Job Opportunities and Skill sets in Software Engineering
What does a Software Engineer Do?
Software engineering:
- Engineering
- Mathematics
Computing
Types of Software:
- Desktop and web applications
- Mobile Applications
- Games
- Operating Systems
Network controllers
Types of technologies:
- Programming languages
- Development environments
- Frameworks
Libs, databases, and servers
Categories of software engineer:
- Back-end engineers or systems developers
Front-end engineers or application developers
Software engineering teams:
- Off-the-shelf software
- Bespoke software
Internal software
And within the teams they might work on:
- Data integration
- Business logic
User interfaces
Software engineering tasks:
- Designing new software systems
- Writing and testing code
- Evaluating and testing software
- Optimizing software programs
- Maintaining and updating software systems
- Documenting code
- Presenting new systems to users and customers
- Integrating and deploying software
Responsibilities:
Skills Required in Software Engineering
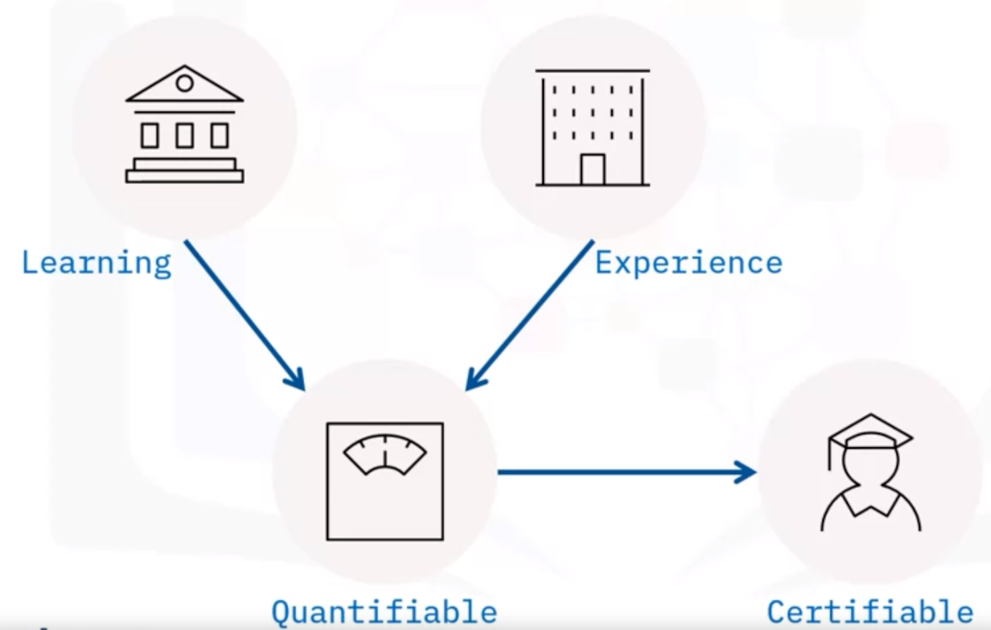
What are hard skills?
Commonly required hard skills in software engineering:
- Programming languages
- Version control
- Cloud computing
- Testing and debugging
- Monitoring
- Troubleshooting
- Agile development
- Database architecture
What are soft skills?
- Hard to define, quantify, or certify
- Easily transferable
Hard skills for software engineers
Analysis and design:
- Analyze users’ needs
Design solutions
Development:
- Computer programming
- Coding
- Languages:
- Java
- Python
- C#
- Ruby
- Frameworks
Test:
- Testing
- Meets functional specification
- Easy to use
Debugging
Deployment:
- Shell scripting
- Containers
- CI/CD
- Monitoring
- Troubleshooting
Soft Skills for Software Engineers
Teamwork:
- Different teams
- Project-based
- Role-based
- Squads
- Pair programming
- Take advantage of strengths
Learn from each other
Communication:
- Peers
- Managers
- Clients
Users
Time management:
- Time-sensitive projects
- Meet deadlines
- Avoid delays
Teams across time-zones
Problem-solving:
- Design an appropriate solution
- Write an effective code
- Locate and resolve bugs
Manage issues
Adaptability:
- Client changes
- Management request
User needs
Open to feedback:
- Peer review
- Mentor
- Stakeholders
Careers in Software Engineering
Job Outlook for Software Engineers
Employment options:
- Employed roles:
- Apprenticeship/internship
- Part-time
- Full-time
- Self-employed/independent:
- Contracting/consulting
- Freelancing
- Volunteer on open source projects
Career Paths in Software Engineering
Technical
Coding and problem-solving
Management
Leadership and soft skills
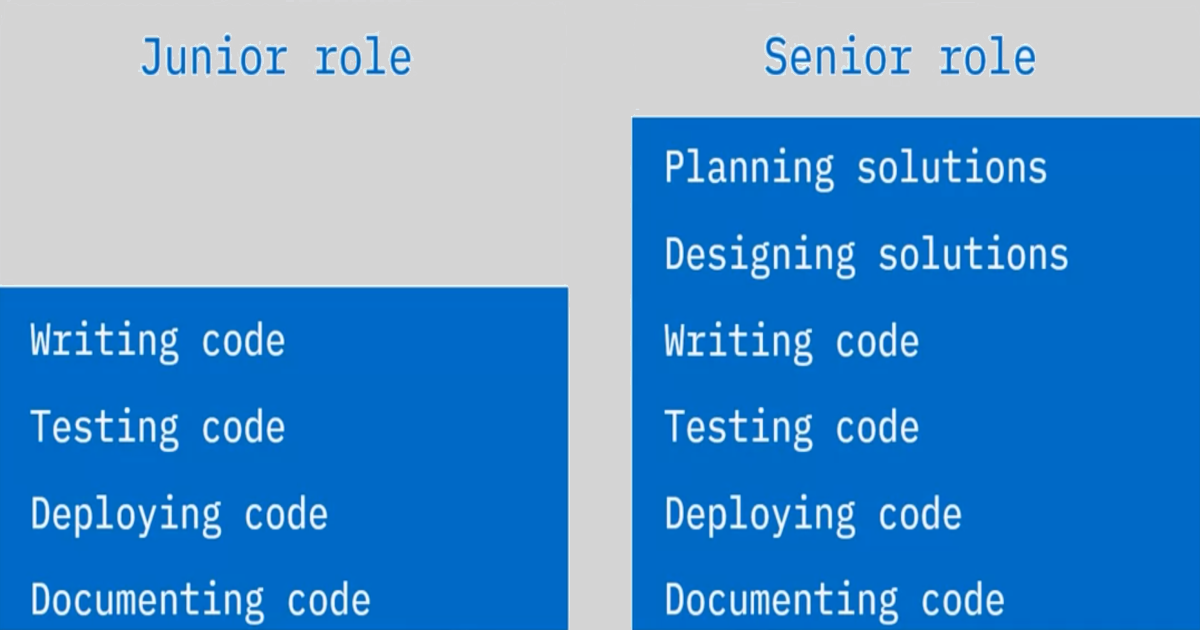
Career progression:
- Junior or Associate Software Engineer
- Develop small chunks of software
- Supported by a team leader or mentor
- Gain new skills and experience
- Software Engineer
- Break tasks down into sub-tasks
- Learn new languages
- Understand the software development lifecycles
- Mentor junior software engineers
- Senior Software Engineer
- Work across a project
- Mentor software engineers and review code
- Solve problems efficiently
- Staff Software Engineer
- Part of the technical team
- Develop, maintain, and extend software
- Ensure software meets expectations
- Ensure software uses resources efficiently
- Technical Lead
- Manage a team of developers and engineers
- Responsible for development lifecycle
- Report to stakeholders
- Principal Engineer/Technical Architect
- Responsible for architecture and design
- Create processes and procedures
- Engineering Manager
- Support team
- Encourage career progression
- Director of Engineering
- Strategic and technical role
- Determine project priority
- Identify hiring needs
- Define goals
- Define new projects
- Specify requirements
- Chief Technology Officer (CTO)
- Oversee research and development
- Monitor corporate technology
- Evaluate new technology and products
Other career directions
- Prefer interacting with clients:
- Technical sales
- Customer support
- Prefer working with numbers and data:
- Data engineering
- Data science
- Database administration
- Database development
- Prefer finding and fixing bugs:
- Software testing
Software Engineering Job Titles
Job Titles:
- Front-end engineer
- Back-end engineer
- Full-stack engineer
- DevOps engineer
- Software Quality Assurance Engineer
- Software Integration Engineer
- Software Security Engineer
- Mobile App Developer
- Games Developer
Code of Ethics
Origins of the code of ethics:
- Developed by the Joint Task Force on Software Engineering Ethics and Professional Practices
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Computer Society (IEEE-CS)
- Association for Computing Machinery (ACM)
- Championed the need to hold software engineers accountable
About the code of ethics:
- Pertains to the analysis, design, development, testing, and maintenance software cycle
- Dedicated to serving the public interest
The 8 principles
1) Public
2) Client/Employer
3) Product
4) Judgement
5) Management
6) Profession
7) Colleagues
8) Self
Supplemental guide to behavior
- Use in conjunction with conscientious decision-making and common sense
- Knowing where to apply principles is at the discretion and wisdom of the individual