Fundamentals of Web Browsers, Applications, and Cloud Computing
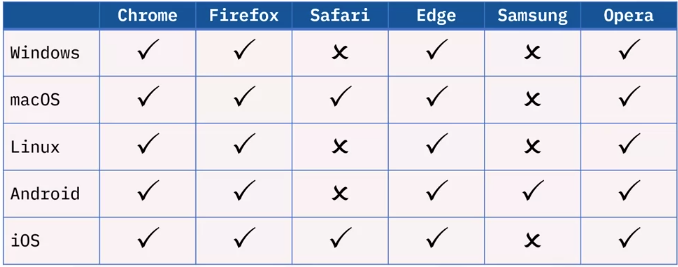
Common Web Browsers
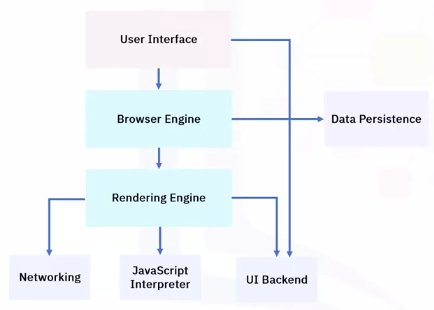
Web Browser components
Browser installs and updates
Importance of browser updates
- Compatibility with websites
- Security
- New features
Frequency of browser updates
Most web browsers update at the same frequency:
- Major updates every four weeks
- Minor updates as needed within the four-week period
- Security fixes, crash fixes, policy updates
- Some vendors offer an extended release:
- Major updates are much less frequent
- Better for structured environments
Malicious plug-ins and extensions
- Malicious plug-ins and extensions typically not displayed in list of installed apps and features.
- Use an anti-malware program to remove them.
- Use trusted sources for plug-ins and extensions to avoid malware.
Basic Browser Security Settings
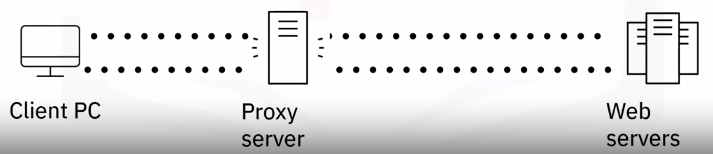
What is a proxy server?
- Acts as go-between when browsing the web.
- The website thinks the proxy is the site visitor.
- Protects privacy or bypass content restrictions.
- Allows organizations to maintain web security, web monitoring, and content filtering.
- Controls what, when, and who.
- Reduces bandwidth consumption and improves speed.
How does a proxy server work?
Proxy servers perform network address translation to request and retrieve web content on behalf of requesting computers on the network.
Managing cookies
- Cookies:
- Small text-based data stores information about your computer when browsing
- Save session information
- More customized browsing experience
- Example: Online shopping basket
- Cookies can be useful but could be malicious too:
- Tracking browsing activity
- Falsifying your identity
What is cache?
- Cache is temporary storage area
- Stores web data, so it can be quickly retrieved and reused without going to original source
- Cache is stored on local disk
- Improves speed, performance, and bandwidth usage
- Cache can be cleared when no longer needed
Browser Security Certificates and Pop-ups Settings
Security certificates
- Good security practice to check websites’ authenticity
- Look for HTTPS in URL and padlock icon
- ‘Connection is secure’
- If it says ‘not secure’ be wary
- Certificate expired
- Issuing CA not trusted
Script and pop-ups blockers
Pop-ups:
- Typically are targeted online ads
- Can be annoying and distracting
- Can be malicious
- Associated with ‘innocent’ actions
Take care when interacting with pop-ups
Popular third-party pop-up blockers:
- Adlock
- AdGuard
- AdBlock
- Ghostery
- Adblock Plus May provide additional features such as ad filtering.
Private Browsing and Client-side Scripting Settings
Private browsing mode that doesn’t save:
- History
- Passwords
- Form data
- Cookies
Cache
Only hidden locally
- ISPs, websites, workplace can view data
Client-side scripting
- Web pages were static in early days of WWW
- Dynamic web pages adapt to situation/user
- Server-side scripting performed by server hosting dynamic pages
- Client-side scripting performed by client’s web browser
- Code is embedded in web page
- JavaScript
Pros
- Client-side scripts are visible to user
- No reliance on web server resources
Cons
- Client-side scripts have security implications
- Malware developers constantly trying to find security flaws
- You may need to disable client-side scripts
Should you disable JavaScript?
Pros of disabling
- Security
- Browsing speed
- Browser support
Disabled cookies
Cons of disabling
- Lack of dynamic content
- Less user-friendly browsing experience
- Website navigation
Introduction to cloud computing and cloud deployment and service models
What is cloud computing?
Delivery of on-demand computing resources:
- Networks
- Servers
- Storage
- Applications
- Services
Data centers Over the Internet on a pay-for-use basis.
Applications and data users access over the Internet rather than locally:
- Online web apps
- Secure online business applications
- Storing personal files
- Google Drive
- OneDrive
- Dropbox
Cloud computing user benefits
- No need to purchase applications and install them on local computer
- Use online versions of applications and pay a monthly subscription
- More cost-effective
- Access most current software versions
- Save local storage space
- Work collaboratively in real time
Cloud computing
- Five characteristics
- Three deployment models
- Three service models
Cloud computing characteristics
- ON-demand self-service
- Broad network access
- Resource pooling
- Rapid elasticity
- Measured service
Cloud deployment models
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid cloud
Cloud service models
- IaaS
- PaaS
- SaaS
Application Architecture and Delivery Methods
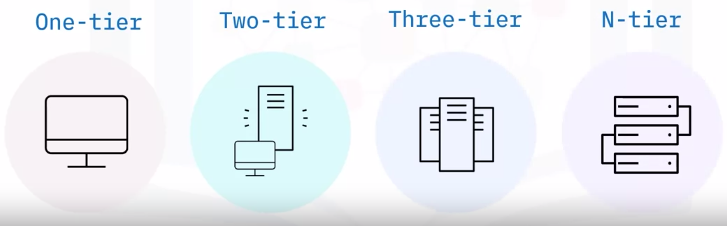
Application Architecture models
One-tier model
- Single-tier model
- Also called monolithic model
- Applications run on a local computer
Two-tier model
- Workspace-based client – Personal computer
- Web server – Database server
Three-tier model
- Workspace-based client
- Application server or web server
Additional server (Database)
Each tier can be:
- Individually developed and updated by a separate team
- Modified and upgraded without affecting the other tiers
N-tier model
- A number of tiers
- Multi-tier model
- Workspace-based client
- Web server or database server
- Security
- Additional servers
Preferred for the microservices pattern and Agile model
Pros
- Changes can be made to specific tiers
- Each tier can have its own security settings
- Different tiers can be load balanced
Tiers can be individually backed up by IT administrators
Cons
- Changes to all tiers may take longer
Application Delivery methods
- Local installation
- Hosted on a local network
- Cloud hosted
Software Development Life Cycle
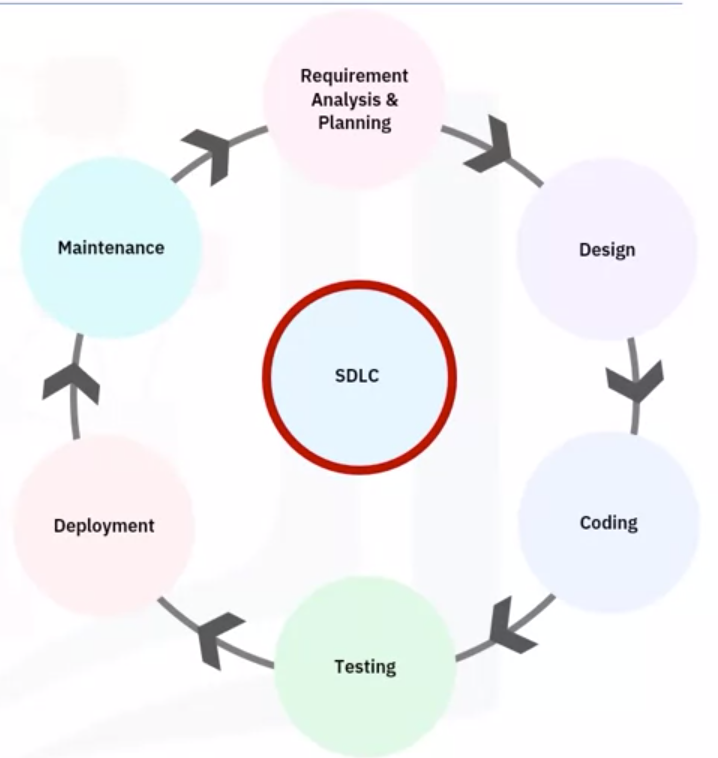
Introduction to the SDLC
- Structured methodology that defines creating and developing software
- Detailed plan to develop maintain, or enhance software
- Methodology for consistent development that ensures quality production
Six major steps
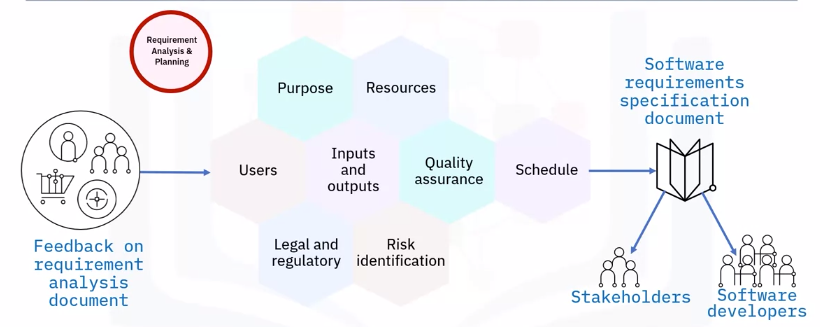
Requirement analysis and planning
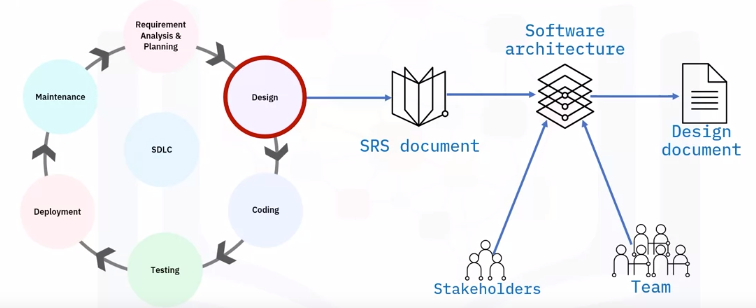
Design
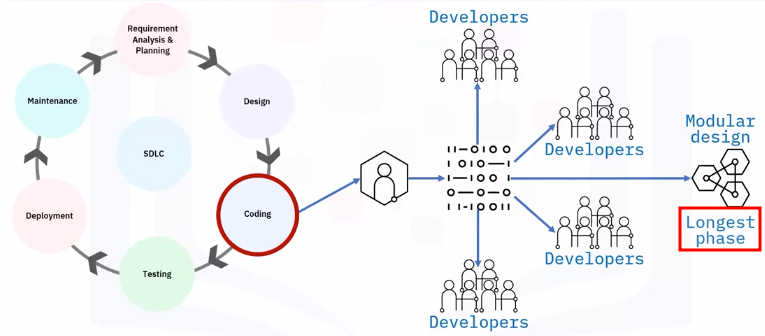
Coding or implementation
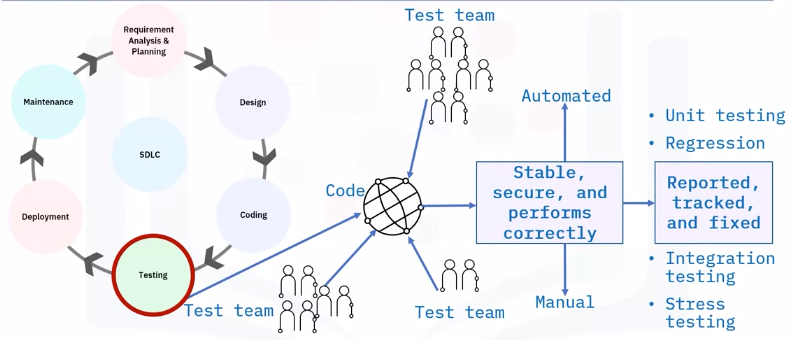
Testing
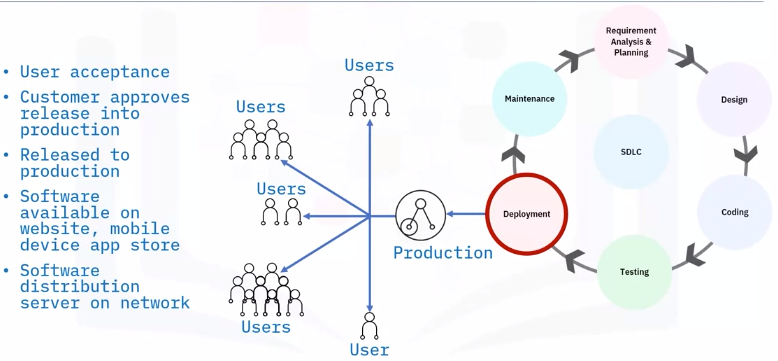
Deployment
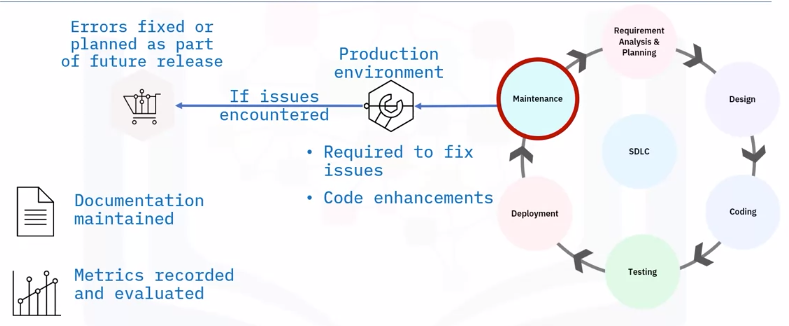
Maintenance
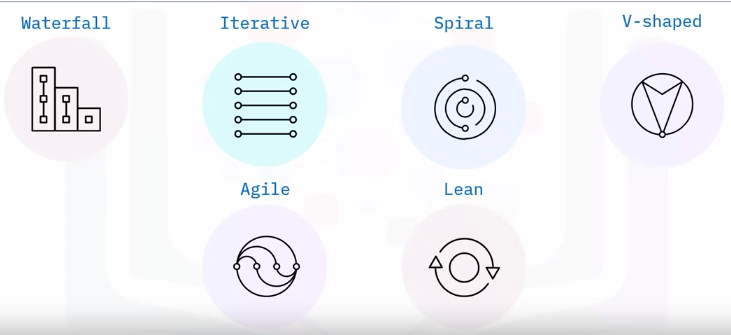
SDLC models
Waterfall
- Linear sequential model
- Output of one phase is input for the next phase
Next doesn’t start until work is completed on the previous phase
Iterative
- Iterative incremental model
- Product features developed iteratively
Once complete, final product build contains all features
Spiral
- Uses waterfall and prototype models
- Good for large projects
- Largely reduces risk
- Planning, risk analysis, engineering, and evaluation
Follows an iterative process
V-shaped
- Verification and validation model
Coding and testing are concurrent, implemented at development stage
Agile
- Joint development process over several short cycles
- Teams work in cycles, typically two to four weeks
- Testing happens in each sprint, minimizes risk
- Iterative approach to development
- At the end sprint, basic product developed for user feedback
Process is repeated every sprint cycle
Four core values of agile model
- Individuals and interactions over process and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
Responding to change over following plan
Lean
- Application of lean principles
- Focuses on delivery speed
- Continuous improvement
Reducing waste each phase
Seven rules of Lean Model
- Build in quality
- Create knowledge
- Defer commitment
- Deliver fast
- Respect people
- Optimize the whole
- DevOps evolved from Agile and Lean principles
- Development and Operations teams work collaboratively
Accelerate software deployment