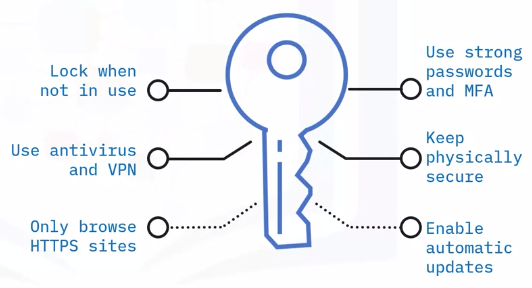
Safe Browsing Practices
Security Concerns and Safe Browsing
Application Ecosystem Security
Mobile applications
Rooting and Jail breaking
- Add functionality but also adds vulnerability
Desktop Software
Business software
Business software automates transactions, mines sales data, manages information, and more.
Corporate network
To protect files, systems, and resources, businesses must limit access.
Public Browsing Risks
Free and Open networks
Public browsing risks
- Session hijacking
- Shoulder surfing
Social Networking Sites
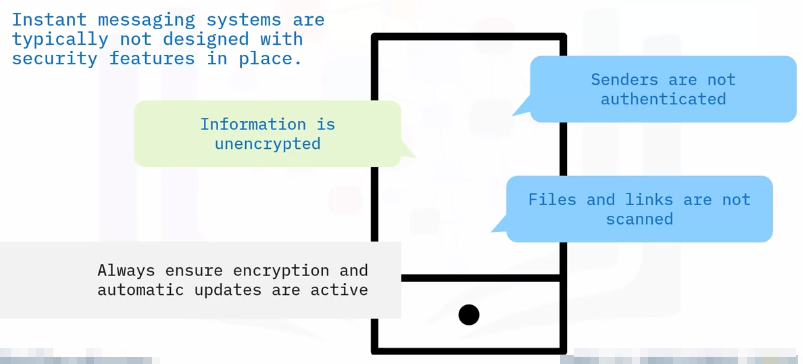
Instant messaging
Internet browser and versions
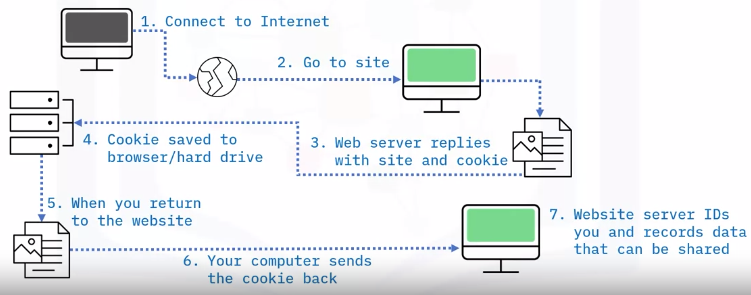
Cookies
Cookies are text files with small pieces of data.
Cookie types:
- Session cookies
- Persistent cookies
- Authentication cookies
- First-party cookies
- Third-party cookies
- Zombie cookies
Security certificates
Secure sockets layer (SSL) certificates authenticate a website’s identity and enable an encrypted connection between a web server and a browser.
Browser updates
Because browsers are a favorite target for hackers, keeping them updated is very important.
Safe Browsing Techniques
Autofill management
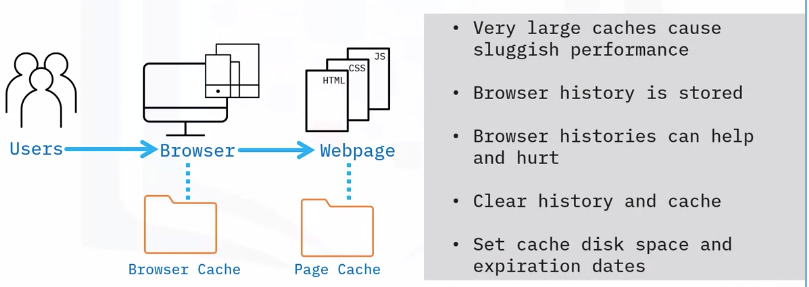
Browser cache and history
A browser cache is a storage data that holds downloads of web pages you’ve visited.
Private browsing
- You appear as a new or unknown user on the sites you visit.
- Other people who use the device won’t see your history.
- Cookies and site data are deleted when you exit the browser.
- But private browsing activity isn’t hidden from your employer, school, or ISP.
- Bookmarks you create will be kept.
- Downloaded files are saved and may be visible to other users.
Malicious websites
Safe websites
Identifying safe websites is more significant than ever.
Safety tips include:
- Use the Whois Lookup tool
- Look for reviews
- Only visit HTTPS sites
- Check the trust seal
- Inspect URLs
Adware and popups
Redirection
The aim of redirection is to point you towards certain types of advertising or dangerous code.
Redirection is caused by:
- Unwanted toolbars or browser extensions
- Malware that alerts searches and URLs
Hacked websites servers that redirect visitors
To avoid hijacking and redirection:
- Set automatic updates for your browser, OS, and security tools.
- Run regular system scans.
Warning signs
Search engines use algorithms to detect harmful sites. Browsers use those results to warn users.
Security Threats: Virtual Private Networks
VPN types:
- Site-to-site VPN
- Host-to-site VPN
- Host-to-host VPN
VPN hardware
VPN hardware devices are:
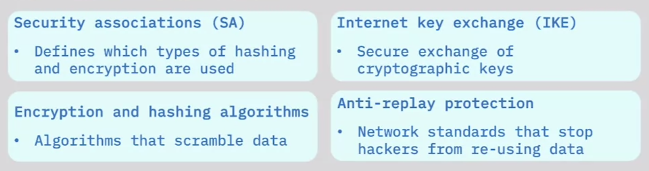
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec)
IPsec is a suite of network standards and protocols that use cryptography to protect data traveling over the Internet.
IPsec suite core protocols:
IPsec Authentication Header (AH) protocol: - Authenticates senders and IP addresses
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) protocol: - Encrypts data - Authenticates data and senders
The IPsec suite has two modes:
The IPsec suite uses: