Security Best Practices
Password Management and Security Best Practices
Password Management Techniques
- Password Policies
- Creating better passwords
- Password Confidentiality
- Password reuse
- Password expiration
- 2FA
- MFA
- Password Managers
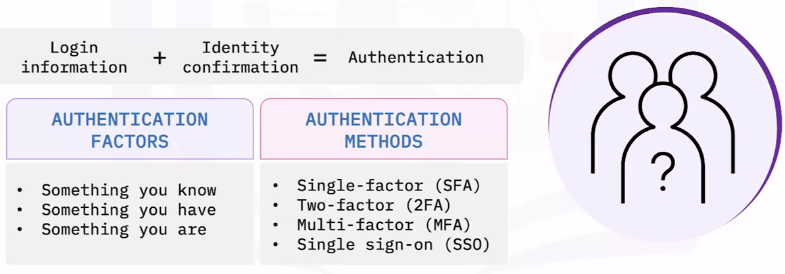
Identification factors
Identification factors are pieces of information that only you and an authentication service know.
Single sign-on
SSO verifies users for connected accounts or apps, so they only have to log in once.
- Businesses use SSO to simplify and speed up access to resources.
- IT departments set up SSO, so employees are automatically logged in when they log into their work networks.
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
The three A’s
There are three processes involved in logging in to a network or account.
Access control
- Rules of the least privilege (ROLP)
- Role-based access control (RBAC) follows a company’s org chart.
Authorization
Authorization is when you have permissions to access a location or do an action.
Access control must be setup before authorization is granted.
Authorization must be set up for your user account before you’re able to log in.
Authentication
Authentication is the act of confirming the identity of a user.
Accounting
Digital accounting is used in troubleshooting, security analysis, forensics, and hacking.
Non-repudiation
Non-repudiation is when you can’t deny being in a specific location. It guarantees a message sent between two parties is genuine.
Ways to Hardening Devices
- Device hardening
- Patching updates
- Firmware updates
- Secure boot
- TPM
- Drive Encryption
- Encryption
- Device lock
- Disable features and ports
- Autorun
- Bluetooth
- NFC
- Apps that harden
- Antivirus
- Anti-malware
- Ani-spyware
- Software firewalls and VPNS
- Change default password and disable admin accounts
Device hardening
Hardening is the process of securing a device to minimize vulnerabilities.
Harden devices by:
- Disabling unneeded features.
- Updating firmware, OS, and software.
Using firewalls, VPN, and anti-malware.
The more layers of security you use, the safer your data and devices will be.
Validation and Device Usage
- Software sources validation
- Use OEM websites
- Avoid third-party websites or use with caution
- Uninstall unwanted software (bloatware)
- Keep your computer safe while browsing
- Firewalls and VPNs
- Disable admin accounts
- Keep software updated
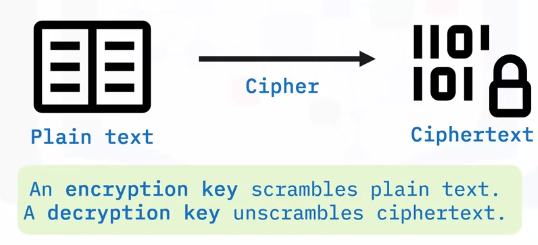
Encryption concepts
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
PKI is when a user is validated with a digital certificate by a Certificate Authority (CA).
Cryptographic hashes
A cryptographic hash is a short string of numbers and letters created by running a password or file through an algorithm.
Email and Spam Management
Managing email
Email management is classifying email messages and deciding whether they should be saved or deleted.
- Keep inbox clean
- Organize with folders
- Filter with rules
- Unsubscribe
- Turn off notifications
Identify and manage spam
Spam is unwanted, unsolicited email. Some spam is harmless, but it can be dangerous when scammers use it for phishing or fraud.
To reduce spam:
- Don’t give out your email address.
- Use throwaway accounts.
- Configure settings to block spam.
- Use a full-featured mail app.