Cloud Computing Models
Overview of Cloud Service Models
- IaaS
- PaaS
- SaaS
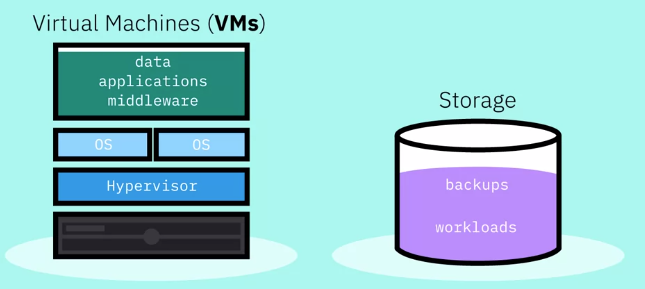
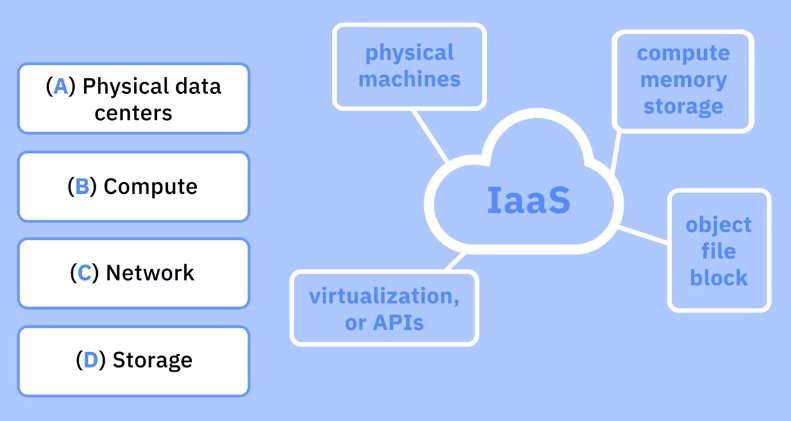
IaaS – Infrastructure as a Service
It is a form of cloud computing that delivers fundamentals:
- compute
- network
storage to consumers on-demand, over the internet, on a pay-as-you-go basis.
The cloud provider hosts the infrastructure components traditionally present in an on-premises data center, as well as the virtualization or hypervisor layer.
IaaS Cloud
The ability to track and monitor the performance and usage of their cloud services and manage disaster recovery.
- End users don’t interact directly with the physical infrastructure, but experience it as a service provided to them.
- Comes with supporting services like auto-scaling and load balancing that provide scalability and high performance.
Object storage is the most common mode of storage in the cloud, given that it is highly distributed and resilient.
IaaS use cases
Test and Development
- Enable their teams to set up test and development environments faster.
- Helping developers focus more on business logic than infrastructure management.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
- Require a significant amount of technology and staff investment.
- Make applications and data accessible as usual during a disaster or outage.
Faster Deployments and Scaling
- To deploy their web applications faster.
- Scale infrastructure up and down as demand fluctuates.
High Performance Computing
- To solve complex problems involving millions of variables and calculations
Big Data Analysis
- Patterns, trends, and associations requires a huge amount of processing power.
- Provides the required high-performance computing, but also makes it economically viable.
IaaS Concerns
- Lack of transparency
- Dependency on a third party
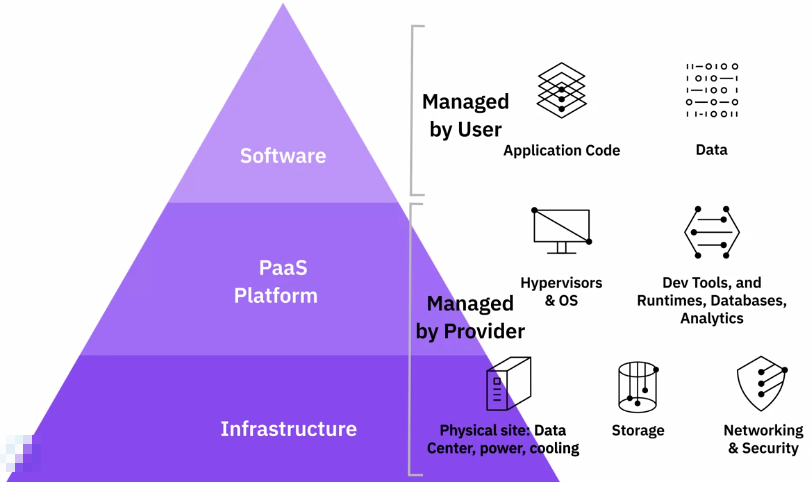
PaaS – Platform as a Service
PaaS
A cloud computing model that provides a complete application platform to:
- Develop
- Deploy
- Run
- Manage
PaaS Providers Host and Manages
Installation, configuration, operation of application infrastructure:
- Servers
- Networks
- Storage
- Operating system
- Application runtimes
- APIs
- Middleware
Databases
User manages: Application Code
Essential Characteristics of PaaS
- High level of abstraction
- Eliminate complexity of deploying applications
- Support services and APIs
- Simplify the job of developers
- Run-time environments
- Executes code according to application owner and cloud provider policies
- Rapid deployment mechanisms
- Deploy, run, and scale applications efficiently
- Middleware capabilities
- Support a range of application infrastructure capabilities
Use Cases of PaaS
- API development and management
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Business analytics/intelligence
- Business Process Management (BPM)
- Master data management (MDM)
Advantages of PaaS
- Scalability
- Faster time to market
- Greater agility and innovation
PaaS available offerings
Risks of PaaS
- Information security threats
- Dependency on service provider’s infrastructure
- Customer lack control over changes in strategy, service offerings, or tools
SaaS – Software as a Service
A cloud offering that provides access to a service provider’s cloud-based software.
Provider maintains:
- Servers
- Databases
- Application Code
Security
Providers manages application:
- Security
- Availability
- Performance
SaaS Supports
- Email and Collaboration
- Customer Relationship Management
- Human Resource Management
- Financial Management
Key Characteristics
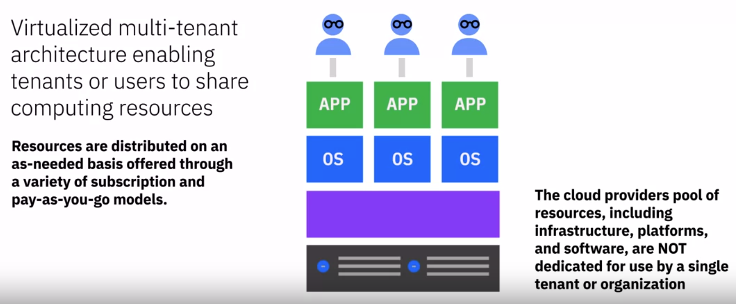
- Multi-tenant architecture
- Manage Privileges and Monitor Data
- Security, Compliance, Maintenance
- Customize Applications
- Subscription Model
- Scalable Resources
Key Benefits
- Greatly reduce the time from decision to value
- Increase workforce productivity and efficiency
- Users can access core business apps from anywhere
- Buy and deploy apps in minutes
- Spread out software costs over time
Use Cases for SaaS
Organizations are moving to SaaS to:
- Reduce on-premise IT infrastructure and capital expenditure
- Avoid ongoing upgrades, maintenance, and patching
- Run applications with minimal input
- Manage websites, marketing, sales, and operations
Gain resilience and business continuity of the cloud provider
Trending towards SaaS integration platforms.
SaaS Concerns
- Data ownership and data safety
- Third-party maintains business-critical data
- Needs good internet connection
Deployment Models
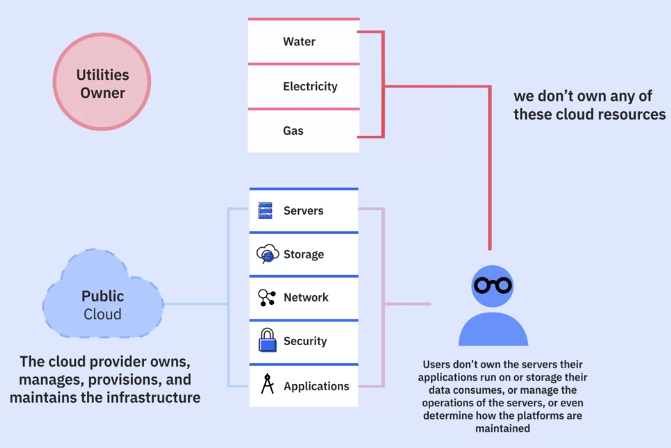
Public Cloud
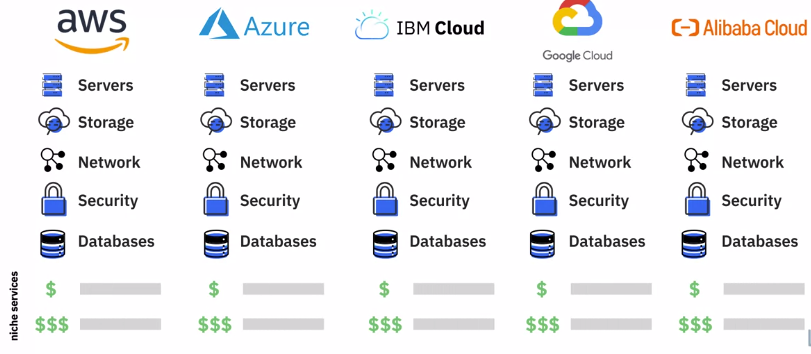
Public Cloud providers in the market today
Public cloud characteristics
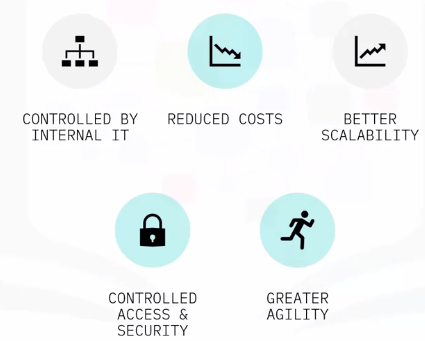
Public cloud benefits
Public cloud concerns
Public cloud use cases
- Building and testing applications, and reducing time-to-market for their products and services.
- Businesses with fluctuating capacity and resourcing needs.
- Build secondary infrastructures for disaster recovery, data protection, and business continuity.
- Cloud storage and data management services for greater accessibility, easy distribution, and backing up their data.
- IT departments are outsourcing the management of less critical and standardized business platforms and applications to public cloud providers.
Private Cloud
“Cloud infrastructure provisioned for exclusive use by a single organization comprising multiple consumers, such as the business units within the organization. It may be owned, managed, and operated by the organization, a third party, or some combination of them, and it may exist on or off premises.”
Internal or External
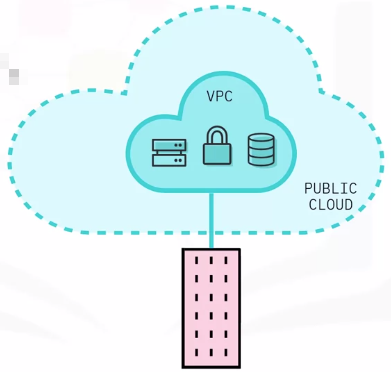
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
An external cloud that offers a private, secure, computing environment in a shared public cloud.
Best of Both Worlds
Benefits of Private Clouds
Common Use Cases
Hybrid Cloud
Connects an organization on-premise private cloud and third-party public cloud.
It gives them:
- Flexibility
- Workloads move freely
Choice of security and regulation features
With proper integration and orchestration between the public and private clouds, you can leverage both clouds for the same workload. For example, you can leverage additional public cloud capacity to accommodate a spike in demand for a private cloud application also known as “cloud bursting”.
The Three Tenets
Types of Hybrid Clouds
Benefits
- Security and compliance
- Scalability and resilience
- Resource optimization
- Cost-saving
- A hybrid cloud lets organizations deploy highly regulated or sensitive workloads in a private cloud while running the less-sensitive workloads on a public cloud.
- Using a hybrid cloud, you can scale up quickly, inexpensively, and even automatically using the public cloud infrastructure, all without impacting the other workloads running on your private cloud.
- Because you’re not locked-in with a specific vendor and also don’t have to make either-or- decisions between the different cloud models, you can make the most cost-efficient use of your infrastructure budget. You can maintain workloads where they are most efficient, spin-up environments using pay-as-you-go in the public cloud, and rapidly adopt new tools as you need them.
Hybrid Cloud Use Cases
- SaaS integration
- Data and AI integration
- Enhancing legacy apps
- VMware migration