Examples and Principles of CIA Triad
Further discussion of confidentiality, integrity, and availability
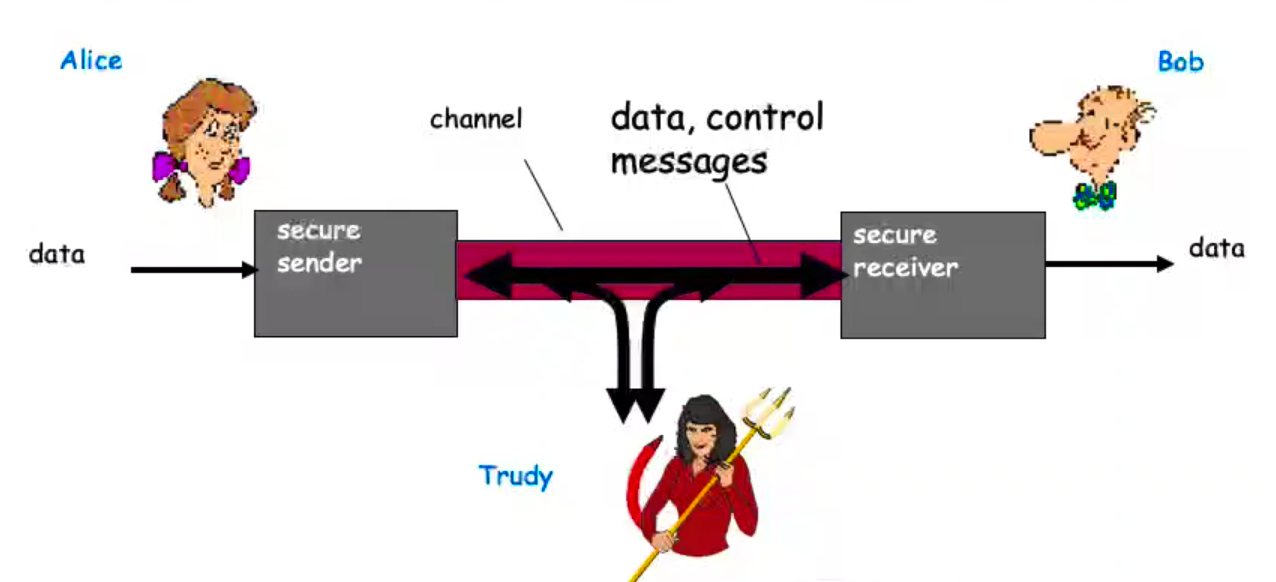
Who are Alice, Bob, and Trudy?
- Well known in network security world.
- Bob, Alice (friends) want to communicate “securely”.
Trudy (intruder) may intercept, delete, add messages.
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability
- Main components of network security.
Confidentiality
- Preserving authorized restrictions on information access and disclosure, including means for protecting personal privacy and proprietary information.
- Loss of confidentiality is the unauthorized disclosure of information.
Integrity
- Guarding against improper information modification or destruction.
- Including ensuring information non-repudiation and authenticity.
- Integrity loss is the unauthorized modification or destruction of information.
Availability
- Timely and reliable access to information.
- Loss of availability is the disruption of access to an information system.
Authenticity and Accountability
- Authenticity: property of being genuine and verifiable.
- Accountability: mapping actions to an identity.
Identification and AAA
- Security token
- Password
- Biometrics
Identification → Authentication → Authorization → Accountability
Authentication methods
- Something you know
- Username/Password
- Something you have
- Smartcard, token
- Something you are
- Fingerprints
- Retina Scanners
- Biometric Signals
Control Types
- Administrative
- Technical
- Physical
Each control type can be
- Corrective
- Preventive
- Dissuasive
- Recovery
- Detective
- Compensatory
Access Control Methods
“Only who has the rights to access or utilize the resources can use them.”
Access control models
MAC – Mandatory Access Control
- Use labels to regulate the access
Military use
DAC – Discretionary Access Control
Each object (folder or file) has an owner and the owner defines the rights and privilege
Role Based Access Control The rights are configured based on the user roles. For instance, sales group, management group, etc.
Other methods
Centralized
- SSO (Single Sing On)
Provide the 3 As
Decentralized
- Independent access control methods
- Local power
- Normally the military forces use these methods on the battlefields
Best practices for the access control field
These concepts are deeply integrated with the access control methodologies and must be followed by the organization in order of the policies and procedures.
- Least privilege
- Information access limit
- Separation of duties
- Verify employee activity
- Rotation of duties
- Tracking and control
Access Control – Physical and Logical
Physical access control methods
- Perimetral
- Building
- Work areas
Servers and network
Technical uses of Physical security controls
- ID badges
- List and logs
- Door access control systems
- Tokens
- Proximity sensors
- Tramps
- Physical block
- Cameras
Logical access control methods
- ACL (Routers)
- GPO’S
- Password policies
- Device policies
- Day and time restrictions
- Accounts
- Centralized
- Decentralized
- Expiration
BYOD, BYOC … BYO Everything…
Popular concepts for moderns times. Each collaborator has the opportunity to bring their own device to the work environment.
Some controls to follow:
- Strict policy and understanding
- Use of technical control MDM
- Training
- Strong perimetral controls
Monitoring the access control process
- IDS/IPs
- HOST IDS and IPS
- Honeypot
- Sniffers