Components of Cloud Computing
Overview of Cloud Infrastructure
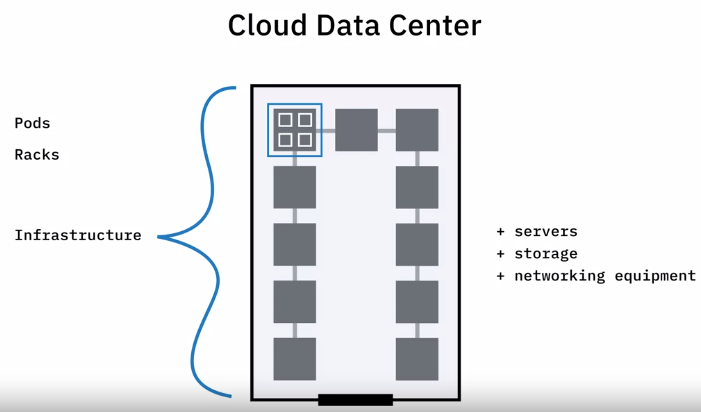
After choosing the cloud service model and the cloud type offered by vendors, customers need to plan the infrastructure architecture. The infrastructure layer is the foundation of the cloud.
Region
It is a geographic area or location where a cloud provider’s infrastructure is clustered, and may have names like NA South or US East.
Availability Zones
- Multiple Availability Zones (AZ)
- Have their own power, cooling, networking resources
- Isolation of zones improves the cloud’s fault tolerance, decrease latency, and more
very high bandwidth connectivity with other AZs, Data Centers and the internet
Computing Resources
Cloud providers offer several compute options:
- Virtual Servers (VMs)
- Bare Metal Servers
- Serverless (Abstraction)
Storage
Virtual servers come with their default local storage, but the stored documents are lost as we destroy the servers. Other more persistent options are:
- Traditional Data Centers:
- Block Storage
- File Storage
- Often struggle with scale, performance and distributed characteristics of cloud.
- The most common mode of storage
- Object Storage
- It is highly distributed and resilient
Networking
Networking infrastructure in a cloud datacenter include traditional networking hardware like:
- routers
switches
For users of the Cloud, the Cloud providers have Software Defined Networking (SDN), which allows for easier networking:
- provisioning
- configuration
management
Networking interfaces in the cloud need:
- IP address
Subnets
It is even more important to configure which network traffic and users can access your resources:
- Security Groups
- ACLs
- VLANs
- VPCs
VPNs
Some traditional hardware appliances:
- firewalls
- load balancers
- gateways
traffic analyzers
Another networking capability provided by the Cloud Providers is:
- CDNs
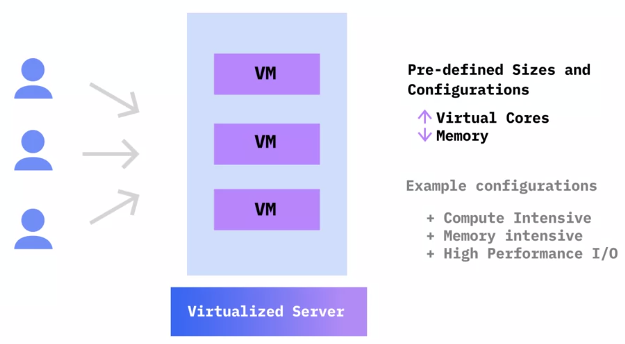
Types of Virtual Machines
Shared or Public Cloud VMs
Transient or Spot VMs
The Cloud provider can choose to de-provision them at any time and reclaim the resources
These VMs are great for:
- Non-production
- Testing and developing applications
- Running stateless workloads, testing scalability
Running big data and HPC workloads at a low cost
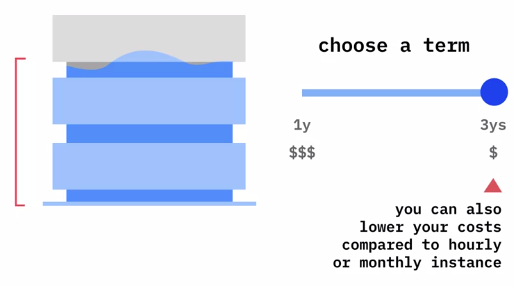
Reserved virtual server instances
- Reserve capacity and guarantee resources for future deployments
If you exceed your reserved capacity, complement it with hourly or monthly VMs Note: Not all predefined VMs families or configuration may be available as reserved.
Dedicated Hosts
- Single tenant isolation
- Specify the data center and pod
- This allows for maximum control over workload placement
- Used for meeting compliance and regulatory requirements or licensing terms
Bare Metal Servers
A bare metal server is a single-tenant, dedicated physical server. In other words, it’s dedicated to a single customer.
- Cloud Provider manages the server up to the OS.
- The Customer is responsible for administering and managing everything else on the server.
Bare Metal Server Configuration
- Preconfigured by the cloud provider
- Custom-configured as per customer specifications
- Processors
- RAM
- Hard drives
- Specialized components
The OS
Add GPUs:
- Accelerating scientific computation
- Data analytics
- Rendering professional grade virtualized graphics
Characteristics
- Can take longer to provision
- Minutes to hours
- More expensive than VMs
- Only offered by some cloud providers
Workloads
- Fully customizable/ demanding environments
- Dedicated or long-term usage
- High Performance Computing
Highly secure / isolated environments
Bare-metal server vs. Virtual Servers
| Bare Metal | Virtual Servers |
|---|---|
| Work best for: CPU and I/O intensive workloads | Rapidly provisioned |
| Excel with the highest performance and security | |
| Satisfy strict compliance requirements | Provide an elastic and scalable environment |
| Offer complete flexibility, control, and transparency | |
| Come with added management and operational over head | Low cost to use |
Secure Networking in Cloud
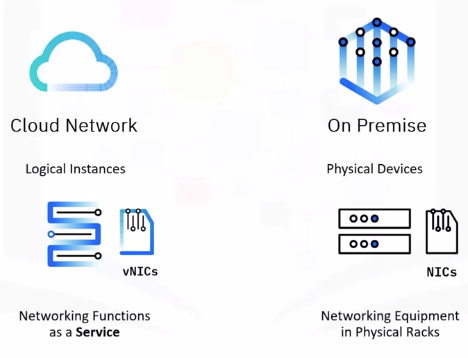
Networking in Cloud vs. On Premise
To create a network in cloud:
Direct Connectivity
Building a Cloud
It entails creating a set of logical constructs that deliver networking functionality akin to data center networks for securing environments and ensuring high performing business applications.
Containers
Containers are an executable unit of software in which application code is packaged, along with its libraries and dependencies, in common ways so that it can be run anywhere—desktops, traditional IT, or the cloud. Containers are lighter weight and consume fewer resources than Virtual Machines.
- Containers streamline development and deployment of cloud native applications
- Fast
- Portable
- Secure
Cloud Storage and Content Delivery Networks
Basics of Storage on the Cloud
- Direct Attached/Local Storage
- Within the same server or rack
- Fast
- Use for OS
- Not suitable
- Ephemeral (Temporary)
- Not shared
- Non-resilient
- File Storage
- Block Storage
- Object Storage
- Disadvantages
- Slowest speed
- Advantages
File Storage
Like Direct attached:
Attached to a compute node to store data
Unlike Direct attached:
- Less expensive
- More resilient to failure
- Less disk management and maintenance for user
Provision much larger amounts of Storage
- Resilient to failure
- Offer Encryption
Managed by service provider
File storage is mounted on compute nodes via Ethernet networks:

Multiple Compute Nodes
- File storage can be mounted onto more than one compute node
- Common Workloads:
- Departmental file share
- ‘Landing zone’ for incoming files
Repository of files
i.e., speed variance is not an issue
- Low cost database storage
IOPS
Input/Output Operations Per Second – the speed at which disks can write and read data.
- Higher IOPS value = faster speed of underlying disk
- Higher IOPS = higher costs
- Low IOPS value can become a bottleneck
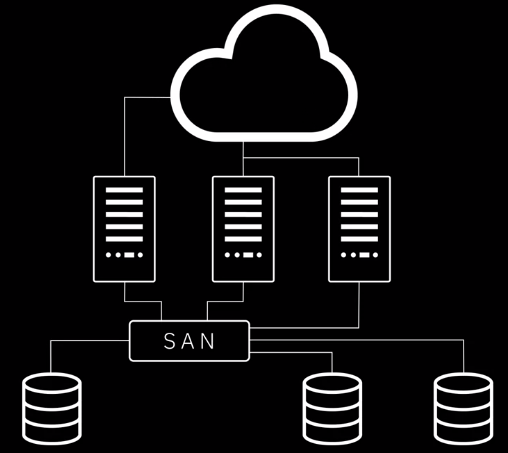
Block Storage
What is Block Storage?
Block storage breaks files into chunks (or block) of data.
- Stores each block separately under a unique address.
Must be attached to a compute node before it can be utilized.
Advantages:
- Mounted from remote storage appliances
- Extremely resilient to failure
Data is more secure
Mounted as a volume to compute nodes using a dedicated network of optical fibers:
- Signals move at the speed of light
- Higher price-point
- Perfect for workloads that need low-latency
- Consistent high speed
- Databases and mail servers
- Not suitable for shared storage between multiple servers
IOPS
For block storage, as it is for file storage, you need to take the IOPS capacity of the storage into account:
- Specify IOPS characteristics
- Adjust the IOPS as needed
- Depending on requirements and usage behavior
Common Attributes of File and Block Storage
- Block and File Storage is taken from appliances which are maintained by the service provider
- Both are highly available and resilient
- Often include data encryption at rest and in transit
Differences: File Storage vs. Block Storage
| File Storage | Block Storage |
|---|---|
| Attached via Ethernet network | Attached via high-speed fiber network |
| Speeds vary, based on load | Only attach to one node at a time |
| Can attach to multiple computer nodes at once | |
| Good for file share where: | |
| 1) Fast connectivity isn’t required | Good for applications that need: |
| 2) Cost is a factor | 1) Consistent fast access to disk |
Remember: Consider workload IOPS requirements for both storage types.
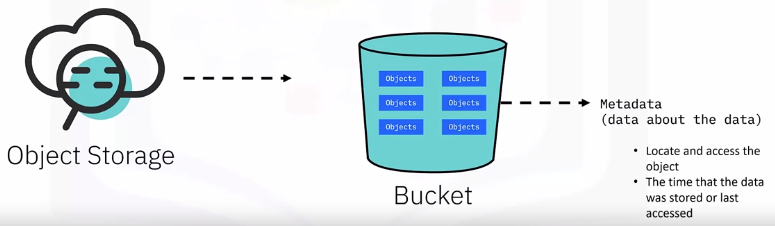
Object Storage
- Object storage can be used without connecting to a particular compute node to use it:
- Object storage is less expensive than other cloud storage options
- The most important thing to note about Object Storage is that it’s effectively infinite - With Object Storage, you just consume the storage you need and pay per gigabyte cost for what you use.
When to use Object Storage:
- Good for large amounts of unstructured data
- Data is not stored in any kind of hierarchical folder or directory structure
Object Storage Buckets
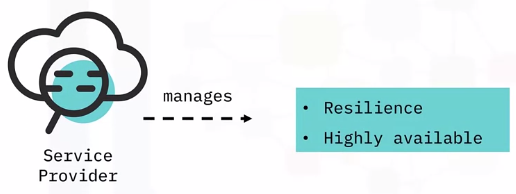
Managed by Service Provider
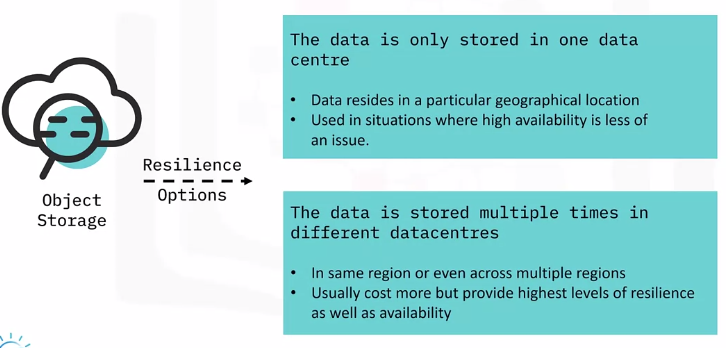
Object Storage – Resilience Options
Object Storage – Use Cases
- Any Data which is static and where fast read and write speeds are not necessary
- Text files
- Audio files
- Video files
- IoT Data
- VM images
- Backup files
Data Archives
Not suitable for operating systems, databases, changing content.
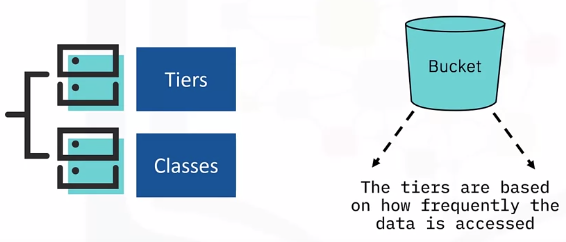
Object Storage – Tiers and APIs
Object Storage Tiers
Standard Tier
- Store objects that are frequently accessed
- Highest per gigabyte cost
Vault/Archive Tier
- Store objects that are accessed once or twice a month
- Low storage cost
Cold Vault Tier
- Store data that is typically accessed once or twice a year
- Costs just a fraction of a US cent per/GB/month
Automatic archiving rules
- Automatic archiving rules for your data
- Automatically be moved to a cheaper storage tier if object isn’t accessed for long
Object Storage – Speed
- Doesn’t come with IOPS options
- Slower than file or block storage
- Data in ‘cold vault’ buckets, can take hours for retrieval
- Object storage not suitable for fast access to files.
Object Storage – Costs
- Object Storage is priced per/GB
Other costs related to retrieval of the data e.g., Higher access costs for cold vault tiers
Ensure data is stored in correct tier based on frequency of access.
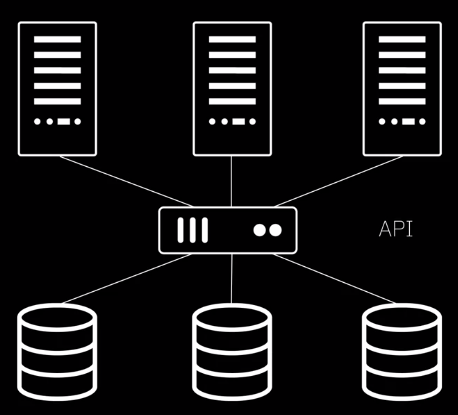
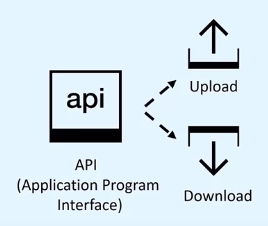
Application Programming Interface, or API
Object Storage – Backup solutions
- Effective solution for Backup and Disaster Recovery
- Replacement for offsite backups
- Many backup solutions come with built-in options for Object Storage on Cloud
- More efficient than tape backups for geographic redundancy
CDN – Content Delivery Network
- Accelerates content delivery to users of the websites, by caching the content in data centers near their locations.
- Makes websites faster.
- Reduction in load on servers
- Increase uptime
- Security through obscurity