Cloud Security, Monitoring, Case Studies, Jobs
Cloud Security and Monitoring
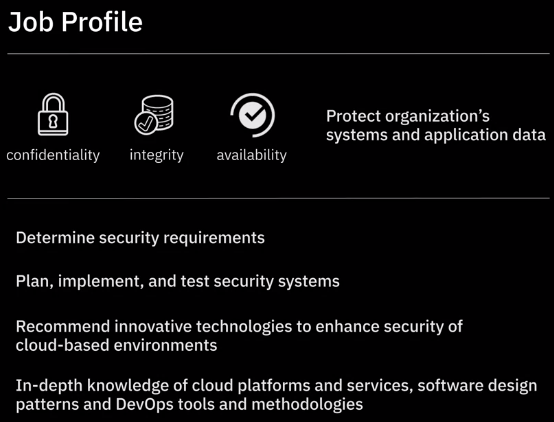
What is Cloud Security
The security in context of cloud is a shared responsibility of:
- User
- Cloud Provider
- Protect data
Manage access
SEC DevOps
- Secure Design
- Secure Build
- Manage Security
- Secure Build
Identity and Access Management
Biggest cloud security concerns are:
- Data Loss and Leakage
- Unauthorized Access
Insecure Interfaces and APIs
Identity and Access Management are:
- First line of defense
- Authenticate and authorize users
- Provide user-specific access
Main types of users
A comprehensive security strategy needs to encompass the security needs of a wide audience:
- Organizational users
- Internet and social-based users
- Third-party business partner organizations
Vendors
There are three main type of users:
- Administrative users
- Developer users
- Application users
Administrative Users
Administrators | Operators | Mangers roles that typically create, update, and delete application and instances, and also need insight into their team members’ activities.
An attacker with administrative access could:
- Steal data from databases
- Deploy malicious applications
- Deface or destroy existing applications
Developer Users
| Application developers | Platform developers | Application publishers |
Can:
- Read sensitive information
- Create applications
- Update applications
- Delete applications
Application Users
Users of the cloud-hosted applications
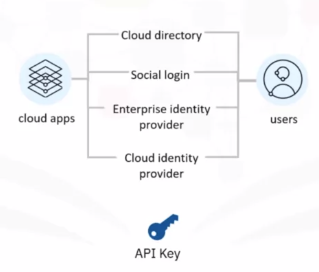
Authentication and User Identity
Multifactor authentication
It is used to combat identity theft by adding another level of authentication for application users.
Cloud Directory Services
They are used to securely manage user profiles and their associated credentials and password policy inside a cloud environment.
- Applications hosted on the cloud do not need to use their own user repository
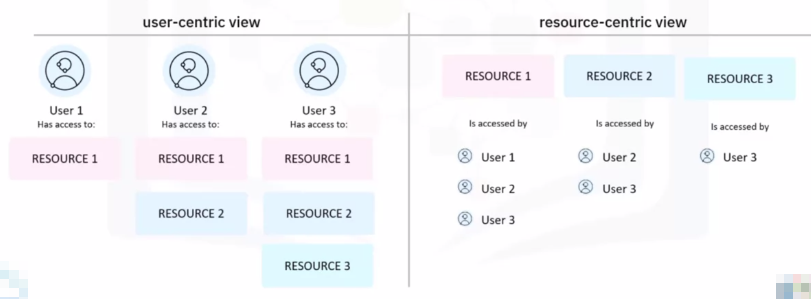
Reporting
It helps provide a user-centric view of access to resources or a resource-centric view of access by users:
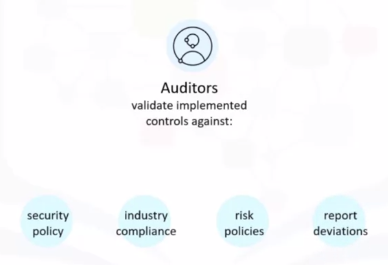
Audit and Compliance
Critical service within identity and access management framework, both for cloud provider, and cloud consumer.
User and service access management
It enables cloud application/service owners to provision and de-provision:
Streamline access control based on:
- Role
- Organization
- Access policies
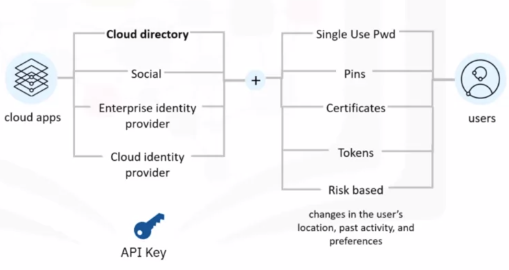
Mitigating Risks
Some of the controls that can help secure these sensitive accounts include:
- Provisioning users by specifying roles on resources for each user
- Password policies that control the usage of special characters, minimum password lengths, and other similar settings
- Multifactor authentication like time-based one-time passwords
- Immediate provisioning of access when users leave or change roles
Access Groups
A group of users and service IDs created so that the same access can be assigned to all entities within the group with one or more access policies.
Access Policies
Access policies define how users, service IDs, and access groups in the account are given permission to access account resources.
Access Group Benefits
Cloud Encryption
Encryption
It plays a key role on cloud, and is often referred to as the last line of defense, in a layered security model.
- Encrypts Data
- Data Access Control
- Key management
- Certificate management
Definition
Scrambling data in a way that makes it illegible.
Encryption Algorithm: Defines rules by which data will be transformed
Decryption Key: Defines how encrypted data will be transformed back to legible data.
It makes sure:
- Only authorized users have access to sensitive data.
- When accessed without authorization, data is unreadable and meaningless.
Cloud Encryption Services
- Can be limited to encryption of data that is identified as sensitive, or
- end-to-end encryption of all data uploaded to the cloud
Data Protection States
Encryption at Rest:
- Protects stored data
- Multiple encryption options:
- Block and file storage
- Built-in for object storage
Database encryption
Encryption in Transit:
- Protects data while transmitting
- Includes encrypting before transmission
- Authenticates endpoints
- Decrypts data on arrival
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
Transport Layer Security (TSL)
Encryption in Use:
- Protects data in use in memory
- Allows computations to be performed on encrypted text without decryption
Client or Server-side Encryption
Cloud storage encryption could be server-side or client-side.
Server-side:
- Create and manage your own encryption keys, or
Generate and manage keys on cloud
Client-side:
- Occurs before data is sent to cloud
Cloud providers cannot decrypt hosted data
There is a need to implement a singular data protection strategy across an enterprise’s on-premise, hybrid, and multi-cloud deployments.
Multi-Cloud Data Encryption
Features:
- Data access management
- Integrated key management
Sophisticated encryption
Multi-cloud encryption console:
- Define and manage access policies
- Create, rotate, and manage keys
- Aggregate access logs
Key Management
Encryption doesn’t eliminate security risk.
- It separates the security risk from the data itself.
- Keys need to be managed and protected against threats.
Key Management Services
They enable customers to:
- Encrypt sensitive data at rest
- Easily create and manage the entire lifecycle of cryptographic keys
- Protect data from cloud service providers
Key Management Best Practices
- Storing encryption keys separately from the encrypted data
- Taking key backups offsite and auditing them regularly
- Refreshing the keys periodically
- Implementing multifactor authentication for both the master and recovery keys
Cloud Monitoring Basics and Benefits
Cloud Monitoring Solutions
Monitoring performance across an entire stack of applications and services can be time-consuming and draining on internal resources.
Cloud Monitoring Assessment
Cloud Monitoring Features
Cloud monitoring includes:
- Strategies
- Practices
Processes
Used for:
- Analyzing
- Tracking
Managing services and apps
It also serves to provide actionable insights that can help improve availability and user experience.
Cloud Monitoring Helps to:
- Accelerate the diagnosis and resolution of performance incidents
- Control the cost of your monitoring infrastructure
- Mitigate the impact of abnormal situations with proactive notifications
- Get critical Kubernetes and container insights for dynamic microservice monitoring
- Troubleshoot your applications and infrastructure
Cloud Monitoring Solutions Provide:
- Data in real-time with round the clock monitoring of VMs, services, databases, apps
- Multilayer visibility into application, user, and file access behavior across all apps
- Advanced reporting and auditing capabilities for ensuring regulatory standards
- Large-scale performance monitoring integrations across multicloud and hybrid cloud
Cloud Monitoring Categories
Infrastructure
- Help identify minor and large-scale failures
- So that developers can take corrective action
Database
- Help track processes, queries, and availability of services
To ensure accuracy and reliability
Application Performance and Monitoring
- Help improve user experience
- Meet app and user SLAs
- Minimize downtime and lower operational costs
Cloud Monitoring Best Practices
To get the most benefit from your cloud-based deployments, you can follow some standard cloud monitoring best practices.
- Leverage end-user experience monitoring solutions
- Move all aspects of infrastructure under one monitoring platform
- Use monitoring tools that help track usage and cost
- Increase cloud monitoring automation
- Simulate outages and breach scenarios
Cloud monitoring needs to be a priority for organizations looking to leverage the benefits of cloud technologies.
Case Studies and Jobs
Case Studies in Different Industry Verticals
- The Weather Company migrating to the cloud to reliably deliver critical weather data at high speed, especially during major weather events such as hurricanes and tornadoes
- American Airlines, using the cloud platform and technologies to deliver digital self-service tools and customer value more rapidly across its enterprise
- Cementos Pacasmayo, achieving operational excellence and insight to help drive strategic transformation and reach new markets using cloud services
- Welch choosing cloud storage to drive business value from hybrid cloud
- Liquid Power using cloud-based SAP applications to fuel business growth