Database Fundamentals
Types of Data, Sources, and Uses
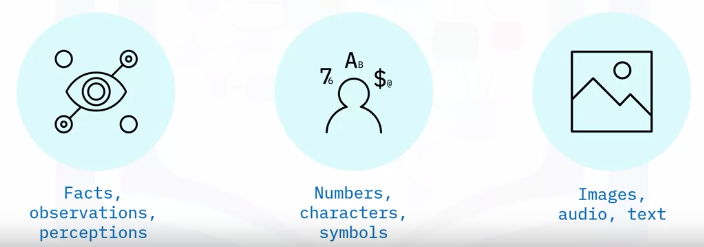
What is data?
A set of characters gathered and translated for some purpose, usually analysis
Common types:
- Single character
- Boolean (true or false)
- Text (string)
- Number (integer or floating point)
- Picture
- Sound
Video
Forms of data
Types of data
Categorized by level and rigidity
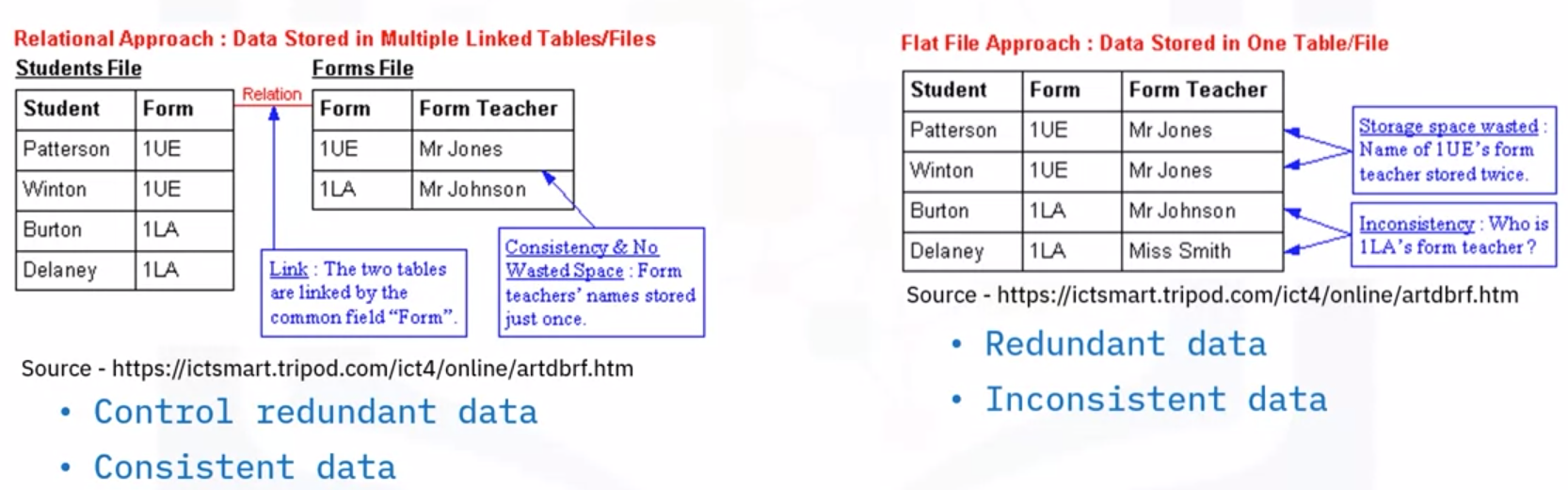
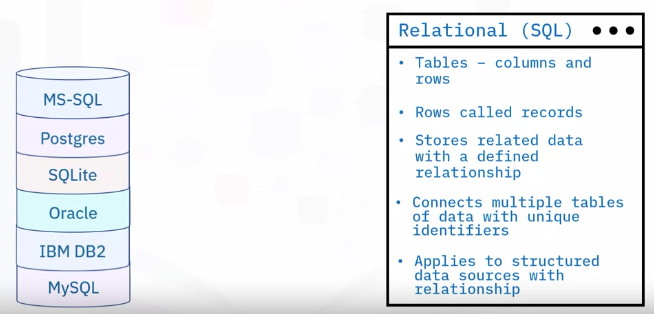
Structured data
- Structured in rows and columns
- Well-defined with rigid structure
- Relational databases
- Microsoft SQL server
- IBM Db2
Oracle database
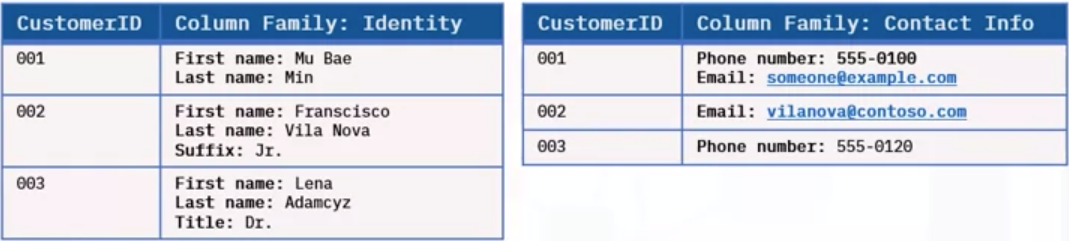
Semi-structured data
- Some organizational properties
- Not in rows or columns
- Organized in hierarchy using tags and metadata
Non-relational database
Unstructured data
- No identifiable structure, specific format, sequence, or rules
- Most common include text, email
Also images, audio files, and log files
Examples of Semi and Unstructured data
- MonoDB
- Hbase
- Cassandra DB
- Oracle NoSQL DB
Data Sources
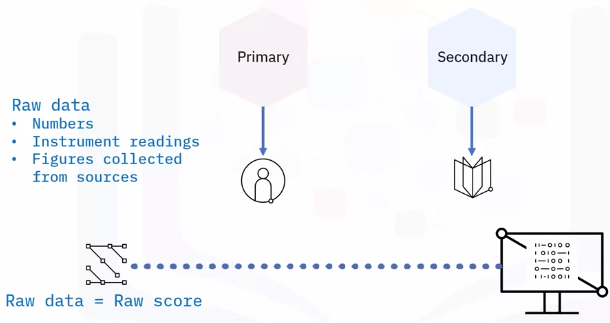
Using data
Data sources may be internal or external
Internal
- Collects data from reports or records from organization
- Known as internal sourcing
- Accounting
- Order processing
- Payroll
Order shipping
External
- Collects data from outside the organization
- Known as external sourcing
- Social media feeds
- Weather reports
- Government
- Database and research
Database Fundamentals and Constructs
What is a database?
Components of a database
Schema
- Collection of tables of data
A database can have more than one schema
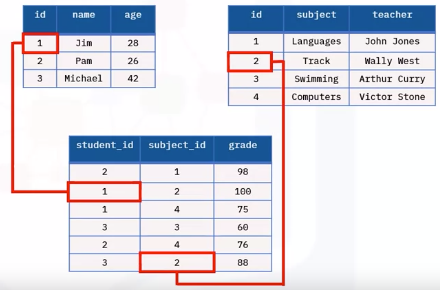
Table
- One or more columns of data
Two or more columns of stored data
Column
- A pillar of information containing one or more data or values
Can contain dates, numeric or integer values, alphabetic values
Row
- A horizontally formatted line of information like rows in Excel
- 100s or 1000s rows of data are typically in a table
Database constructs
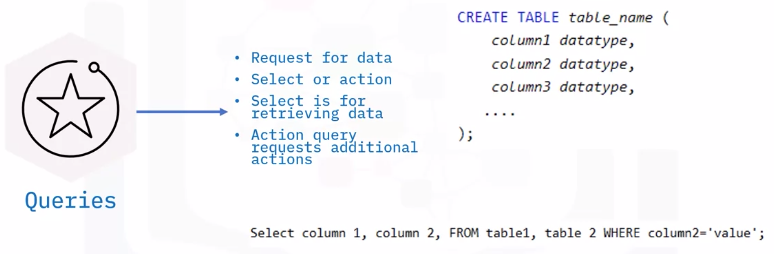
Queries
- Request for data
- Provide answers
- Perform calculations
- Combine data
Add, change, or delete data
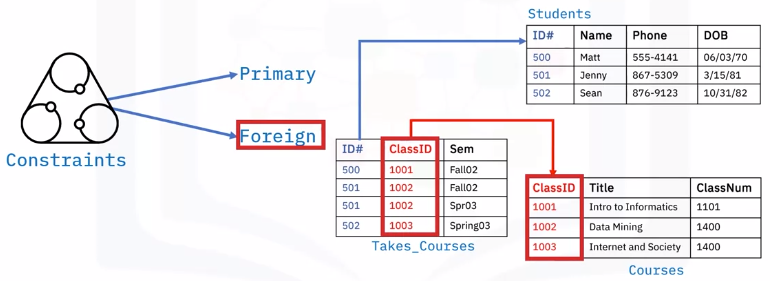
Constraints
- Primary and foreign key enforce rules
- Values in columns not repeated
- Limit the type of data
- Ensure data accuracy and reliability
Database query
Database constraints
Database characteristics
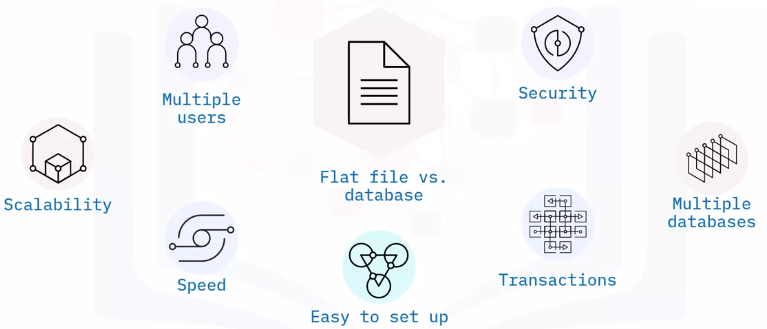
Flat file vs. database
| Flat File | Database |
|---|---|
| Stores data in single table | Uses multiple table structures |
| Set in various application types | Tables are organized in rows and columns |
| Sorted based on column values | One piece of data per column |
| Solution for simple tasks | Faster, more efficient, more powerful |
Database Roles and Permissions
Database permissions
Three types of permissions:
Database
- Right to execute a specific type of SQL statement
- Access second person’s object
- Controls use of computing resources
Does not apply to DBA
System
- Right to perform any activity
Ability to add or delete columns and rows
Object
- Right to perform specific actions
- Allows user to INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE, or SELECT data
- Object’s owner has permissions for object
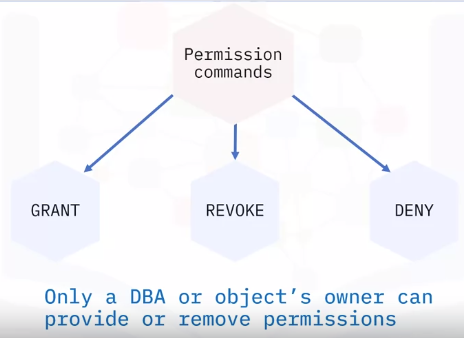
Permission commands
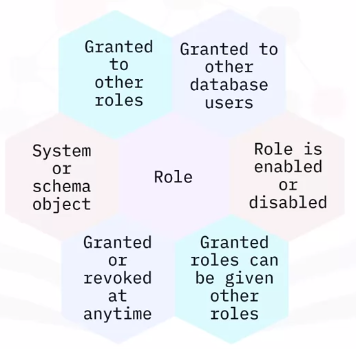
Database roles
Benefits of roles
Database types
Structured data type
- Tabular data, columns, and rows
- These databases are called relational databases
- Formed set of data
All rows have same columns
Semi-structured data type
- Some structure
- Documents in JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) format
Include key-value stores and graph database
Unstructured data type
- Not in pre-defined structure or data model
- Text heavy files, but may contain numbers and dates
Videos, audio, sensor data, and other types of information
Relational database
| Relational | Non-Relational |
|---|---|
| Structured to recognize relations among stored items of information | Stores data in a non-tabular form, and tends to be more flexible than the traditional, SQL-based, relational database structures |
Non-relational database
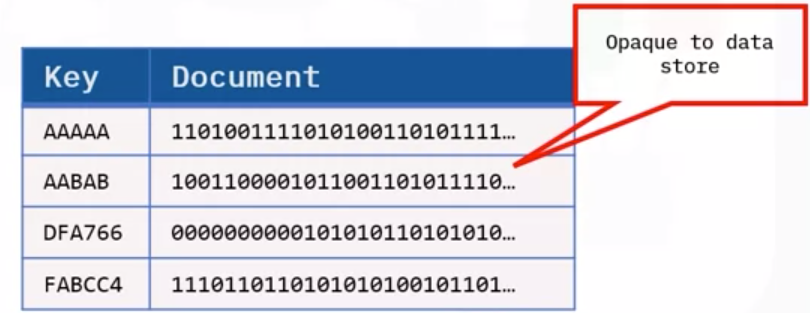
Permit storing, store data in a format that closely meets the original structure.
Most common types of data stores:
- Document data stores
Key-value stores
Column-oriented databases
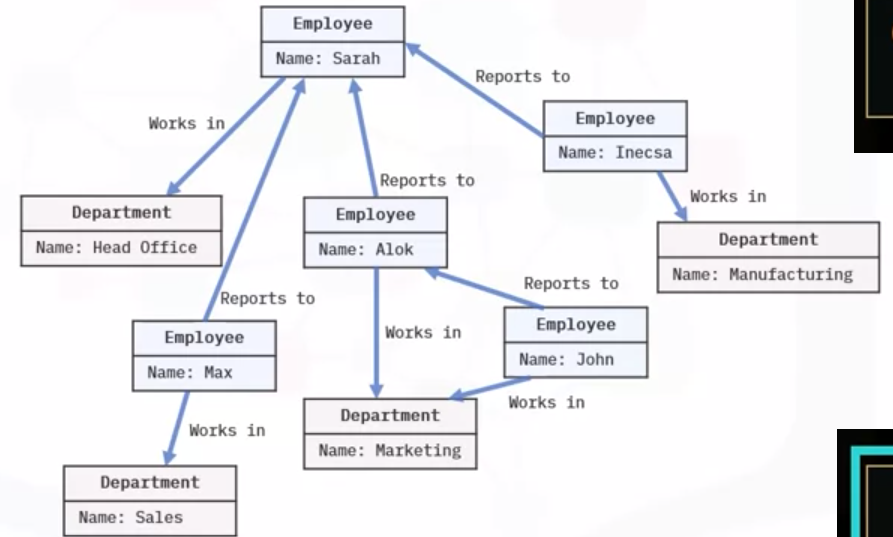
Graph databases
Interfacing with Databases
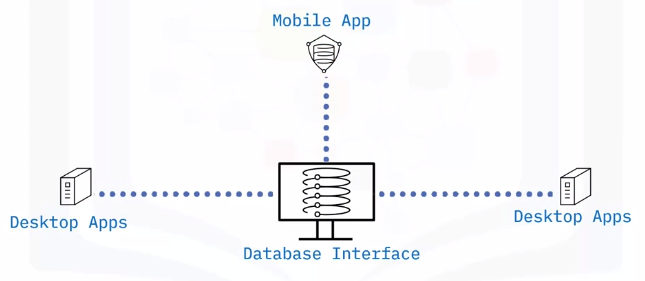
What is a database interface?
Enable users to input queries to a database
Principles of a database interface
How to access a database
Types of access:
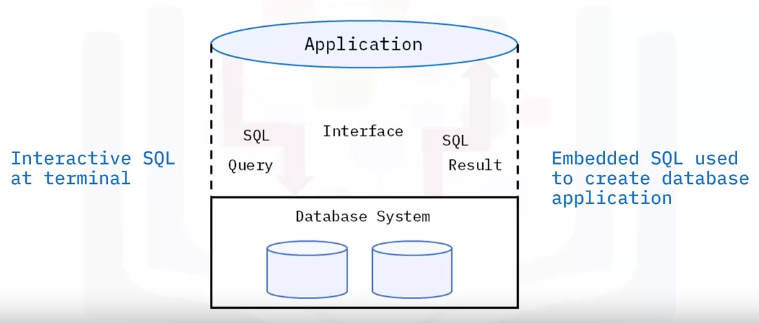
Direct
- Enters SQL commands
- Selects a menu
- Accesses tables directly
Works well with locally stored database or local area network
Programmatic
- Accesses’ database using programming language
- Enables data to be used in more ways
- Safer than using direct access
- Oracle databases support access from many languages
Might be necessary to perform a query with a supported language
User interface
- Microsoft Access permits access to user interface
- Optional user interface may be needed
- Oracle offers MySQL Workbench as a graphical user interface
- Allows ability to input queries without the query language
- Menu-base interface
- Forms-based interface
- GUI displays schema in diagrammatic form
- Specific query by manipulating diagram
- GUIs utilize both menus and forms
- GUIs using point device to pick sections of displayed schema diagram
- Natural language interfaces accepts user requests and tries to interpret it
- These interfaces have own schema like database conception schemas
Search engine example of entering and retrieving information using natural language
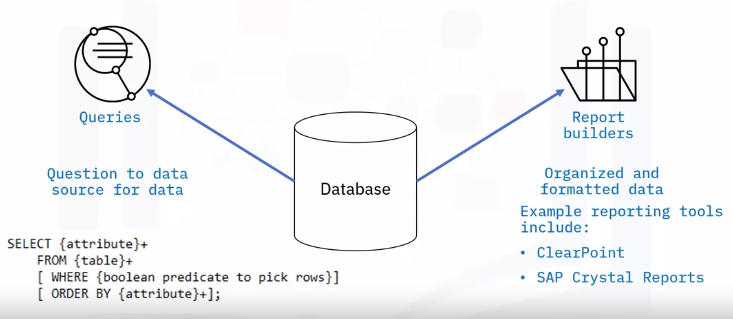
Query
- Find specified data using SELECT statement
- Query and reporting function included with software like Microsoft Access
- Query Builder’s GUI is designed to enhance productivity and simplify query tasks
- SQL or SQL displayed visually
- Has pane displaying SQL text
- Related tables determined by Query Builder that constructs join command
- Query and update database using SELECT statement
- Quickly view and edit query results
- Examples:
- Chartio Visual SQL
- dbForge Query Builder for SQL Server
- Active Query Builder
- FlySpeed SQL
- QueryDbVis Query Builder
- Drag multiple tables, views, and columns to generate SQL statements
Database Management
Managing databases with SQL commands
- Queries refer to request information from a database
- Queries generate data of different formats according to function
Query commands perform the data retrieval and management in a database
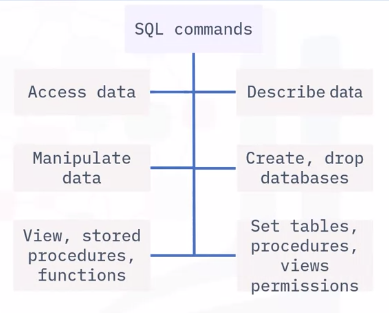
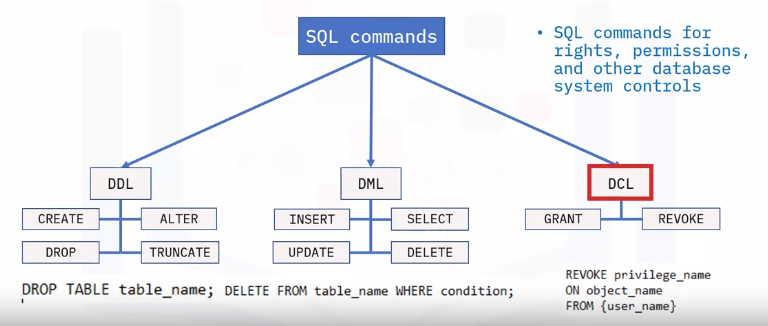
SQL command Categories
DDL
- SQL commands that define database schema
- Create, modify, and delete database structures
Not set by general user
DML
SQL commands that manipulate data
DCL
SQL commands for rights, permissions, and other database system controls
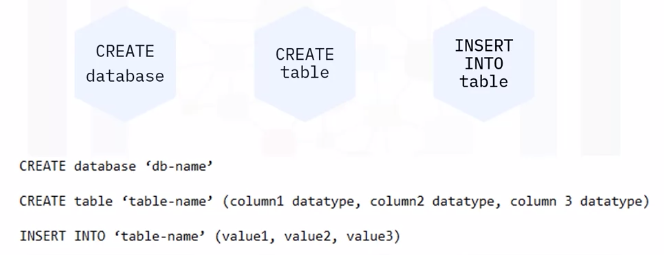
Inputting and importing data
Data is input manually into a database through queries.
Another way is through importing data from different sources.
- SQL Server Import Export Wizard
- SQL Server Integrated Services (or SSIS)
- OPENROWSET function
Extracting data from a database
Backing Up Databases
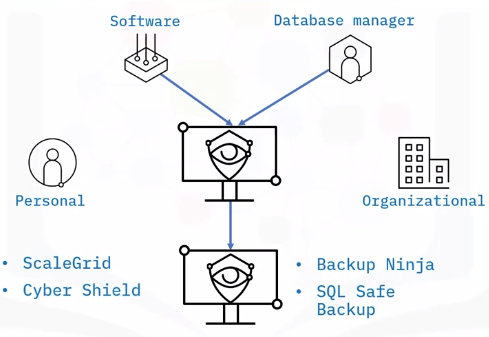
What is a database backup?
Two backup types:
Physical database backups
- Needed to perform full database restoration
- Minimal errors and loss
- Full or incremental copies
Logical database backups
- Copies of database information
- Tables, schemas, procedures
Backup pros and cons
| Physical backup | Logical backup |
|---|---|
| Pros: | Pros: |
| Simple and fast, despite format | Only selected data is backed up |
| Mirror copy loaded to another device | Saves time and storage |
| Cons: | Cons: |
| Used only to recreate system | No file system information |
| Cannot do full restore | Complications restoring process |
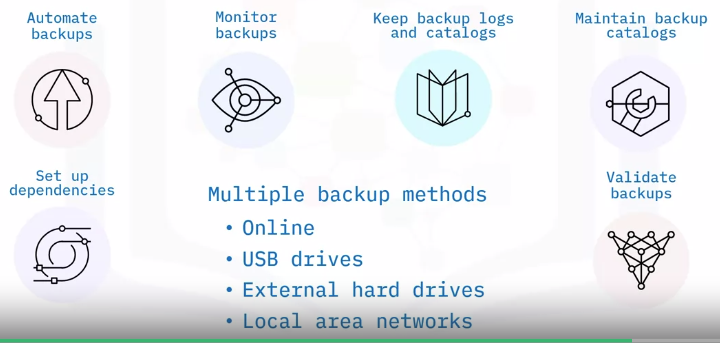
Database backup methods
Full
- Stores copies of all files
- Preset schedule
Files are compressed but may need large storage capacity
Differential
- Simplifies recovery
- Requires last full backup
Last differential back up for full recovery
Incremental
- Saves storage
Back up files generated or updated since last backup
Virtual
- Uses’ database to track and maintain data
- Helps avoid pitfalls of other backup methods