Interfaces and Connectors
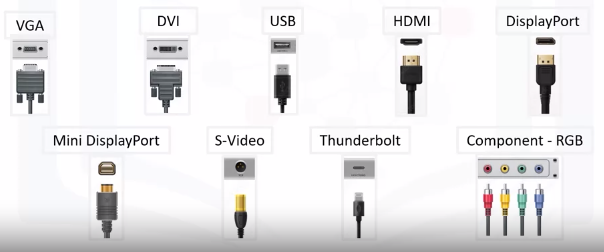
Identifying Ports and Connectors
- Ports enable devices to connect to computers
- Connectors plug into ports
Each port has a unique function and accepts only specific connectors
Interfaces
- Point of communication between two or more entities
Can be hardware or software based
Common Interfaces are:
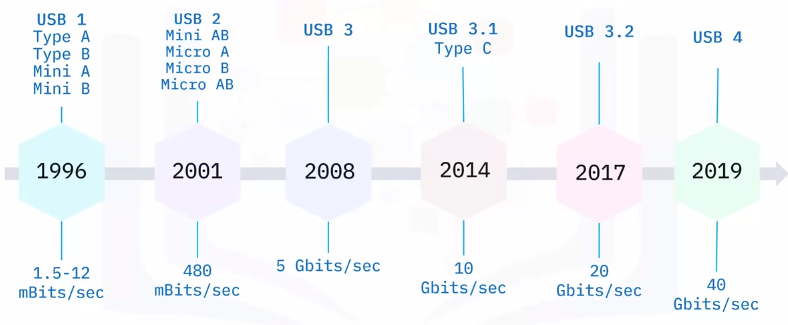
- USB
- USB connectors
Thunderbolt
- Combines data transfer, display, and power
- Initial versions reused Mini DisplayPort
- New versions reuse USB-C connectors
Identified with a thunderbolt symbol
FireWire
- Predecessor to Thunderbolt
- FireWire 400 = 400 mBits/second
- FireWire 800 = 800 mBits/second
- Uses a serial bus to transfer data on e bit at a time
- Still used for audio/video connections on older computers (before 2011), and in the automobile and aerospace industries
PS/2
- Developed for IBM PS/2
- Connects keyboard and mice
- Ports are device specific
- Green for mice
- Purple for keyboard
Considered a legacy port
eSATA
- Standard port for connecting external storage devices
- Allows hot swapping of devices
- Since 2008, Upgraded eSATAp that supports both eSATA and USB on the same port
- eSATA revisions:
Identifying Graphic Devices
Display Unit
- Display unit (GPU) connected to the computer via a display card or adapter
- Low-end generic graphic cards come built into the computer
- Require specialized adapters for high-end functions
- ATI/AMD, nVIDIA, SiS, Intel, and Via are leading manufacturers
Display System
VGA Display System
LED Display System
Display Connectors
- Different cables and connectors for different display adapters
Each connector has specific function and benefits
HDMI Interface
- Most widely used digital audio and video interface
- Also offers remote control and content protection
- Uses a proprietary 19-pin connector
- Offers up to 8K UHD resolutions
DisplayPort
- Royalty-free complement to HDMI
- First interface to use packetized data transmission
- Uses a 20-pin connector
- Can support even different transmission modes of increasing bandwidth
Thunderbolt
- Developed by Intel and Apple, primarily for Apple laptops and computers
- Can be used as either a display or peripheral interface
- Initial versions used the MiniDP interface
- Version 3 and now version 4 use the USB-C interface
- Thunderbolt features don’t work with a standard USB-C cable and port
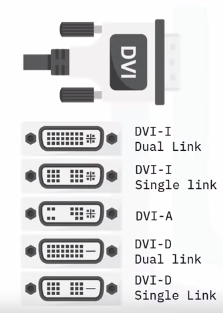
Digital Visual Interface (DVI)
- Designed as a high-quality interface for flat-paneled devices
- Support both analog and digital devices
- DVI-I supports both analog and digital
- DVI-A supports only analog
- DVI-D supports only digital
- Single-link for lower resolutions and Dual-link for HDTV
Superseded by HDMI and Thunderbolt
Video Graphics Array (VGA)
- A legacy interface, used for analog video on PC
- Has a 15-pin connector that can be secured with screws
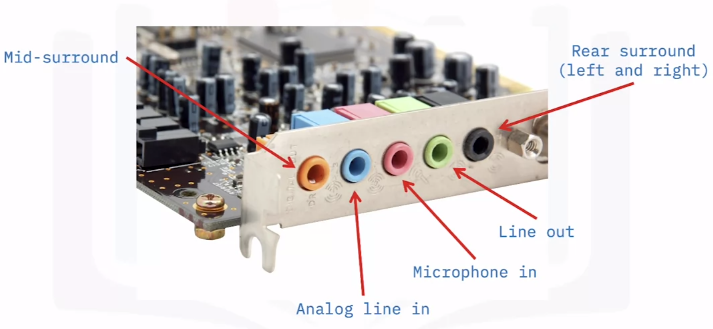
Identifying Audio Connectors
The audio connection
- Onboard or internal expansion
- Has multiple ports to connect a variety of devices
Used for multimedia application, education and entertainment, presentation, and teleconferencing
Audio connectors
- Sound cards
- Bluetooth
- Game ports/USB ports
- External audio interfaces
External audio interfaces
- Single device for multiple input and output ports
- Mostly used in professional studies
- Use USB, FireWire, Thunderbolt, or similar connectors
Wired and Wireless Connections
Data packets
- Communication technology allows components to communicate over a network
- Data packets are sent from one smart object to another
- Information about the sending and receiving device, along with the message
- Devices built to talk over a network can communicate with each other
Network types
- Closed (limited number of devices can connect)
- Open (unlimited number of devices can connect)
- Either could be wired or wireless
Wired connectors
Wire connection benefits
- Faster data transmission
- Up to 5 Gbps
- More reliable than wireless
- Immune to signal drops and dead zones
- Less prone to radio interference
- More secure
- Less likely to be hacked
Wireless connections
- Use different technologies based on connection requirements
- Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi)
- Connects a router to a modem for network access
- Bluetooth
- 1998
- Pairing
- Radio-frequency identification (RFID)
- Identification and tracks objects using tags
- Range up to several hundred meters
- Collection of road tolls
- Other uses of RFID tags
- Livestock tracking, tacking pharmaceuticals through warehouses, preventing theft, and expediting checkout in stores
- NFC (Near Field Communication)
- Based on RFID
- Extremely short range
- Transmits data through electromagnetic radio fields
Wireless connection advantages
- Increased mobility
- Reduced time to set up
- Flexibility and scalability
- Wider reach
- Lower cost of ownership
Peripherals and Printer Connections
Common installation steps
Computers require software that enables peripheral or printer device recognition and communication using:
- Onboard Plug and Play software
- Device driver software
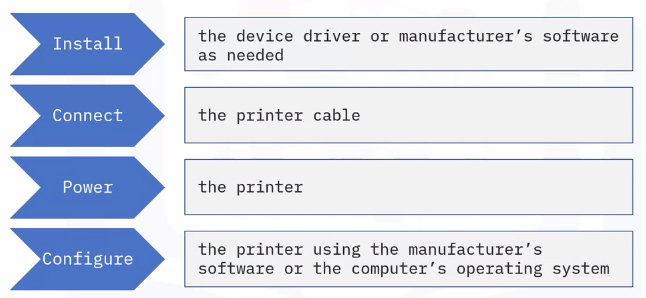
- Device application software Initial stand-alone, peripheral installation often still requires a wired connection or network connection 1) Connect the printer to the computer using a cable 2) Turn on the printer Frequently used stand-alone peripherals are:
- USB
- Bluetooth
- Wi-Fi
- NFC Three other connection methods are:
- Serial port
- Parallel port
- Network
Serial cable connections
- Are less common
- Transmit data more slowly
- RS232 protocol remains in use
- Data can travel longer distances
- Better noise immunity
- Compatibility among manufacturers
Cables commonly feature 9-pin connections and two screws to secure the cable
Parallel port cable connection
- Are less common
- Send and receive multiple bits of data simultaneously
- Feature 25-pin connections
Include two screws to keep the cable connected
Network connections
- Generally, are Wi-Fi or wired Ethernet connections
- Before you begin, verify that your computer has a network connection
Connecting to local printers
Installation Types
1) Plug and Play 2) Driver Installation
PnP vs. driver installation
- PnP devices work as soon as they’re connected to a computer
- Examples include mice and keyboards
- A malfunctioning device should be investigated in Device Manager.
- Possible cause of malfunction is an outdated driver
IP-based peripherals
- Hardware connected to a TCP/IP network
- Examples of such devices include wireless routers and security cameras
- These devices must be connected to a local area network (LAN) or the Internet to function
Web-based configuration
- Different from installation
- Used for networking devices such as routers
- Is an easier process to set up a device
- Completed on a web page
- Often on the manufacturer’s site
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.