Configuring and Troubleshooting Networks
Network Setup and Tools
Configuring a Wired SOHO Network
What is a SOHO Network?
A SOHO (small office, home office) network is a LAN with less than 10 computers that serves a small physical space with a few employees or home users.
It can be a wired Ethernet LAN or a LAN made of both wired and wireless devices.
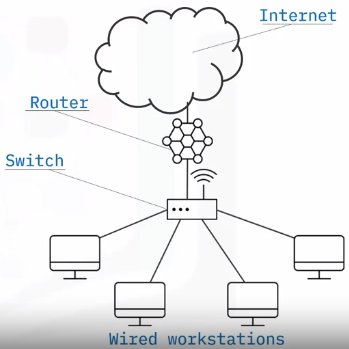
A typical wired SOHO network includes:
Setup steps – plan ahead
When setting up a SOHO network, knowing the compatibility requirements is very important.
Before setting up any SOHO network, review and confirm everything in your plan to ensure a successful installation.
Setup steps – gather hardware
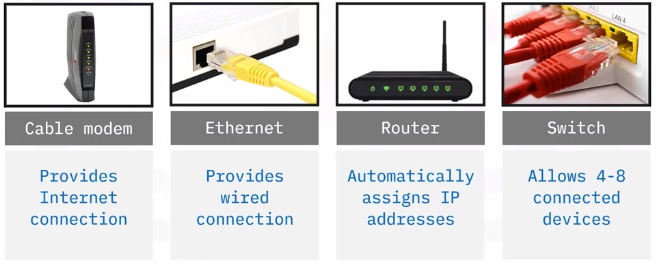
- SOHO networks need a switch to act as the hub of the network
If Internet is desired, a router can be added or used instead
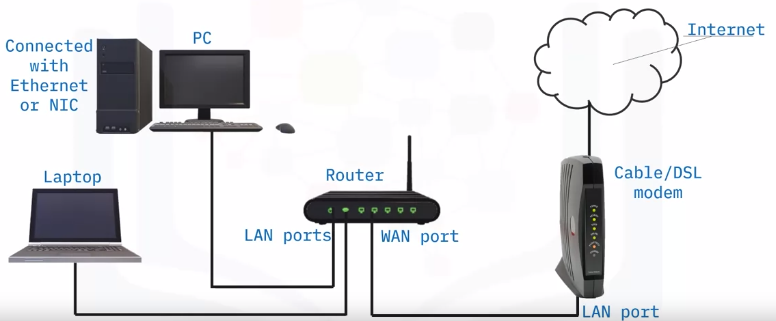
Setup steps – connect hardware
Setup steps – router settings
Log in to router settings
- Enter ‘ipconfig’ in a command prompt window to find your router’s public IP address (listed next to default gateway)
Enter it into a browser and log in
Update username and password
- All routers have default administrator usernames and passwords
To improve security, change the default username password
Update firmware
- Updating router firmware solves problems and enhances security
- Check the manufacturer website for available firmware updates
- Download and install if your firmware is not up-to-date
Setup steps – additional settings
- SOHO wired network security depends on a firewall
- Most routers have a built-in firewall, additional software can be installed on individual machines
- Servers and hardware have built-in DHCP and NAT actions
- DHCP servers use IP addresses to provide network hosts
- NAT maps public IPv4 address to private IP addresses
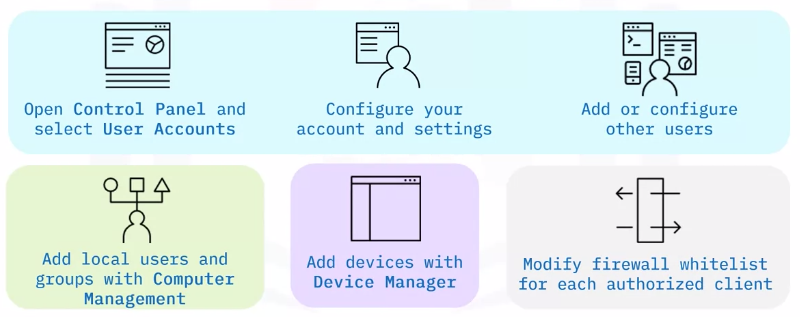
Setup steps – user accounts
User account setup is included in most operating systems.
Setup steps – test connectivity
Network performance depends on Internet strength, cable specification, installation quality, connected devices, and network and software settings.
Test and troubleshoot to ensure proper network performance.
To troubleshoot performance:
- Run security tools
- Check for updates
- Restart devices
- Run diagnostic
- Reboot the router or modem
Configuring a (wireless) SOHO network
What is a SOHO wireless network?
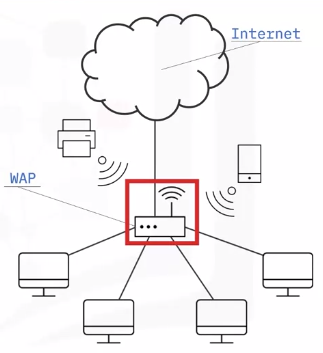
A SOHO wireless network is a WLAN that serves a small physical space with a few home users.
A SOHO wireless network can be configured with the help of a central WAP, which can cover a range of wireless devices within a small office or home.
Common broadband types
Common broadband types that enable network connection:
- DHCP:
- The most common broadband type, used in cable modem connections.
- PPPoE:
- Used in DSL connections in areas that don’t have newer options.
- Static IP:
More common in business.
DHCP is the easiest broadband type to use. Internet Service Providers can provide other options if needed.
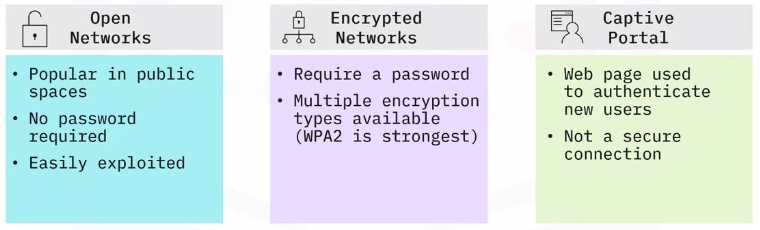
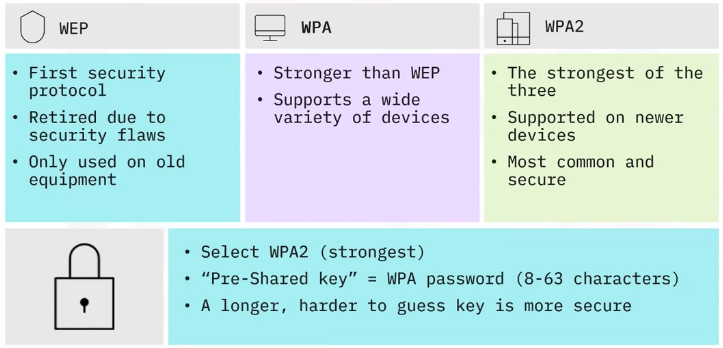
Wireless security factors
Wireless networks can be setup to be either open (unencrypted) or encrypted.
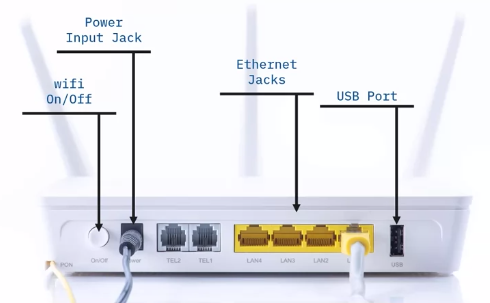
Get to know your wireless router
Connect to router admin interface
To manage router settings, you must find its default IP address, paste it into a browser and hit enter.
Assign a SSID
- SSID is the name of a wireless network.
- This name is chosen during setup.
- Unique names help to identify the network.
- Each country determines band and available modes.
- 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz have specific supported modes.
- Every router has as a default option.
Wireless encryption security modes
Going wireless
Once the router is configured, your wireless network is ready.
Users will see it among the available wireless networks when they click the Wi-Fi icon.
Test and troubleshoot connectivity
Test network performance and Internet connectivity on each wireless device in the vicinity of the WAP.
If required, troubleshoot performance issues (network lags, glitches, or network cannot be accessed) with the following actions:
- Check router configuration settings.
- Run security tools.
- Check for updates.
- Restart devices.
- Run diagnostics.
- Reboot the router or modem.
- Check equipment for damage.
Mobile configuration
IMEI vs. IMSI
IMEI and IMSI are used to identify cellular devices and network users when troubleshooting device and account issues.
Internation Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI)
- ID# for phones on GSM, UMTS, LTE, and iDEN networks
Can be used to block stolen phones
International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI)
- ID# for cell network subscribers
- Stored in a network sim card
Troubleshooting Network Connectivity
Symptoms of connectivity problems
“Can’t connect” or “slow connection” are two of the most common network problems. These symptoms can be caused by several things.
Causes of Connectivity Problems
Common causes of network connectivity problems: 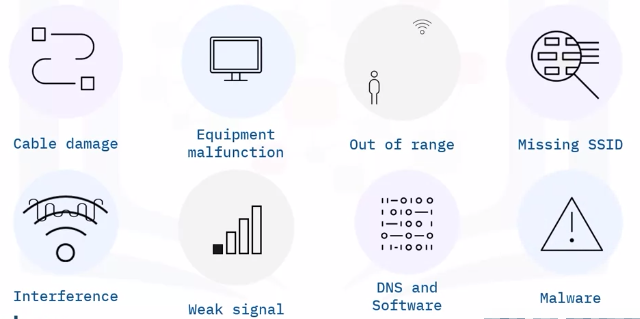
Cable Damage
Cable damage slows or stops network connections. The damage can be obvious or hidden from view.
Ways to solve:
- Check for physical damage
- Test the cable using different devices or a specialized tool
- Replace the cable
Equipment malfunction
An equipment malfunction can slow or stop network connections.
Ways to solve:
- Check network adapter drivers in Device Manager
- Check switch or router port settings in the management software
- Replace the equipment
Out of range
When a user is too far away from a wireless signal, their connection will lag or fail.
Ways to solve:
- Move physically closer to the source of the wireless connection
- Move the wireless connection source closer to the affected user(s)
- Use stronger devices to boost the signal strength
- Use more devices to ensure the Wi-Fi reaches users who are farther away
Missing SSID
Network connections can fail when a user can’t find the network name (SSID) in the available networks list.
Ways to solve:
- Move physically closer to the Wi-Fi source
- Reconfigure the network to ensure the SSID is not hidden
- Upgrade devices or use compatibility mode on newer network, so older devices can still connect
- Compatibility mode can slow a network
- Reserve 2.4 GHz band for legacy devices
Interference
Interference is when a radio or microwave signal slows or breaks a wireless connection.
Ways to solve:
- Remove the source of the interference signal
- Use a different Wi-Fi frequency (wireless)
- Use shielded cables to connect (wired)
- Remodel the building with signal-blocking materials
Weak signal strength
When signal strength is weak, a wireless adapter might slow speeds down to make the connection more reliable.
Weak signals cause:
- Lags
- Dropped connection
- Back-and-forth network hopping
- Out of range
- Interference
Physical obstacles
Ways to solve:
- Move closer to signal
- Adjust Wi-Fi frequency
Realign router antennae
Wireless access points should be placed up high and in the middle of the space.
DNS and software configuration
Network connections can fail when DNS or software is configured incorrectly.
DNS issue:
- Domain not recognized
IP addresses recognized
OS and apps issue:
Software affecting connection
Ways to solve:
- For DNS servers, test domains using ipconfig in a command prompt
- For apps and OSes, use the network troubleshooter in Windows Settings
Malware
Malware slows or stops network connections intentionally, or as a result of overloading a system with other tasks.
Ways to solve:
- Use antimalware tools
- Adjust firewall settings
- Configure Privacy settings
- Windows
- Browser
Network Troubleshooting with Command Line Utilities
Common command line utility commands that you would use to troubleshoot or diagnose network issues:
- ipconfig
- IP address
- Subnet mask
- Default gateway
- ping
- You can ping:
- IP addresses, or
- Domains
- You can ping:
- nslookup
- It lists:
- Your DNS server
- Your DNS server’s IP address
- Domain name
- It lists:
- tracert
- Tracert lists:
- Sent from
- Sent to
- Number of transfers
- Transfer locations
- Duration
- Tracert lists:
- netstat: It shows if a server’s email and ports are open and connecting to other devices.
- Netstat lists:
- Protocol
- Local address
- Foreign address
- Current state
- Netstat lists: