Securing Your Networks
Secure Network Architecture
Network Hardening Best Practices
- Disable the network services that are not needed.
- Monitoring network traffic
- Analyze the network logs
- Network separation
Network hardening
The process of securing a network by reducing its potential vulnerabilities through configuration changes and taking specific steps.
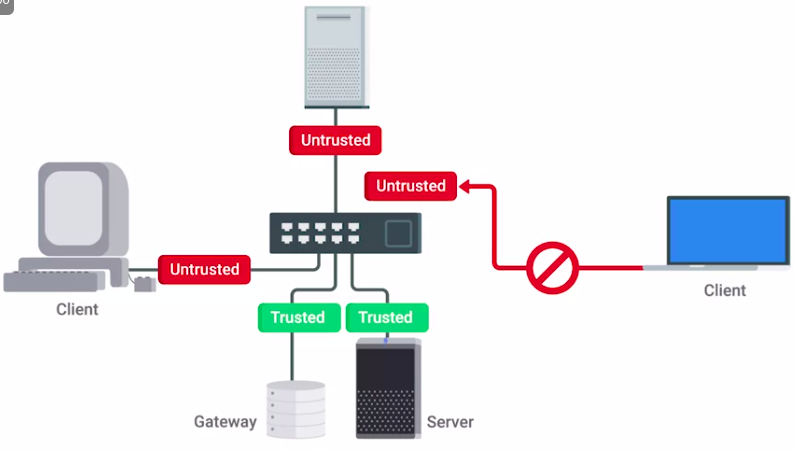
Implicit deny
A network security concept where anything not explicitly permitted or allowed should be denied.
Analyzing logs
The practice of collecting logs from different network and sometimes client devices on your network, then performing an automated analysis on them.
- Log analysis systems are configured using user-defined rules to match interesting or atypical log entries.
- Normalizing log data is an important step, since logs from different devices and systems may not be formatted in a common way.
- This makes correlation analysis easier.
Correlation analysis
The process of taking logs data from different systems and matching events across the systems.
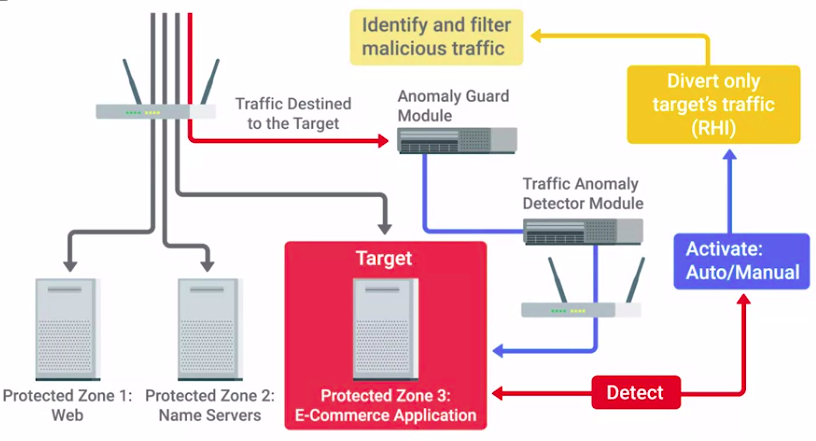
Flood guards
Provide protection against DoS or Denial of Service attacks.
- fail2ban
Network Hardware Hardening
To protect against Rogue DHCP server attack, enterprise switches offer a feature called DHCP snooping.
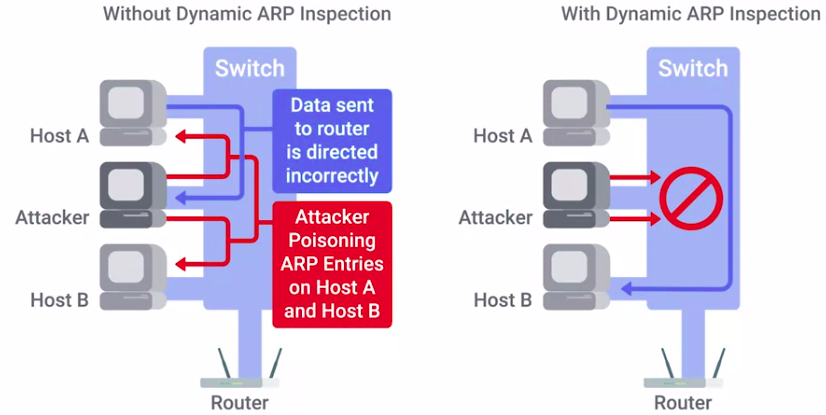
Another form of network hardening is Dynamic ARP inspection.
Dynamic ARP inspection is also a feature of enterprise switches.
IP Source Guard is used to protect against IP spoofing attacks in enterprise switches.
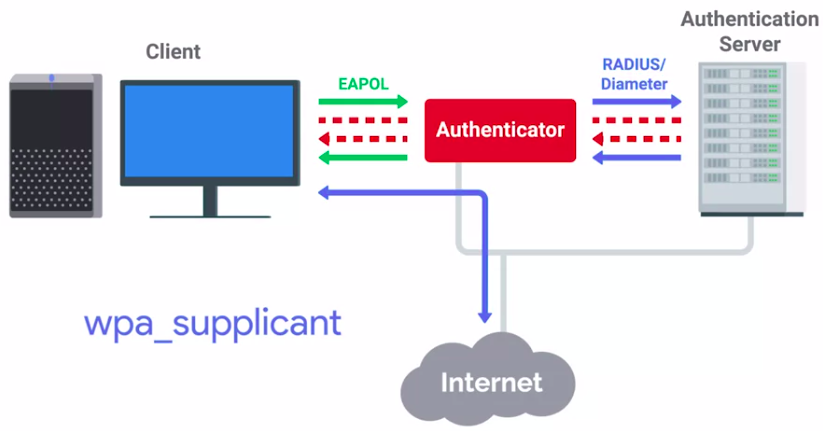
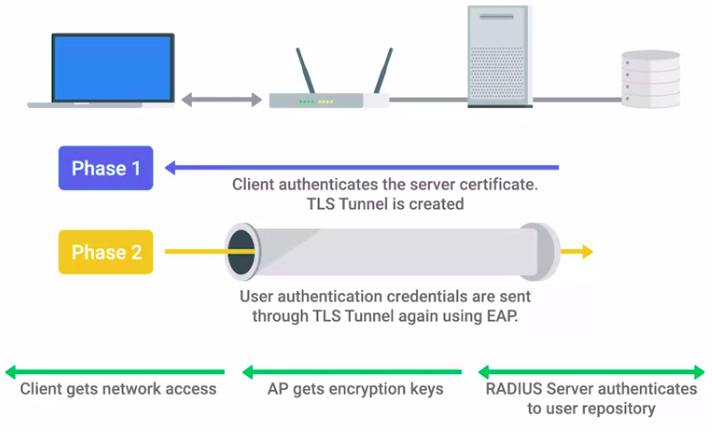
To really hardened your network, you should apply IEEE 802.1X recommendation.
IEEE 802.1x is a protocol developed to let clients connect to port based networks using modern authentication methods.
- There are three nodes in the authentication process: supplicant, authenticator, and authentication server.
- The authentication server uses either a shared key system or open access system to control who is able to connect to the network.
- Based on the criteria of the authentication server, the supplicator will grant the authentication request and begin the connection process, or it will be sent an Access Reject message and terminate the connection.
EAP-TLS
An authentication type supported by EAP that uses TLS to provide mutual authentication of both the client and the authenticating server.
Network Software Hardening
- Firewalls
- Proxies
- VPNs
Reverse proxies:
Wireless Security
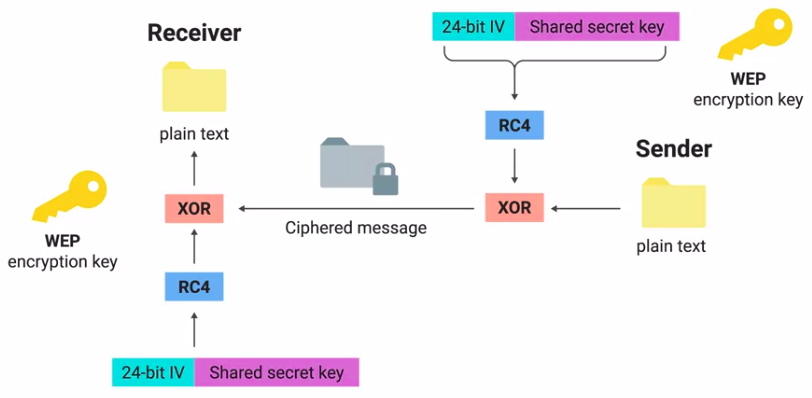
WEP Encryption and Why You Shouldn’t Use It
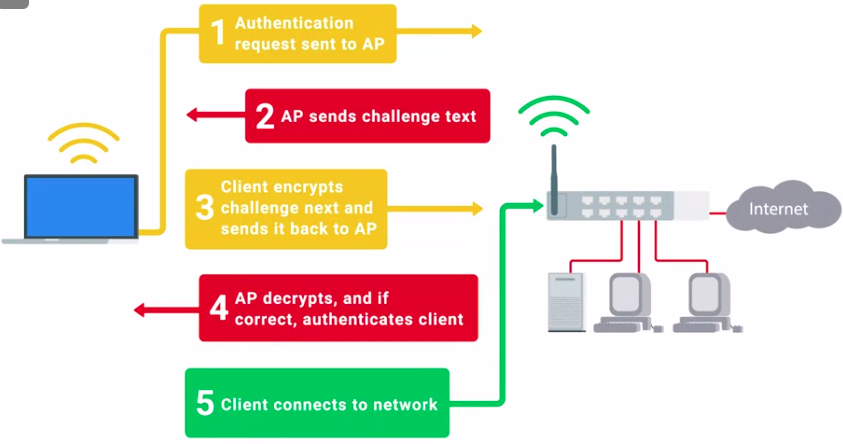
WEP supported two types of authentications:
- Open System authentication
- Shared Key authentication
Why WEP is for everyone:
- Seriously bad for privacy and confidentiality purposes
- It was abandoned in 2004, in favor of more strong encryption methods.
- Inherent weaknesses in RC4 Encryption Algorithm use in WEP.
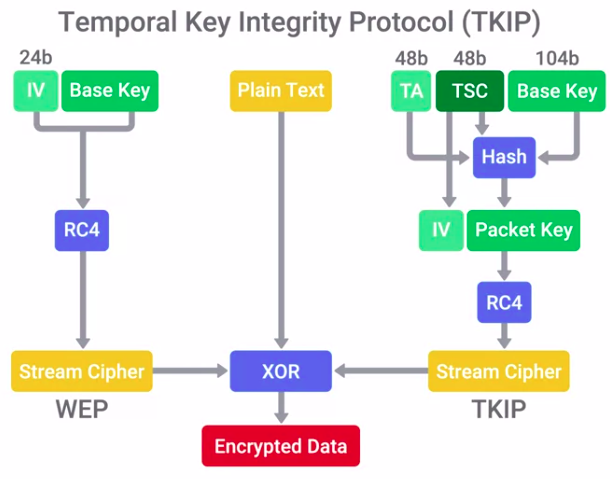
Let’s Get Rid of WEP! WPA/WPA2
The replacement for WEP from the Wi-Fi Alliance:
- WPA – Wi-Fi Protected Access
- WPA2 – Introduced in 2004
WPA
Designed as a short-term replacement that would be compatible with older WEP-enabled hardware with a simple firmware update.
Under WPA, the pre-shared key is the Wi-Fi password you share with people when they come over and want to use your wireless network.
WPA2
For security, it uses:
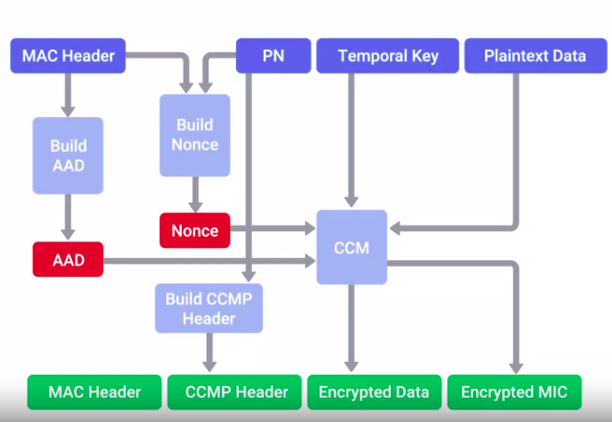
- Uses AES.
- CCMP (Counter Mode CBC-MAC Protocol)
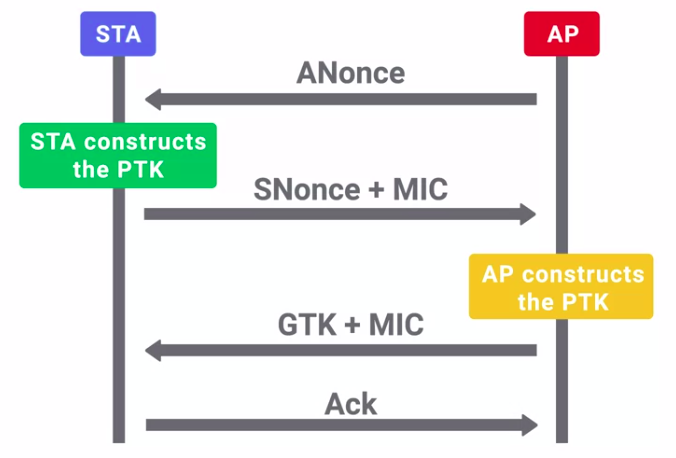
Four-way handshake
PMTK is generated through:
- PMK
- AP nonce
- Client nonce
- AP MAC address
- Client MAC address
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Access) support:
- PIN entry authentication
- NFC or USB
- Push-button authentication
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) PIN brute force vulnerability
Wireless Hardening
In the ideal world, we all should protect our wireless networks with 802.1X with EAP-TLS.
- If 802.1X is too complicated for a company, the next best alternative would be WPA2 with AES/CCMP mode.
- But to protect against Rainbow tables attack, we need some extra measures.
- A long and complex passphrase that wouldn’t find in a dictionary would increase the amount of time and resources an attacker would need to break the passphrase.
- If your company values security over convenience, you should make sure that WPS isn’t enabled on your APs.
Network Monitoring
Sniffing the Network
There are number of network sniffing open source tools like:
- Aircrack-ng
- Kismet
Packet sniffing (packet capture)
The process of intercepting network packets in their entirety for analysis.
Promiscuous Mode
A type of computer networking operational mode in which all network data packets can be accessed and viewed by all network adapters operating in this mode.
Port mirroring
Allows the switch to take all packets from a specified port, port range, or entire VLAN and mirror the packets to a specified switch port.
Monitor mode
Allows us to scan across channels to see all wireless traffic being sent by APs and clients.
Wireshark and tcpdump
Tcpdump
A super popular, lightweight, command-line based utility that you can use to capture and analyze packets.
Wireshark
A graphical tool for traffic monitoring, that is more powerful and easier to use than tcpdump.
Intrusion Detection/Prevention System
IDS or IPS systems operate by monitoring network traffic and analyzing it.
- They look for matching behavior for malicious packets.
- IDS on logs the packets, while IPS can change firewall rules on the fly to drop malicious packets.
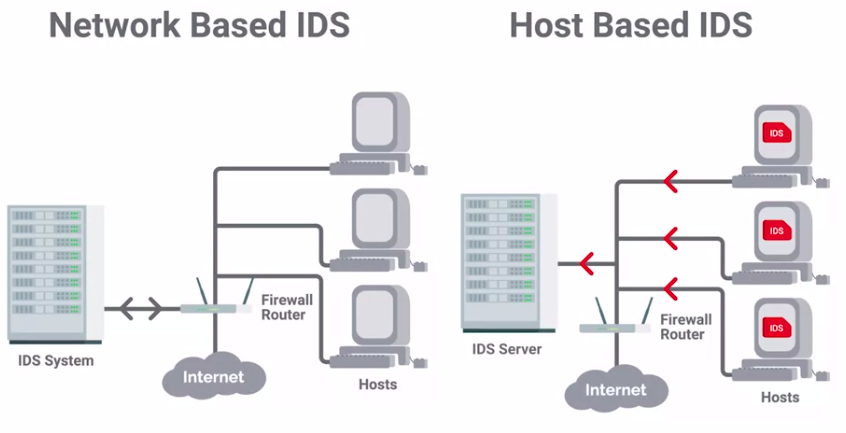
- IDS/IPS may be host-based or network-based.
Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS)
The detection system would be deployed somewhere on a network, where it can monitor traffic for a network segment or subnet.
Some popular NIDS system are:
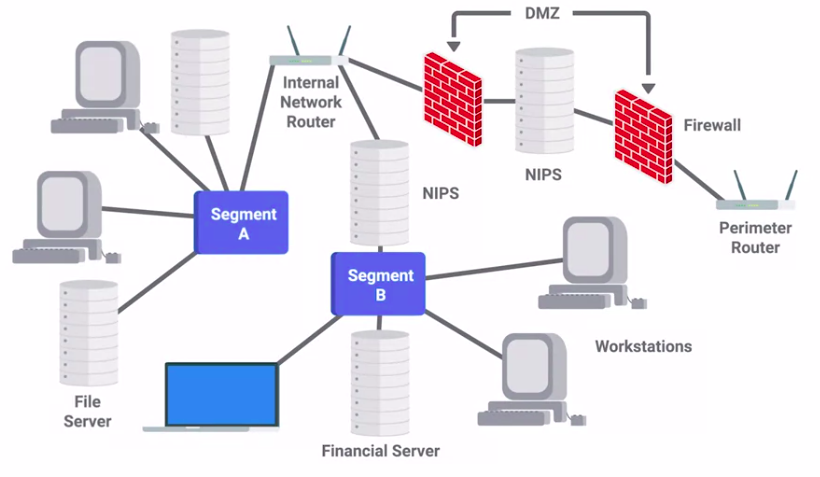
Unified Threat Management (UTM)
UTM solutions stretch beyond the traditional firewall to include an array of network security tools with a single management interface. UTM simplifies the configuration and enforcement of security controls and policies, saving time and resources. Security event logs and reporting are also centralized and simplified to provide a holistic view of network security events.
UTM options and configurations
UTM solutions are available with a variety of options and configurations to meet the network security needs of an organization:
UTM hardware and software options:
- Stand-alone UTM network appliance
- Set of UTM networked appliances or devices
- UTM server software application(s)
Extent of UTM protection options:
- Single host
- Entire network
UTM security service and tool options can include:
- Firewalls
- IDS
- IPS
- Antivirus software
- Anti-malware software
- Spam gateway
- Web and content filters
- Data leak/loss prevention (DLP)
- VPN
Stream-based vs. proxy-based UTM inspections
UTM solutions offer two methods for inspecting packets in UTM firewalls, IPS, IDS, and VPNs:
- Stream-based inspection, also called flow-based inspection: UTM ddevices,inspects data samples from packets for malicious content and threats as the packets flow through the device in a stream of data. This process minimizes the duration of the security inspection, which keeps network data flowing at a faster rate than a proxy-based inspection.
- Proxy-based inspection: A UTM network appliance works as a proxy server for the flow of network traffic. The UTM appliance intercepts packets and uses them to reconstruct files. Then the UTM device will analyze the file for threats before allowing the file to continue on to its intended destination. Although this security screening process is more thorough than the stream-based inspection technique, proxy-based inspections are slower in the transmission of data.
Benefits of using UTM
- UTM can be cost-effective
- UTM is flexible and adaptable
- UTM offers integrated and centralized management
Risk of using UTM
- UTM can become a single point of failure in a network security attack
- UTM might be a waste of resources for small businesses
Home Network Security
Employees, who work from home, use home networks to access company files and programs. Using home networks creates security challenges for companies. Companies can provide employees guidance for protecting their home networks from attacks. This reading will cover common attacks on home networks and steps to make home networks more secure.
Common security vulnerabilities
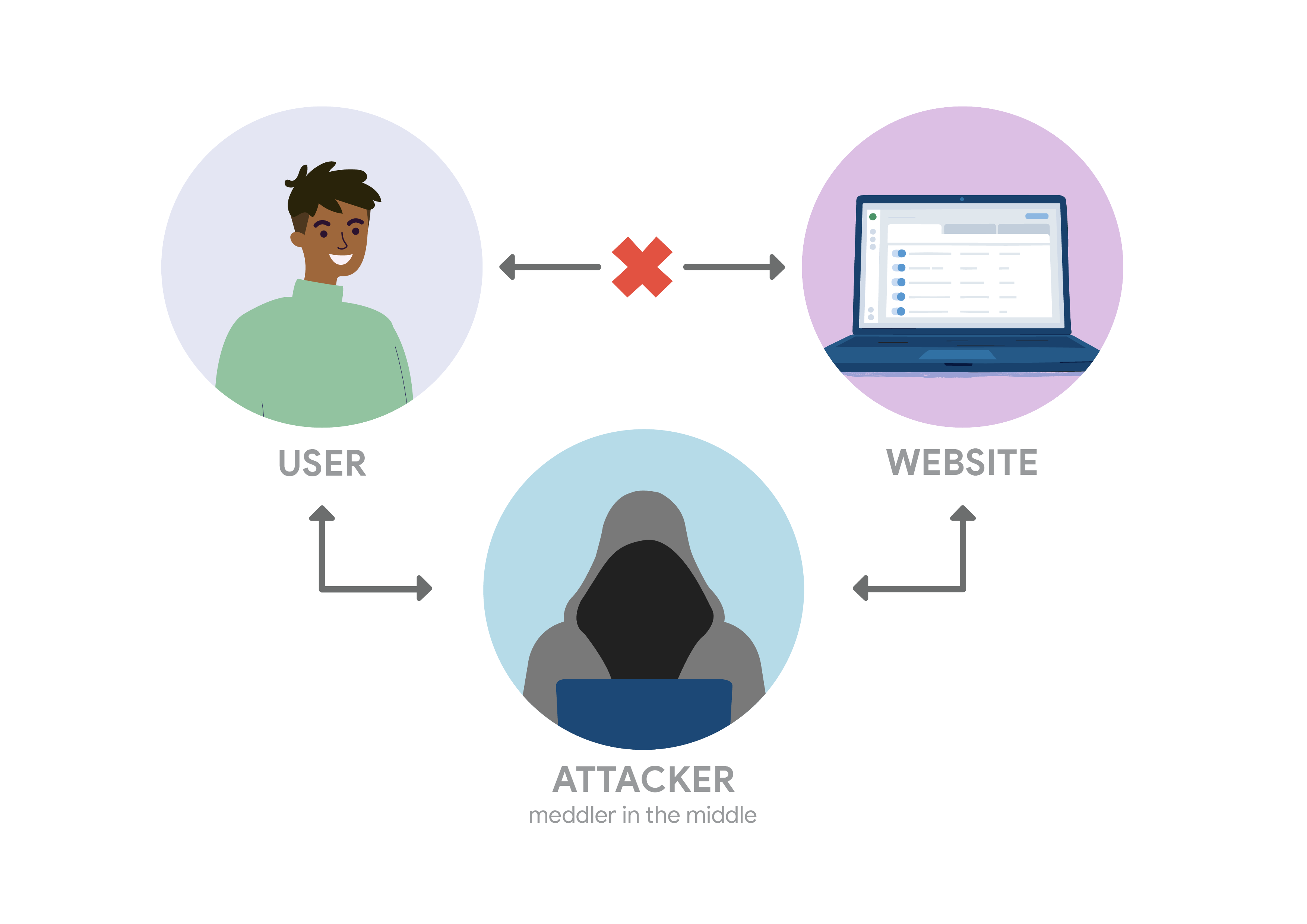
Meddler in the middle attacks allows a meddler to get between two communication devices or applications. The meddler then replies as the sender and receiver without either one knowing they are not communicating with the correct person, device, or application. These attacks allow the meddler to obtain login credentials and other sensitive information.
- Data Theft is when data within the network is stolen, copied, sent, or viewed by someone who should not have access.
- Ransomware uses malware to keep users from accessing important files on their network. Hackers grant access to the files after receiving a ransom payment.
Keeping home networks secure
- Change the default name and password
- Limit access to the home network
- Create a guest network
- Turn on Wi-Fi network encryption
- Turn on the router’s firewall
- Update to the newer Wi-Fi standard