Emerging Trends and Practices
Hybrid Multi-Cloud, Microservices, and Serverless
Hybrid Multi-cloud
A computing environment that connects an organization’s on-premise private cloud and third-party public cloud into a single infrastructure for running the organization’s applications.
Hybrid Multicloud use cases
- Cloud scaling
- Composite cloud
- Modernization
- Data and AI
- Prevent lock-in to a particular cloud vendor and having a flexibility to move to a new provider of choice
Microservices
Microservices architecture:
- Single application
- coupled and independently deployable smaller components or services
- These services typically have their own stack running on their own containers.
- They communicate with one another over a combination of:
- APIs
- Even streaming
- Message brokers
What this means for businesses is:
- Multiple developers working independently
- Different stacks and runtime environments
- Independent scaling
Serverless Computing
Offloads responsibility for common infrastructure management tasks such as:
- Scaling
- Scheduling
- Patching
- Provisioning
Key attributes
Attributes that distinguish serverless computing from other compute models:
- No provisioning of servers and runtimes
- Runs code on-demand, scaling as needed
- Pay only when invoked and used i.e., not when underlying computer resources are idle.
Serverless
- Abstracts the infrastructure away from developers
- Code executed as individual functions
- No prior execution context is required
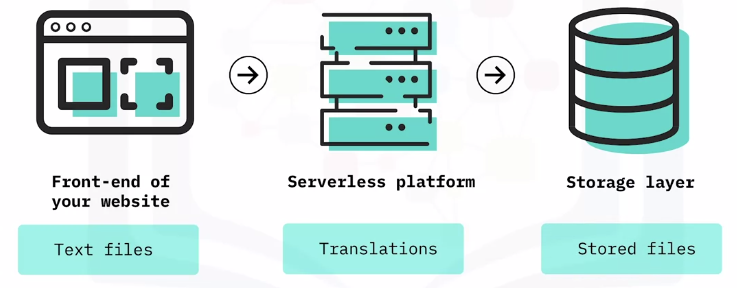
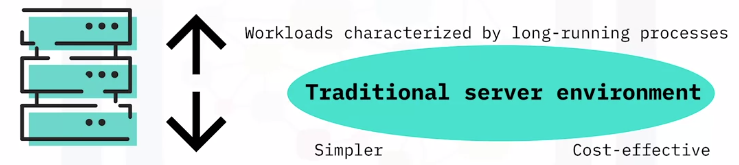
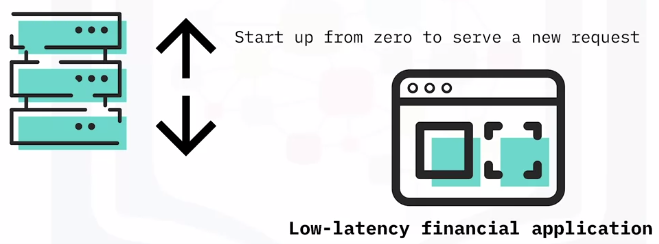
A Scenario
Serverless computing services
- IBM Cloud Functions
- AWS Lambda
- Microsoft Azure Functions
Determining Fit with Serverless
- Evaluate application characteristics
Ensure that the application is aligned to serverless architecture patterns
Applications that qualify for a serverless architecture include:
- Short-running stateless functions
- Seasonal workloads
- Production volumetric data
- Event-based processing
- Stateless microservices
Use Cases
Serverless architecture are well-suited for use cases around:
- Data and event processing
- IoT
- Microservices
Mobile backends
Serverless is well-suited to working with:
- Text
- Audio
- Image
Video
Tasks:
- Data enrichment
- Transformation
- Validation and cleansing
- PDF processing
- Audio normalization
- Thumbnail generation
- Video transcoding
- Data search and processing
Genome processing
Data Streams:
- Business
- IoT sensor data
- Log data
- Financial market data
Challenges
Vendor Dependent Capabilities
Cloud Native Applications, DevOps, and Application Modernization
Cloud Native Applications
- Developed to work only in the cloud environment
- Refactored and reconfigured with cloud native principles
Development Principles
Whether creating a new cloud native application or modernizing an existing application:
- Microservices Architecture
- Rely on Containers
- Adopt Agile Methods
Benefits
- Innovation
- Agility
- Commoditization
DevOps on the Cloud
What is DevOps?
Dev Teams:
- Design Software
- Develop Software
- Deliver Software
Run Software
Ops Teams
- Monitoring
- Predicting Failure
- Managing Environment
Fixing Issues
A collaborative approach that allows multiple stakeholders to collaborate:
- Business owners
- Development
- Operations
- Quality assurance
The DevOps Approach
It applies agile and lean thinking principles to all stakeholders in an organization who develop, operate, or benefit from the business’s software systems, including customers, suppliers, partners. By extending lean principles across the software supply chain, DevOps capabilities improve productivity through accelerated customer feedback cycles, unified measurements and collaboration across an enterprise, and reduced overhead, duplication, and rework.
Using the DevOps approach:
- Developers can produce software in short iterations
- A continuous delivery schedule of new features and bug fixes in rapid cycles
- Businesses can seize market opportunities
- Accelerated customer feedback into products
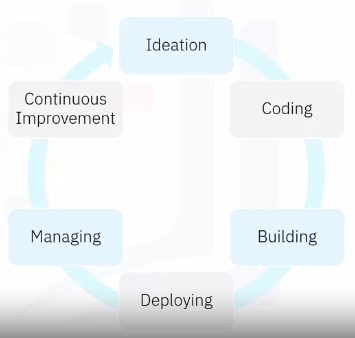
DevOps Process
- Continuous Delivery
- Continuous Integration
- Continuous Deployment
- Continuous Monitoring
Delivery Pipeline
DevOps and Cloud
With its near limitless compute power and available data and application services, cloud computing platforms come with their own risks and challenges, which can be overcome by DevOps:
- Tools
- Practices
Processes
DevOps provides the following solutions to cloud’s complexities:
- Automated provisioning and installation
- Continuous integration and deployment pipelines
- Define how people work together and collaborate
- Test in low-cost, production-like environments
- Recover from disasters by rebuilding systems quickly and reliably
Application Modernization
Enterprise Applications
Application Modernization
Architecture: Monoliths > SOA (Service Oriented Architecture) > Microservices
Infrastructure: Physical servers > VM > Cloud
Delivery: Waterfall > Agile > DevOps