Penetration Testing
What is Penetration Testing?
“Penetration testing is security testing in which assessors mimic real-world attacks to identify methods for circumventing the security features of an application, system, or network. It often involves launching real attacks on real systems and data that use tools and techniques commonly used by attackers.”
Operating Systems
| Desktop | Mobile |
|---|---|
| Windows | iOS |
| Unix | Android |
| Linux | Blackberry OS |
| macOS | Windows Mobile |
| ChromeOS | WebOS |
| Ubuntu | Symbian OS |
Approaches
- Internal vs. external
- Web and mobile application assessments
- Social Engineering
- Wireless Network, Embedded Device & IoT
- ICS (Industry Control Systems) penetration
General Methodology
- Planning
- Discovery
- Attack
- Report
Penetration Testing Phases
Penetration Testing – Planning
- Setting Objectives
- Establishing Boundaries
- Informing Need-to-know employees
Penetration Testing – Discovery
Vulnerability analysis
Vulnerability scanning can help identify outdated software versions, missing patches, and misconfigurations, and validate compliance with or deviations from an organization’s security policy. This is done by identifying the OSes and major software applications running on the hosts and matching them with information on known vulnerabilities stored in the scanners’ vulnerability databases.
Dorks
A Google Dork query, sometimes just referred to as a dork, is a search string that uses advanced search operators to find information that is not readily available on a website.
What Data Can We Find Using Google Dorks?
- Admin login pages
- Username and passwords
- Vulnerable entities
- Sensitive documents
- Govt/military data
- Email lists
- Bank Account details and lots more…
Passive vs. Active Record
| Passive | Active |
|---|---|
| Monitoring employees | Network Mapping |
| Listening to network traffic | Port Scanning |
| Password cracking |
Social Engineering
“Social Engineering is an attempt to trick someone into revealing information (e.g., a password) that can be used to attack systems or networks. It is used to test the human element and user awareness of security, and can reveal weaknesses in user behavior.”
Scanning Tools
- Network Mapper → NMAP
- Network Analyzer and Profiler → WIRESHARK
- Password Crackers → JOHNTHERIPPER
- Hacking Tools → METASPLOIT
Passive Online
- Wire sniffing
- Man in the Middle
- Replay Attack
Active Online
- Password Guessing
- Trojan/spyware/keyloggers
- Hah injection
- Phishing
Offline Attacks
- Pre-computed Hashes
- Data structures that use a hash function to store, order, and/or access data in an array.
- Distributed Network Attack (DNA)
- DNA is a password cracking system sold by AccessData.
- DNA can perform brute-force cracking of 40-bit RC2/RC4 keys. For longer keys, DNA can attempt password cracking. (It’s computationally infeasible to attempt a brute-force attack on a 128-bit key.)
- DNA can mine suspect’s hard drive for potential passwords.
- Rainbow Tables
- A rainbow table is a pre-computed table for reversing cryptographic hash functions, usually for cracking password hashes.
Tech-less Discovery
- Social Engineering
- Shoulder surfing
- Dumpster Diving
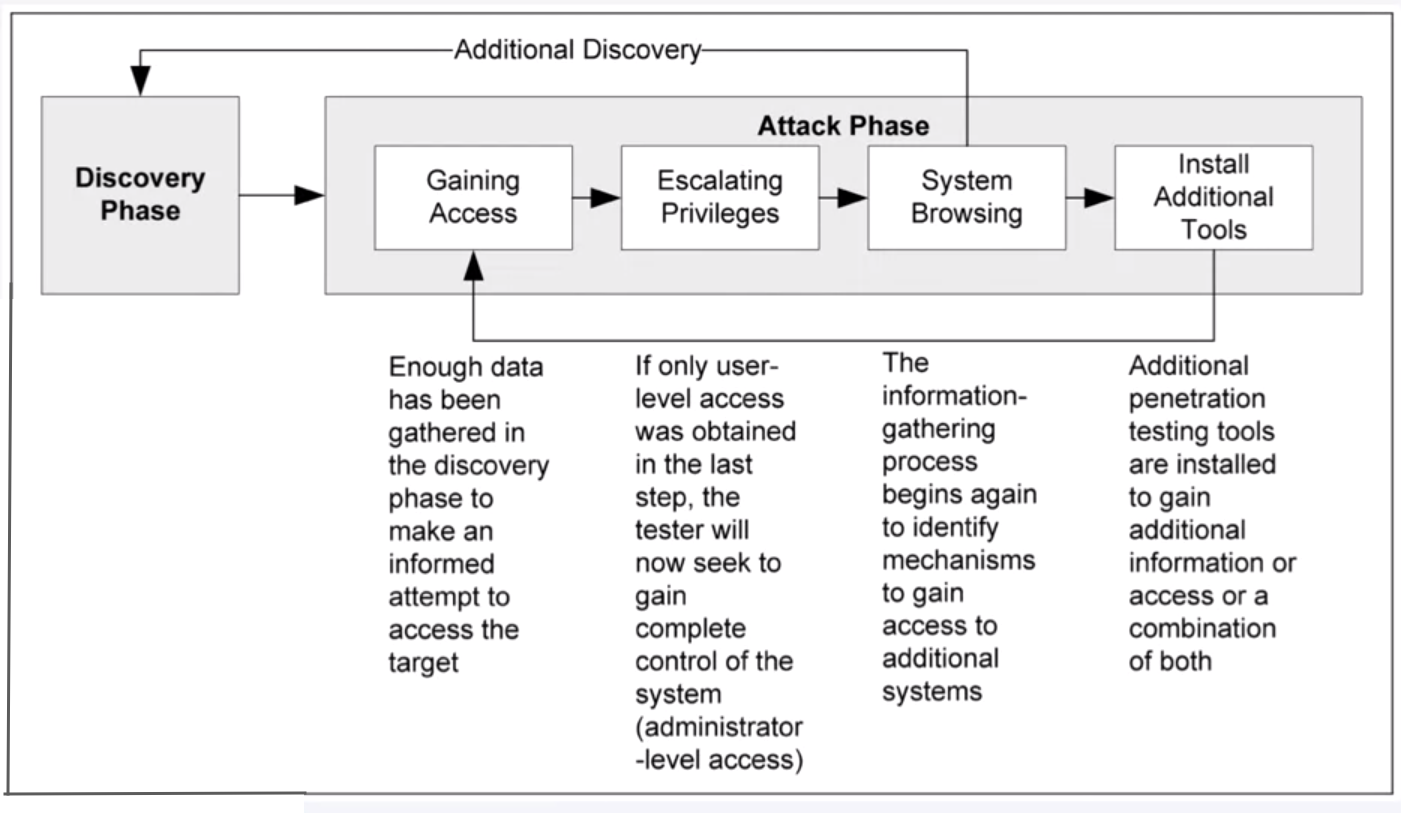
Penetration Testing – Attack
“While vulnerability scanners check only for the possible existence of a vulnerability, the attack phase of a penetration test exploits the vulnerability to confirm its existence.”
Types of Attack Scenarios
- White Box Testing: In this type of testing, the penetration tester has full access to the target system and all relevant information, including source code, network diagrams, and system configurations. This type of testing is also known as “full disclosure” testing and is typically performed during the planning phase of penetration testing.
- Grey Box Testing: In this type of testing, the penetration tester has partial access to the target system and some knowledge of its internal workings, but not full access or complete knowledge. This type of testing is typically performed during the Discovery phase of penetration testing.
- Black Box Testing: In this type of testing, the penetration tester has no prior knowledge or access to the target system and must rely solely on external observations and testing to gather information and identify vulnerabilities. This type of testing is also known as “blind” testing and is typically performed during the Attack phase of penetration testing.
Exploited Vulnerabilities
Penetration Testing – Reporting
Executive Summary
“This section will communicate to the reader the specific goals of the Penetration Test and the high level findings of the testing exercise.”
- Background
- Overall Posture
- Risk Ranking
- General Findings
- Recommendations
- Roadmap
Technical Review
Introduction
- Personnel involved
- Contact information
- Assets involved in testing
- Objectives of Test
- Scope of test
- Strength of test
- Approach
Threat/Grading Structure
Scope
- Information gathering
- Passive intelligence
- Active intelligence
- Corporate intelligence
Personnel intelligence
Vulnerability Assessment In this section, a definition of the methods used to identify the vulnerability as well as the evidence/classification of the vulnerability should be present.
Vulnerability Confirmation This section should review, in detail, all the steps taken to confirm the defined vulnerability as well as the following:
- Exploitation Timeline
- Targets selected for Exploitation
Exploitation Activities
Post Exploitation
- Escalation path
- Acquisition of Critical Information
- Value of information Access to core business systems
- Access to compliance protected data sets
- Additional information/systems accessed
- Ability of persistence
- Ability for exfiltration
- Countermeasure
Effectiveness
Risk/Exposure This section will cover the business risk in the following subsection:
- Evaluate incident frequency
- Estimate loss magnitude per incident
- Derive Risk
Penetration Testing Tools
- Kali Linux
- NMAP (Network Scanner)
- JohnTheRipper (Password cracking tool)
- MetaSploit
- Wireshark (Packet Analyzer)
- HackTheBox (Testing playground)
- LameWalkThrough (Testing playground)