Internal Computer Components
Internal Computer Components
Motherboard
- Main printed circuit board (PCB) in computers
- Contains significant subsystems
- Allows communication among many of the crucial internal electronic components
- Enables communications and power distribution for peripherals and other components
Chip sets
- A set of electronic components in an integrated circuit
- Manage data flow
- Have two distinct parts: the northbridge and the southbridge
- Manage communications between the CPU and other parts of the motherboard
Chip sets: Northbridge and southbridge
- Northbridge – the first half of the core logic chip set on a motherboard
- Directly connected to the CPU
- Responsible for tasks that require the highest performance
- Southbridge – the second half of the core logic chip set
- Implements slower-performance tasks
- Not directly connected to the CPU
What is a bus?
- A high-speed internal connection on a motherboard
- Used to send control signals and data internally
- The front-side bus carries data between the CPU and the memory controller hub (northbridge)
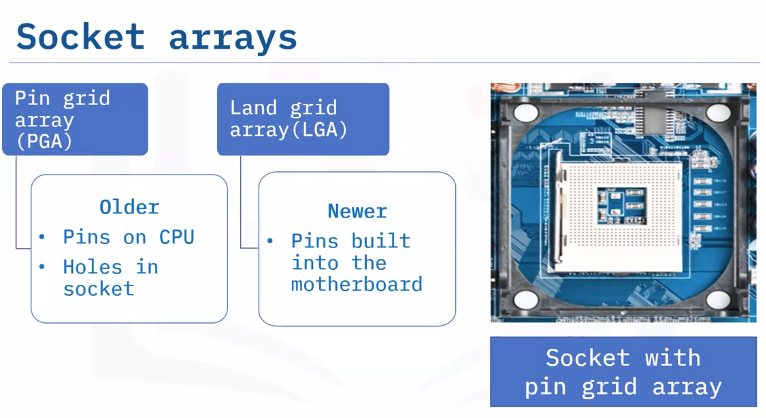
Sockets
“Components not directly attached to a motherboard connect via sockets”
- Array of pins holding a processor and connecting the processor to the motherboard
Differ based on the motherboard
Power connectors
- Found on a motherboard
- Allow an electrical current to provide power to a device
- ATX-style power connectors are larger than most
- Join the power supply to the motherboard
Data Processing and Storage
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Silicon chip in a special socket on the motherboard
- Billions of microscopic transistors
- Makes calculations to run programs
- 32-bit is like a two-lane information highway
- 64-bit is like a four-lane information highway
Memory (RAM)
- Typically used to store working data
- Volatile: Data existing in RAM is lost when power is terminated
- Is cold pluggable (cold swappable)
- Speed measured in Megahertz (MHz)
- Available in varying speeds
- Available in varying storage capacities
Types of Memory
- Choice depends on the motherboard
- Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DRAM)
- Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (SDRAM)
- Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR-SDRAM)
- Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Access Memory (DDR3 and DDR4)
- Small outline Dual Input Memory Module (SO-DIMM)
Memory Slots
- Hold RAM chips on the motherboard
- Allow the system to use RAM by enabling the motherboard to communicate with memory
- Most motherboards include two to four memory slots
- Type determines which RAM is compatible
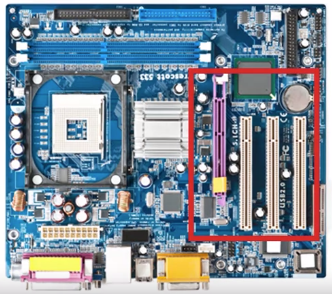
Expansion Slots
- Use PCI or PCIe slots
- Add additional capabilities
- Peripherals (such as sound cards)
- Memory
- High-end graphics
- Network interfaces
Availability depends on the motherboard configuration
Disk Controllers
- Circuit that enables the CPU to communicate with hard disk drive
- Interface between the hard disk drive and the bus
- Integrated Drive Electronics is a standard
- IDE controller-circuit board guides how the hard disk drive manages data
- Have memory that boosts hard drive performance
BIOS (Basic Input Output System)
- Manages your computer’s exchange of inputs and outputs
- Preprogrammed into the motherboard
- Needs to always operate
- Update in a flash
- Use the System Summary window
CMOS: Battery and chip
- Uses a coin-sized battery
- Is attached to the motherboard
- Powers the memory chip that stores hardware settings
- Replace the computer’s system data, time, and hardware settings
Internal Storage
Hard drive characteristics
Introduced by IBM in 1956, internal hard drives provide: - Stable, long-term data storage - Fast access time - Fast data transfer rates
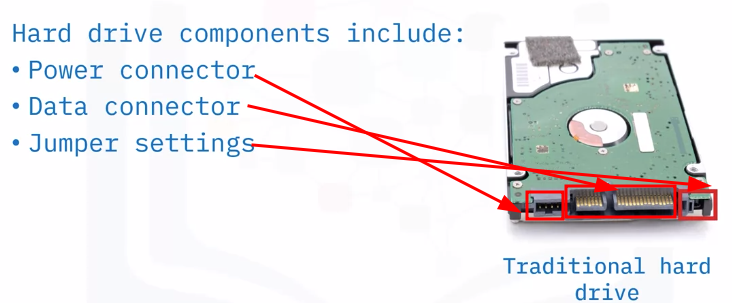
Traditional hard drive technology
IDE and PATA drives
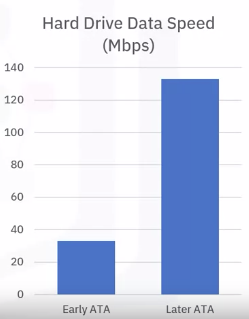
1980s to 2003:
- Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) hard drives and Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment (PATA) drives were popular industry standard storage options
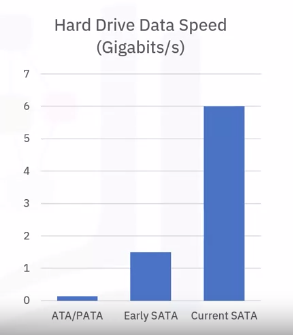
SATA drives
2003 to today:
- Serial advanced technology attachment drives (SATA) became an industry standard technology
- Communicate using a serial cable and bus
- Initial data processing of 1.5 Gbps
Current processing of 6 Gbps
- Available in multiple sizes
- Spin at 5400 or 7200 rpm
- Capacity: 250 GB to over 30 TB
- Still dominate today’s desktop and laptop market
- Each SATA port supports a single drive
- Most desktop motherboards have at least four SATA ports
SCSI drives
1986:
- Small computer system interface, pronounced “scuzzy” (SCSI) drives
Historical speeds: 10,000 or 15,000 rpm
1994:
Discontinued usage
Solid-state drives
1989:
- Solid-state drives (SSDs) came to market
- Consist of nonvolatile flash memory
- Provide faster speeds: 10 to 12 Gbps
- Capacity: 120 GB to 2 TB
Cost: More expensive than SATA or SCSI drives but also more reliable
- Available as internal, external, and hybrid hard drives
- As part of an internal hybrid configuration:
- SSD serves as a cache
- SATA drive functions as storage
- Hybrid drives tend to operate slower than SSD drives
Optical Drives
1992:
- Invented in the 1960s, but came to the market in 1992.
- CDs and DVDs provide nonvolatile storage.
- Optical drives use low-power laser beams to retrieve and write data.
- Data is stored in tiny pits arranged in a spiral track on the disc’s surface.
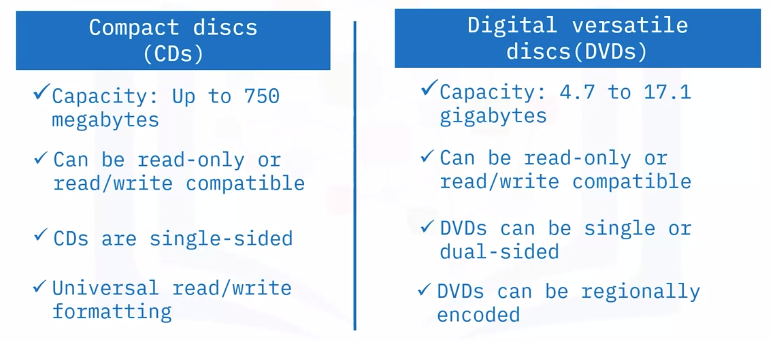
CDs and DVDs compared
Blu-ray discs
- Media specific for movies and video games
- Provide high resolution
- Single-sided, but with up to four layers
- Store 25 GB per layer
- Writable Blu-ray discs exist in 100 GB and quad-layer 128 GB formats
Writable Blu-ray discs require BD-XL-compatible drives
Expansion Slots
- Locations on the motherboard where you can add additional capabilities, including hard drive storage
Display Cards and Sound Cards
Video card
- An expansion card installed in an empty slot on the motherboard
- Or a chip built into a system’s motherboard
- Allows the computer to send graphical information to a video display device
- Also known as a display adapter, graphics card, video adapter, video board, or video controller
Graphics processing unit (GPU)
- Specialized processor originally designed to accelerate graphics rendering
- Process many pieces of data simultaneously
- Machine learning, video editing, and gaming applications
- Several industries rely on their power processing capabilities
Audio card
- Also known as a sound card
- Integrated circuit that generates an audio signal and send it to a computer’s speakers
- Can accept an analog sound and convert it to digital data
- Usually built into PC motherboard
- Users desiring higher-quality audio can buy a dedicated circuit board
MIDI controller
- A simple way to sequence music and play virtual instruments and play virtual instruments on your PC
- Works by sending musical instrument digital interface (MIDI) data to a computer or synthesizer
- Interprets the signal and produces a sound
- Frequently used by musicians
Network Interface Cards
- A hardware component without which a computer cannot connect to a network
- A circuit board that provides a dedicated network connection to the computer
- Receives network signals and translates network signals and translates them into data that the computer displays
Types of NIC
- Provides a connection to a network
- Usually, the Internet
- Onboard: built into motherboard
- Add-on: fit into expansion slot
- No significant difference in speed or quality
Wired and wireless network cards
- Wireless – use an antenna to communicate through radio frequency waves on a Wi-Fi connection
- Wired-use an input jack and a wired LAN technology, such as fast Ethernet
Modems
- Connects your system to the Internet.
- Translates ISP signals into a digital format.
- Then feeds those digitized signals to your router, so you can connect to a network.
Cooling and Fans
System cooling
- Computers generate heat
- Excessive heat can damage internal components
- Never operate a computer w/out proper cooling
- Designed to dissipate heat produced by the processor
- Allow the accumulated heat energy to flow away from vital internal parts
Cooling methods
- Passive
- Active
- Fans draw cool air through front vents and expel warm air through the back
- Forced convection
- Using thermal paste and a baseplate
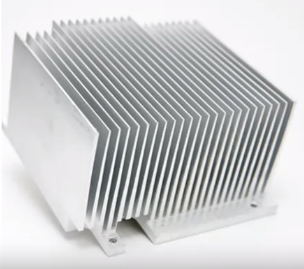
Cooling methods – heat sink
- Heat sink
- Use heat sink compound to fill gaps
- Place the heat sink over the CPU
- Excess heat is drawn away
Before warm air can damage the internal components
Liquid-based cooling
- Quieter and more efficient than fans
- Water blocks rest atop the chip
- Cool liquid in the blocks cool the chip
- Heated fluid is pumped to a radiator-cooled by fans.
- That fluid goes back to the water block to repeat the cycle.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.