Storage Types and Network Sharing
Common Storage and Sharing Options
Types of Local Storage Devices
Hard Drive (HD or HDD)
HDDs:
- Large storage capacity
- Up to 200 MB/s
- Can overheat
- Were the standard PC storage for decades
Solid-state Drive (SSD)
Solid-state Hybrid Drive (SSHD)
SSHDs integrate the speed of an SSD and the capacity of an HDD into a single device. It decides what to store in SSD vs. HDD based on user activity.
SSHDs are:
Optical Disk Drive (ODD)
ODDs are also called:
- CD Drives
- DVD Drives
- BD Drives
- Disc Drives
- Optical Drives
Flash Drive
Flash drives store data on solid-state drives (SSDs). Less energy is needed to run flash drives, as they don’t have moving parts that require cooling. High-end versions deduplicate and compress data to save space.
Local Storage wit Multiple Drives
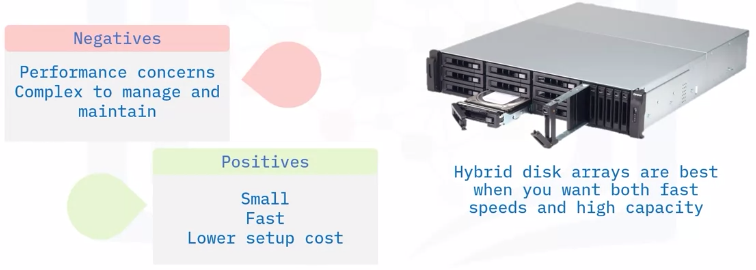
Hybrid disk arrays physically combine multiple SSD and HDD devices into an array of drives working together to achieve the fast and easy performance of solid-state and the lower costs and higher capacities of hard-disk.
Direct Attached Storage (DAS)
DAS is one or more storage units within an external enclosure that is directly attached to the computer accessing it.
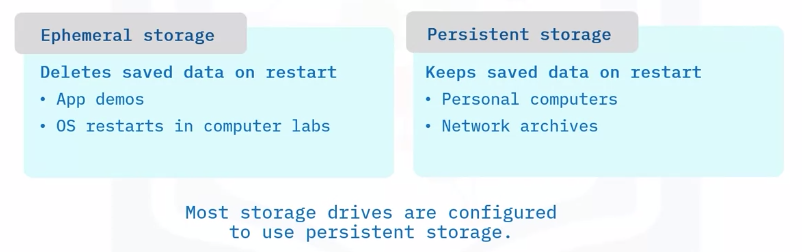
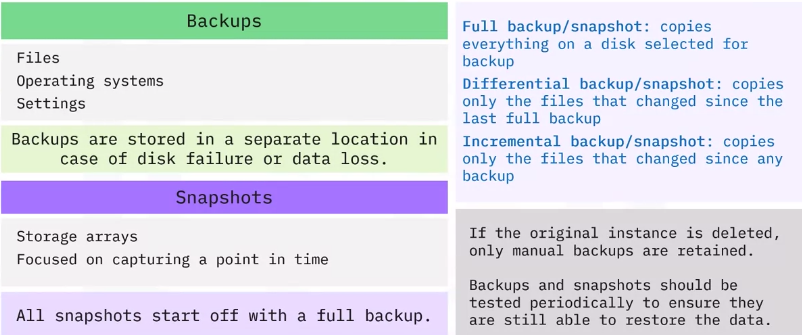
Ephemeral and Persistent storage
In DAS units and other storage devices, you can configure storage settings to be Ephemeral or Persistent.
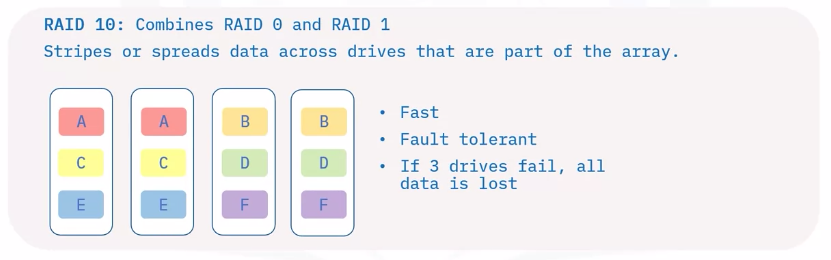
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID)
A RAID spread data across multiple storage drives working in parallel.
Companies choose RAID devices for their durability and performance.
- Maintain RAID devices
- Keep spare drives
- Perform routine backups
Troubleshooting Storage Issues
Disk Failure symptoms
Disk failure can be caused by wear and tear over time, faulty manufacturing, or power loss.
- Read/write failure
- Blue screen of Death (BSoD)
- Bad sectors
- Disk thrashing
- Clicking and grinding noises
Chkdsk and SMART
The chkdsk tools and the SMART program are used to monitor and troubleshoot disk health.
SMART: Self-Monitoring Analysis, and Reporting Technology
wmic/node: localhost diskdrive get status
Check disk tools
chkdsk /rlocates bad sectorschkdsk /fattempts to fix file system errors
Boot failures
When a computer fails to boot:
Computer power up
- Lights and sound
Plugged in
Drive configuration
- Correct firmware boot sequence
- No removable disks
- Cables connected and undamaged
Motherboard port enables
Filesystem error Boot into recovery and enter
C:in command prompt.- If invalid media type, reformat disk with
bootrectool (erases all data). - If invalid drive specification, partition structure with
diskparttool.
Boot block repair
Errors like “Invalid drive specification” or “OSS not found” indicate boot errors (caused by disk corruption, incorrect OS installation, or viruses).
- Try antivirus boot disk and recovery options
- Original product disk > Repair
- Startup repair
- Command prompt
- Fix MBR:
bootrec /fixmbr - Fix boot sector:
bbotrec /fixboot - Correct missing installation in BCD:
bootrec /rebuild bcd
- Fix MBR:
File recovery options
For computers that won’t boot, you can try to recover files by removing the hard drive and connecting it to another computer.
Recovery options:
- Windows disk management
- chkdsk
- Third-Party file recovery
Disk Performance issues
Disk performance can slow if a disk is older, too full, or its files are not optimized.
To improve performance:
- Defragment the drive
- Add RAM
- Upgrade to a solid state or hybrid drive
- Remove files and applications
- Add additional drive space
Troubleshooting optical drives
Optical drives are laser-based and don’t physically touch disks.
- Cleaning kits solve read/write errors
- CD-ROM drives cannot play DVDs and Blu-rays
- DVD and Blu-ray drives have third-party support
Writable discs have recommended write speeds
Buffer underrun When the OS is too slow for the optical drive’s write process, errors occur.
To fix buffer underrun:
- Use latest writes
- Burn at lower speeds
- Close apps during burn
- Save to hard drive instead
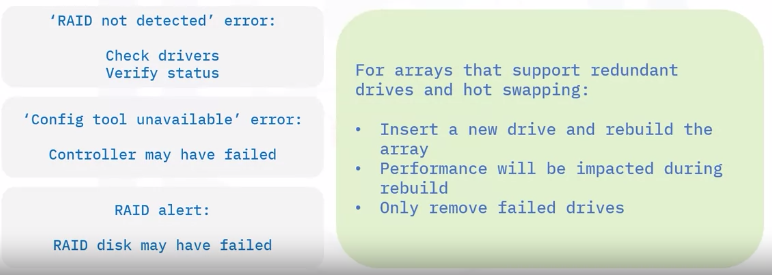
Troubleshooting RAID issues
Here are some common RAID troubleshooting steps:
Types of Hosted Storage and Sharing
Storage as a Service (STaaS)
STaaS is when companies sell network storage space to customers, so they don’t have to buy and maintain their own network equipment.
- Dropbox
- OneDrive
- Google Drive
- box
- Amazon Drive
Email and social media storage
Email Companies store your data, emails, and attachments in their data centers.
Social Media Companies store your photos, videos, and messages in their data centers.
- Gmail waits 30 days before permanent removal.
- Facebook deleted after 90 days, but keeps certain user data indefinitely.
Workgroup and homegroup
A workgroup or homegroup is a group of computers on a SOHO network, typically without a server.
- To share files and folders, users set them to ‘public’
- Data is stored on the user device that created it.
- The added points of failure create higher risk of data loss.
Newer cloud solutions provide the same features more securely.
Workgroups and homegroups are less common. Homegroups have been removed from Windows 10 altogether.
Repositories
A repository is a network location that lets a user store, manage, track, collaborate on, and control changes to their code.
Repositories save every draft. Users can roll things back if problems occur. This can save software developers months of time.
- GitHub
- DockerHub
Active Directory Domain Service (AD DS)
AD is a Microsoft technology that manages domain elements such as users and computers.
- Organizes domain structure.
- Grants network access.
- Connects to external domains.
It can be managed remotely from multiple locations.
Active Directory Domain Services:
- Stores centralized data, manages communication and search.
- Authenticates users so they can access encrypted content.
- Manages single-sign on (SSO) user authentication.
- Limits content access via encryption.
Network drives
Network drives are installed on a network and shared with selected users. They offer the same data storage and services as a standard disk drive.
- Network drives can be located anywhere.
- Network drives appear alongside local drive.
- Network drives can be installed on computers, servers, NAS units, or portable drives.
Network file and print sharing
File and Printer Sharing is part of the Microsoft Networks services.
- Appear alongside local drives
- Accessed via a web browser
- Appears in the printer options
Network Storage Types
Network storage is digital storage that all users on a network can access.
- Small networks might rely on a single device for the storage needs of 1–5 people.
- Large networks (like the Internet) must rely on hundreds of datacenters full of servers.
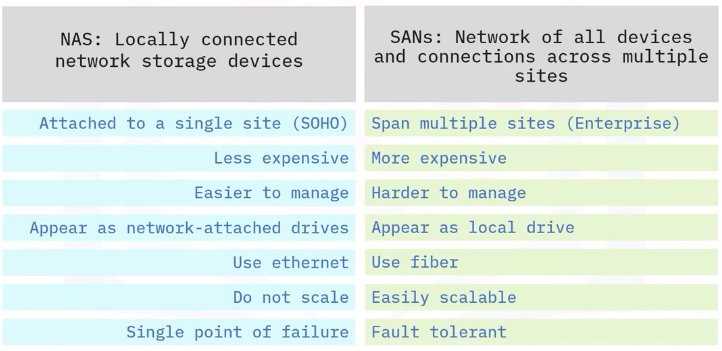
Storage Area Network (SAN)
A SAN combines servers, storage systems, switches, software, and services to provide secure, robust data transfers.
- Better application performance.
- Central and consolidated.
- Offsite (data protected and ready for recovery)
- Simple, centralized management of connections and settings.
Network Attached Storage (NAS)
A NAS device is a local file server. It acts as a hard drive for all devices on a local network.
- Convenient sharing across network devices.
- Better performance through RAID configuration.
- Remote Access
- Work when the Internet is down.
Difference between NAS and SAN
Cloud-based Storage Devices
Cloud storage
Cloud storage is when files and applications are stored and engaged with via the Internet.
Cloud companies manage data centers around the world to keep applications functioning properly, and user data stored securely.
Public Cloud: Provide offsite storage for Internet users.
Private Cloud: Provides collaboration and access to private network users.
Hybrid Cloud: A mix of both. Provides public sharing and restricted private areas via cloud storage and cloud-hosted apps.
File, Block, and Object storage
Cloud companies use multiple data storage types depending on how often they need to access different data and the volume of that data.
File Storage
File storage saves all data in a single file and is organized by a hierarchical path of folders and subfolders. File storage uses app extensions like .jpg or .doc or .mp3.
- Familiar and easy for most users
- User-level customization
- Expensive
- Hard to manage at larger scale
Block Storage
Block Storage splits data into fixed blocks and stores them with unique identifiers. Blocks can be stored in different environments (like one block on Windows, and the rest in Linux). When a block is retrieved, it’s reassembled with associated blocks to recreate the original data.
- Default storage for data that is frequently updated.
- Fast, reliable, easy to manage.
- No metadata, not searchable, expensive.
- Used in databases and email servers.
Object Storage
Object Storage divides data into self-contained units stored at the same level. There are no subdirectories like in file storage.
- Users metadata for fast searching.
- Each object has a unique number.
- Requires an API to access and manage objects.
- Good for large amounts of unstructured data.
- Important for AI, machine learning, and big data analytics.
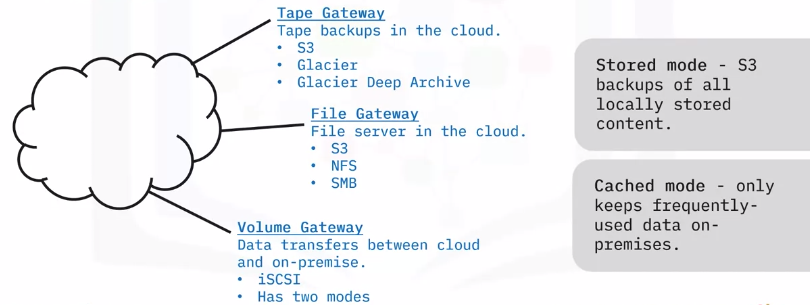
Storage gateways
A storage gateway is a service that connect on-premises devices with cloud storage.