the source code and the user of the software.
- It specifies who owns the software, outlines copyrights for the software, and specifies the terms and duration of the license.
- Likewise, it states where the software can be installed, how many copies can be installed, and how it can be used.
- Not only that, but it can be lengthy and full of definitions, restrictions, and penalties for misuse.
Agreeing to licensing terms
- If you want to use software, you must agree to the licensing terms and requirements, called an End-User License Agreement (EULA).
- Agreeing means you accept the terms of the license, such as how many computers the software can be installed on, how it can be used, and what the limitations on developer liability are.
- Different software programs and applications have various ways of presenting their EULAs.
Types of software licenses
Single-use license
- Allows single installation.
- Allows installation on only one computer or device.
- Ideal for a single user to install on computers or devices owned only by the user.
Group use, corporate, campus, or site license
- Allows multiple installation for specified number of multiple users.
- Allows installation on many computers or devices.
- Idea for use with computers and devices that are required and owned by organizations.
Concurrent license
- Allows installation on many computers, but can only use concurrently by a lower number.
- Allows many users to have access, but is not used often by a lot of people at once.
- Ideal for companies that do not have all workers using the software at the same time.
Software licensing cost
- Costs vary, depending on the type of software, how it will be used, and how much was spent to develop the software.
- The cost is for the license to use the software.
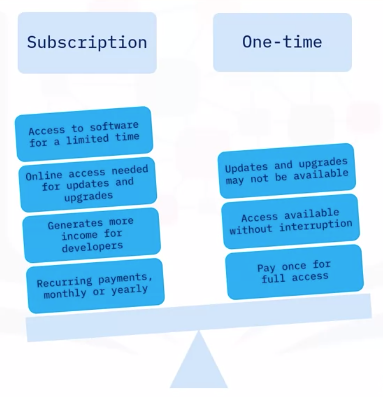
- Several options are available, such trial subscription, and one-time purchase.
- Trial licenses are usually free for a limited time, for a user to decide if they want to purchase the software.
Subscription or one-time licenses
Software Installation Management
Before installing software
- Read application details and be selective.
- Avoid ads or other unwanted software.
- Avoid downloading software that contains malware.
- Review permissions requests to access other apps and hardware on your device.
- Be selective when allowing application privileges.
Installing software
Consider minimum system requirements, such as:
- Minimum processor speed
- Minimum amount of RAM
- Minimum amount of hard disk space available
Compatible OS versions
Additional requirements may be:
- Specific display adapter
- Amount display adapter RAM
- Internet connection to use the software.
Software versions
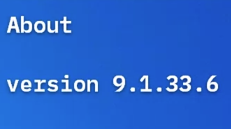
- Software versions are identified by version number.
- Version numbers indicate:
- When the software was released.
- When it was updated.
- If any minor changes or fixes were made to the software.
- Software developers use versioning to keep track of new software, updates, and patches.
Version numbers
- Version numbers can be short or long, with 2,3, or 4 sets.
- Each number set is divided by a period.
- An application with a 1.0 version number indicated the first release.
- Software with many releases and updates will have a larger number.
- Some use dates for versioning, such as Ubuntu Linux version 18.04.2 released in 2018 April, with a change shown in the third number set.
What do version numbers mean?
Some version numbers follow the semantic numbering system and have 4 parts separated by a period.
- The first number indicates major changes to the software, such as a new release.
- The second number indicated that minor changes were made to a piece of software.
- The third number in the version number indicates patches or minor bug fixes.
The fourth number indicates build numbers, build dates, and less significant changes.
Version compatibility
- Older versions may not work as well in newer versions.
- Compatibility with old and new versions of software is a common problem.
- Troubleshooting compatibility issues by viewing the software version.
- Update software to a newer version that is compatible.
- Backwards-compatible software functions properly with older versions of files, programs, and systems.
Productivity, Business, and Collaboration Software
Types of software
- Productivity software enables users to be productive in their daily activities.
- Business software is related to work tasks and business-specific processes.
- Collaboration software enables people to work together and communicate with each other.
Utility software helps manage, maintain, and optimize a computer.
Note: A program or application can be categorized as multiple types of software.
What is productivity software?
“Productivity software is made up of programs and application that we use every day.”
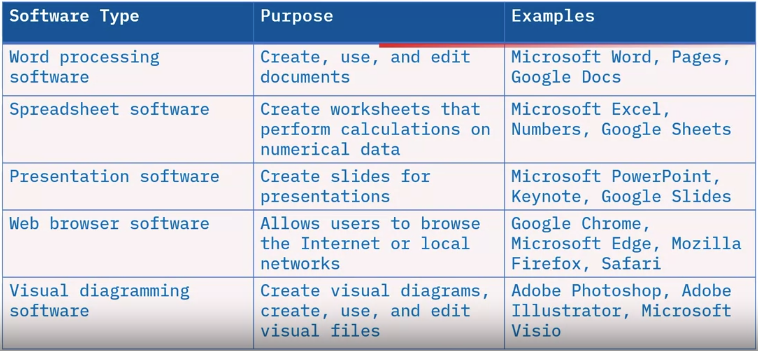
Types of productivity software
What is business software?
- Programs and applications that help businesses complete tasks and function more efficiently are considered business software.
- Some business software is uniquely designed to meet an industry-specific need.
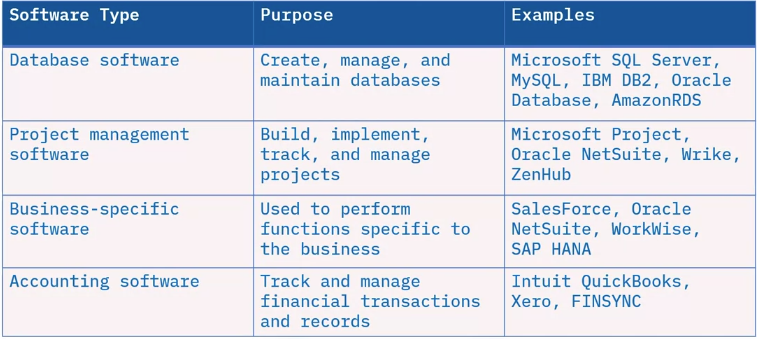
Types of business software
What is collaboration software?
- Collaboration software helps people and companies communicate and work together.
- Collaboration software can also be business software, but they are not interchangeable.
- The primary purpose is to help users create, develop, and share information collaboratively.
Types of collaboration software
What is utility software?
- Utility software runs continuously on a computer without requiring direct interaction with the user.
- These programs keep computers and networks functioning properly.
Utility software
Types of File Formats
Executable files
Executable files run programs and applications.
Some executable file format extensions are:
- EXE or .exe for Windows applications
- BAT or .bat for running a list of commands
- SH or .sh for shell commands on Linux/Unix
- CMD or .cmd for running command in order
- APP or .app for Mac application bundles
- MSI or .msi for installer package on Windows
Common compression formats
Common audio and video formats
Audio and video formats often share the same extensions and the same properties.
Some audio formats:
- WAV
- MPEG, including MP3 and MP4
- AAC
MIDI
Some video formats:
- AVI
- FLV
- MPEG, including MP4 and MPG
- WMV
Images formats
Some common image formats are:
Document formats
Some examples of document formats and extensions:
- TXT / .txt for text files
- RTF / .rtf for rich text format
- DOCX and DOC / .docx and .doc for Microsoft Word
- XLSX and XLS / .xlsx and .xls Microsoft Excel
- PDF / .pdf for Adobe Acrobat and Adobe Reader
- PPTX and PPT / .pptx and .ppt for PowerPoint