People processes and technology
Frameworks and their Purpose
Best practices, baseline, and frameworks
- Used to improve the controls, methodologies, and governance for the IT departments or the global behavior of the organization.
- Seeks to improve performance, controls, and metrics.
- Helps to translate the business needs into technical or operational needs.
Normative and Compliance
- Rules to follow for a specific industry.
- Enforcement for the government, industry, or clients.
- Event if the company or the organization do not want to implement those controls for compliance.
Best practices, frameworks & others
- Frameworks
- COBIT (Control Objective for Information and Related Technologies)
COBIT is a framework created by ISACA for IT management and IT governance. The framework is business focused and defines a set of generic processes for the management of IT, with each process defined together.
- ITIL (The Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
ITIL is a set of detailed practices for IT activities such as IT service management (ITSM) and IT asset management (ITAM) that focus on aligning IT services with the needs of business.
- ISOs (International Organization for Standardization)
- COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organization of the Tread way Commission)
COSO is a joint initiative to combat corporate fraud.
- COBIT (Control Objective for Information and Related Technologies)
- Project manager methodologies
- Industry best practices
- Developer recommendations
- Others
Roles in Security
- CISO (Chief Information Security Officer)
The CISO is a high-level management position responsible for the entire computer security department and staff.
- Information Security Architect
- Information Security Consultant/Specialist
- Information Security Analyst
This position conducts Information security assessments for organizations and analyzes the events, alerts, alarms and any Information that could be useful to identify any threat that could compromise the organization.
- Information Security Auditor
This position is in charge of testing the effectiveness of computer information systems, including the security of the systems, and reports their findings.
- Security Software Developer
- Penetration Tester / Ethical Hacker
- Vulnerability Assessor etc.
Business Process Management (BPM) and IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Basics
Introduction to Process
- Processes and tools should work in harmony
- Security Operations Centers (SOC) need to have the current key skills, tools, and processes to be able to detect, investigate and stop threats before they become costly data breaches.
- As volumes of security alerts and false positives grow, more burden is placed upon Security Analyst and Incident Response Teams.
Business Process Management (BPM) Overview
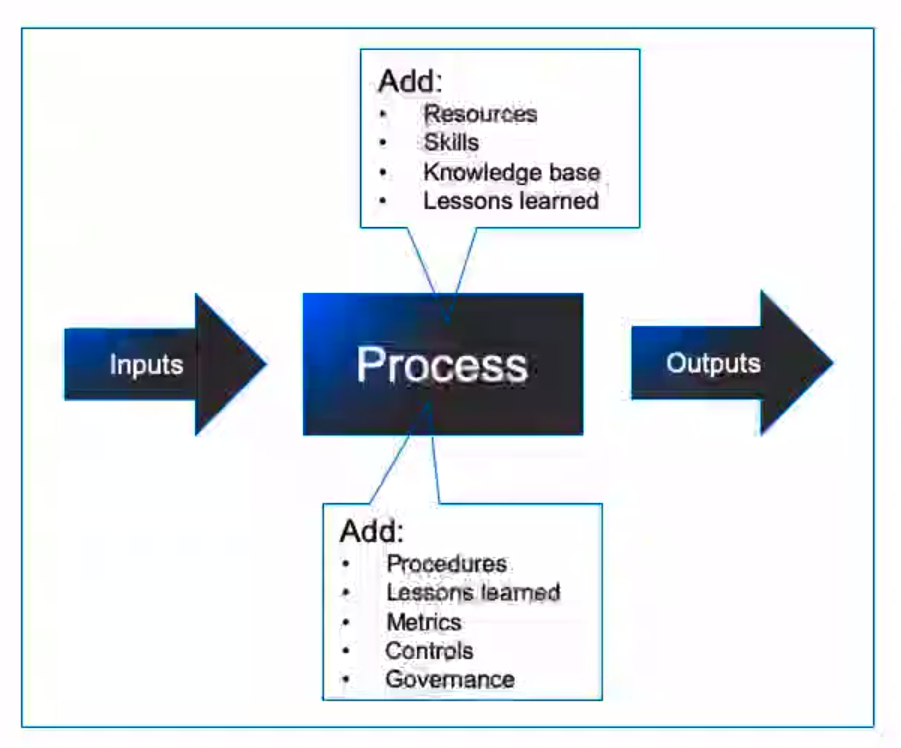
“A set of defined repeatable steps that take inputs, add value, and produce outputs that satisfy a customer’s requirements.”
Attributes of a Process
- Inputs: Information or materials that are required by the process to get started.
- Outputs: Services, or products that satisfy customer requirements.
- Bounds/Scope: The process starts when and end when.
- Tasks/Steps: Actions that are repeatable.
- Documentation: For audit, compliance, and reference purposes.
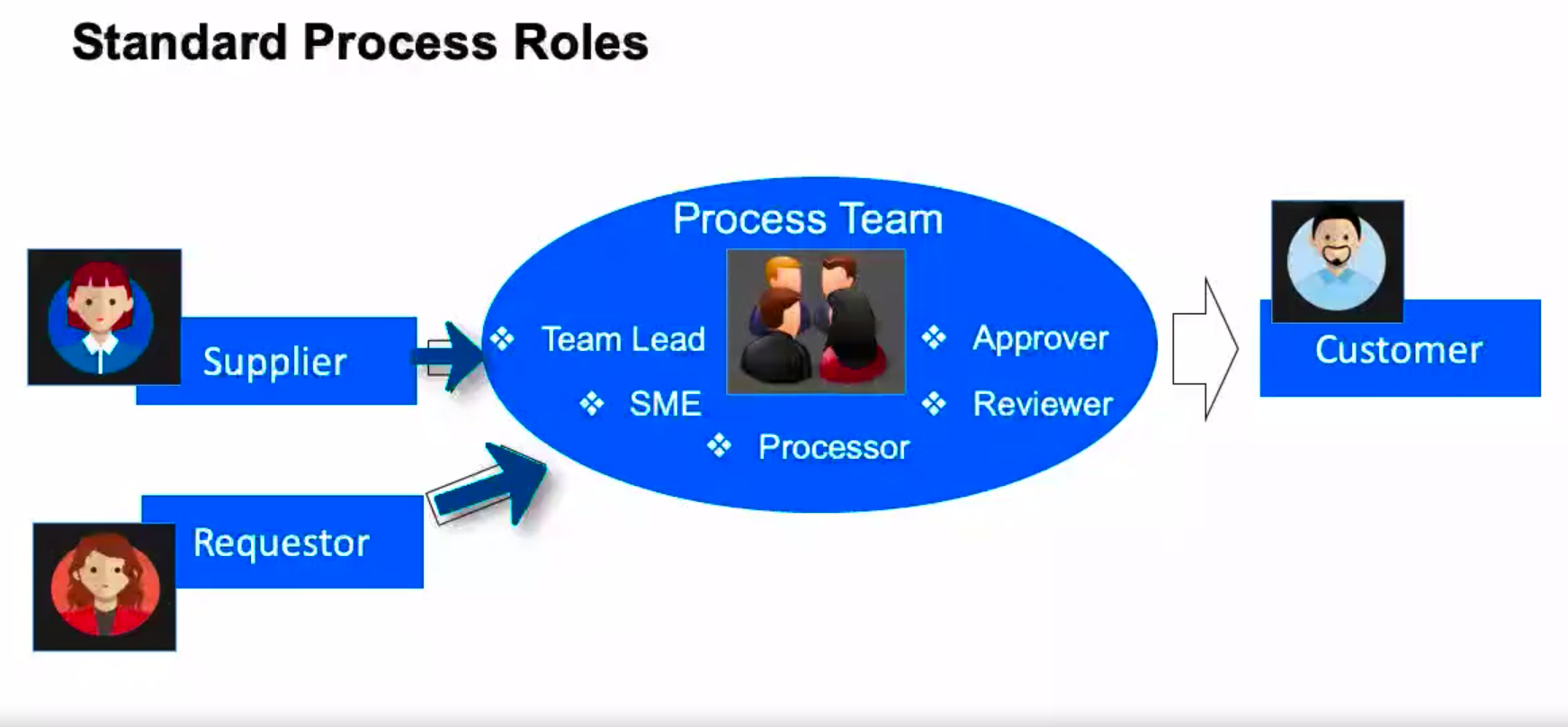
Standard Process Roles
What makes a Process Successful?
- Charter
- Clear Objectives
- Governance/Ownership
- Repeatability (reduced variation)
- Automation
- Established Performance indicators (metrics)
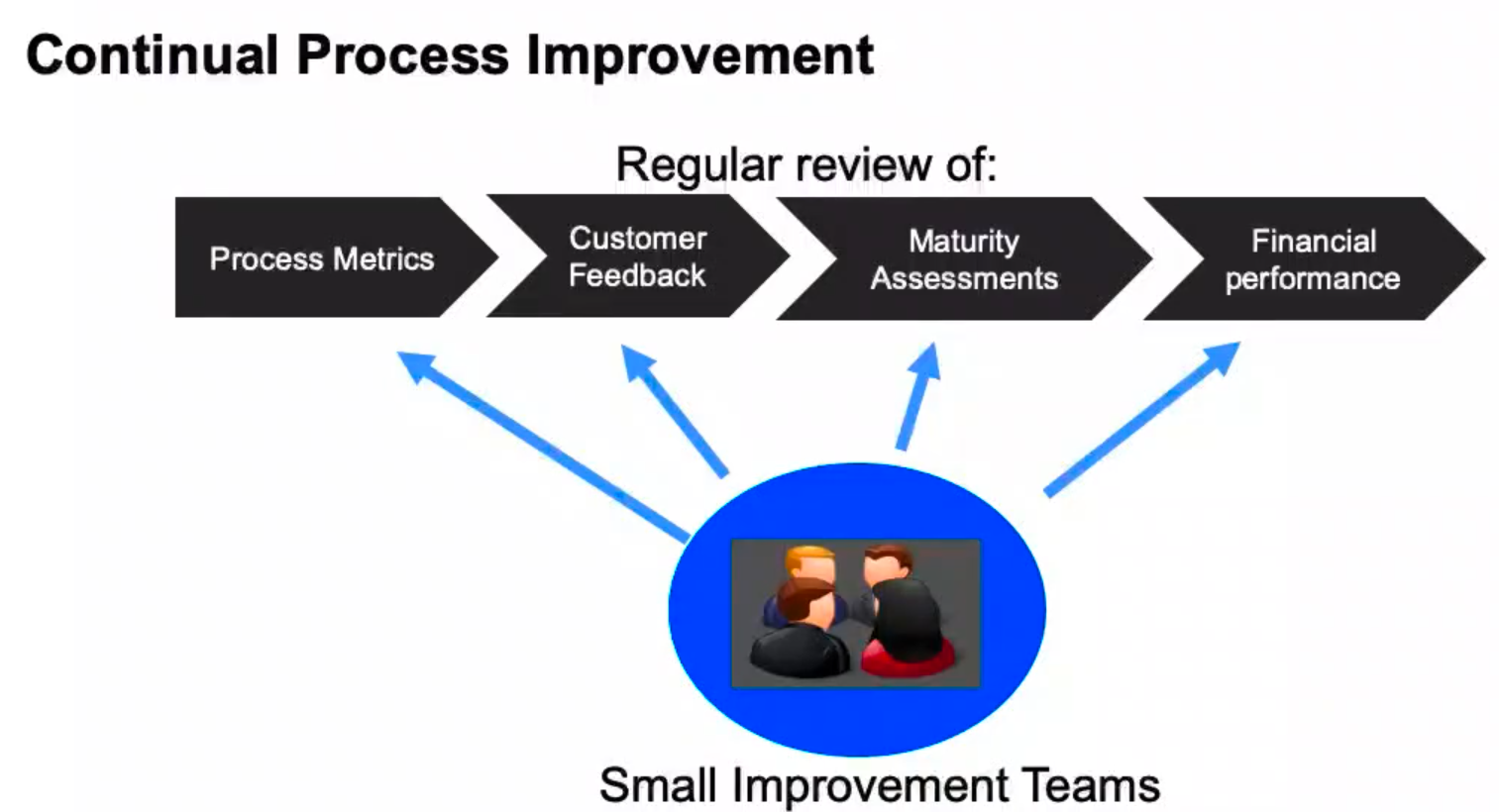
Process Performance Metrics
“It is critical that we measure our processing, so understand if they are performing to specifications and producing the desired outcome every time; and within financial expectations.”
- Typical Categories
- Cycle Time
- Cost
- Quality (Defect Rate)
- Rework
Continual Process Improvement
Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Overview
- ITIL is a best practice framework that has been drawn from both the public and private sectors internationally.
- It describes how IT resources should be organized to deliver Business value.
- It models how to document processes and functions, in the roles of IT Service Management (ITSM).
- ITIL Life-cycle – Service Phases
- Service Strategy
- Service Design
- Service Transition
- Service Operations
- Service Improvements
ITIL Life-cycle – Service Strategy
- Service Portfolio Management
- Financial Management
- Demand Management
- Business Relationship Management
ITIL Life-cycle – Service Design
- Service Catalog Management
- Service Level Management
- Information Security Management
- Supplier Management
ITIL Life-cycle – Service Transition
- Change Management
- Project Management
- Release & Deployment Management
- Service validation & Testing
- Knowledge Management
ITIL Life-cycle – Service Operations
- Event Management
- Incident Management
- Problem Management
ITIL Life-cycle – Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
- Review Metrics
- Identify Opportunities
- Test & Prioritize
- Implement Improvements
Key ITIL Processes
Problem Management
- The process responsible for managing the Life-cycle of all problems.
ITIL defines a ‘problem’ as ‘an unknown cause of one or more incidents.’
Change Management
- Manage changes to baseline service assets and configuration items across the ITIL Life-cycle.
Incident Management
An incident is an unplanned interruption to an IT Service, a reduction in the quality of an IT Service, and/ or a failure of a configuration item.
Log → Assign → Track → Categorize → Prioritize → Resolve → Close
Event Management
- Events are any detectable or discernible occurrence that has significance for the management of IT Infrastructure, or the delivery of an IT service.
Service Level Management
- This involves the planning coordinating, drafting, monitoring, and reporting on Service Level Agreements (SLAs). It is the ongoing review of service achievements to ensure that the required service quality is maintained and gradually improved.
Information Security Management
- This deals with having and maintaining an information security policy (ISP) and specific security Policies that address each aspect of strategy, Objectives, and regulations.
Difference between ITSM and ITIL
Information Technology Service Management (ITSM)
“ITSM is a concept that enables an organization to maximize business value from the use of information Technology.”
IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL)
“ITIL is a best practice framework that gives guidance on how ITSM can be delivered.”