Overview of Cloud Computing
Definition and Essential Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing (NIST)
A model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
Examples of computing resources include:
- Networks
- Servers
- Applications
- Services
Cloud model
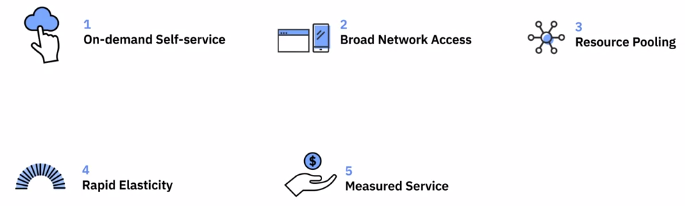
- 5 Essential characteristics
- 3 Deployment models
- 3 Service models
5 Essential characteristics
3 Types of cloud deployment models
- Public
- Hybrid
- Private
3 Service models
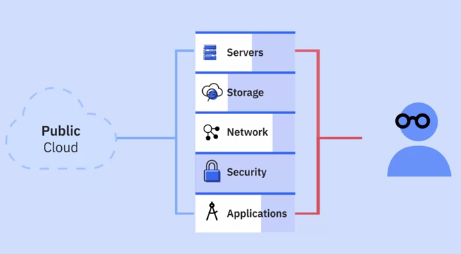
Three layers in a computing stack:
- Infrastructure (IaaS)
- Platform (PaaS)
- Application (SaaS)
History and Evolution of Cloud Computing
In the 1950s:
- Large-scale mainframes with high-volume processing power.
- The practice of time-sharing, or resource pooling, evolved.
Multiple users were able to access the same data storage layer and CPU power.
In the 1970s:
- Virtual Machine (VM)
- Mainframes to have multiple virtual systems, or virtual machines, on a single physical node
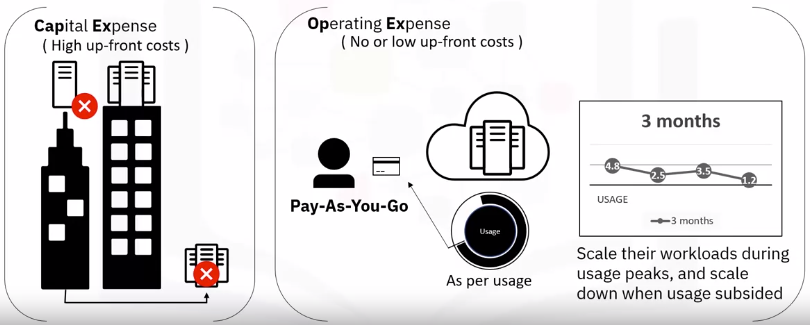
Cloud: Switch from CapEx to OpEx
Key Considerations for Cloud Computing
Key Drivers for moving to cloud
Infrastructure and Workloads
- The cost of building and operating data centers can become astronomical.
- Low initial costs and pay-as-you-go attributes of cloud computing can add up to significant cost savings.
SaaS and development platforms
- Organizations need to consider if paying for application access is a more viable option than purchasing off-the-shelf software and subsequently investing in upgrades
Speed and Productivity
- Organizations also need to consider what it means to them to get a new application up and running in ‘x’ hours on the cloud versus a couple of weeks, even months on traditional platforms.
- Also, the person-hour cost efficiencies increases from using cloud dashboards, real-time statistics, and active analytics.
Risk Exposure
- Organizations need to consider the impact of making a wrong decision – their risk exposure.
- Is it safer for an organization to work on a 12-month plan to build, write, test, and release the code if they’re certain about adoption?
- And is it better for them to “try” something new paying-as-you-go rather than making long-term decisions based on little or no trial or adoption?
Benefits of cloud adoption
- Flexibility
- Efficiency
- Strategic Value
Challenges of cloud adoption
- Data security, associated with loss or unavailability of data causing business disruption
- Governance and sovereignty issues
- Legal, regulatory, and compliance issues
- Lack of standardization in how the constantly evolving technologies integrate and interoperate
- Choosing the right deployment and service models to serve specific needs
- Partnering with the right cloud service providers
- Concerns related to business continuity and disaster recovery
Key Cloud Service Providers and Their Services
Future of Cloud Computing
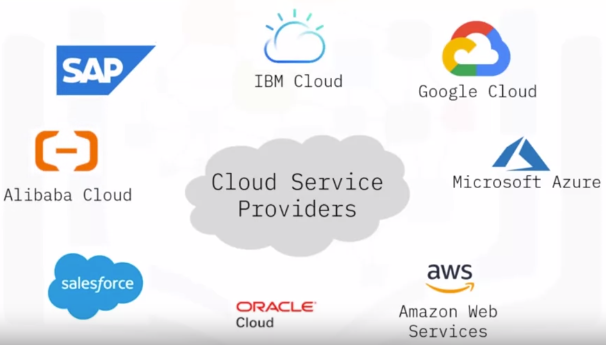
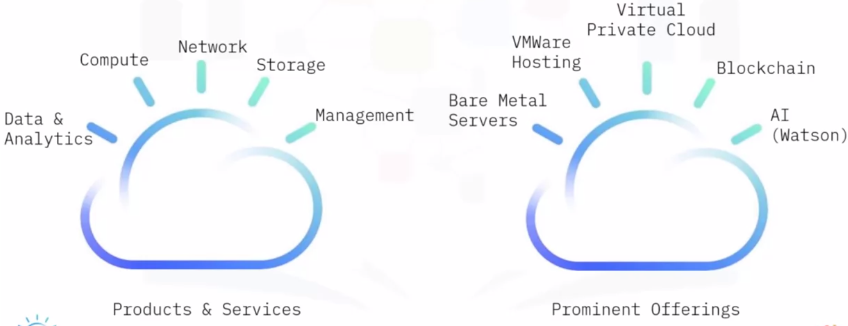
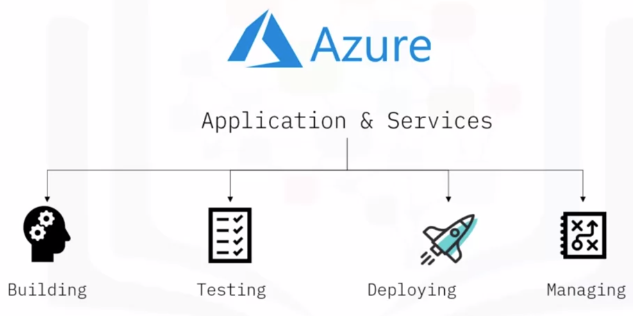
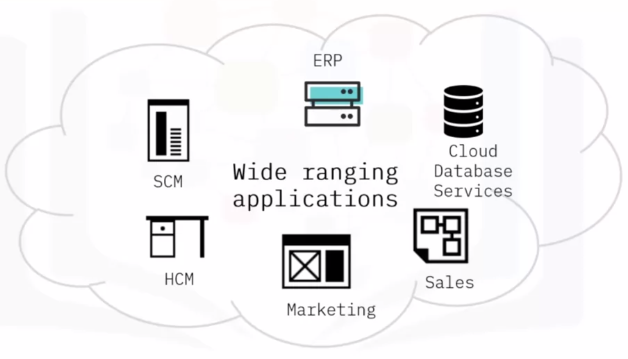
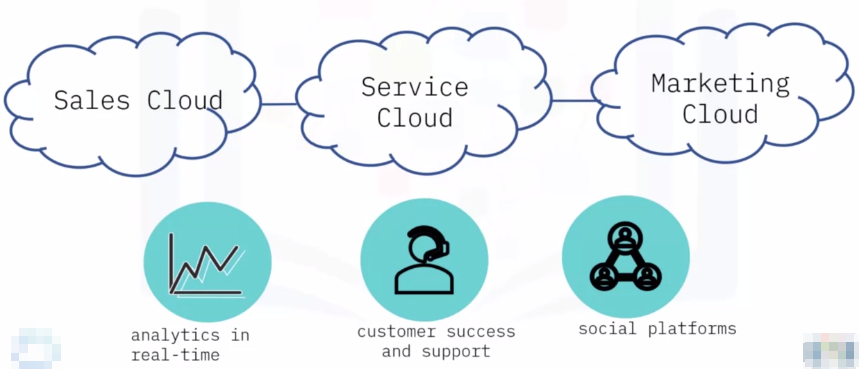
Cloud Service Providers
Alibaba Cloud
Amazon Web Services
Google Cloud Platform
IBM Cloud
Microsoft Azure
Oracle Cloud
Salesforce
SAP
Business Case for Cloud Computing
Cloud Adoption – No longer a choice
- It is no longer a thing of the future
Single individual to Global multi-billion dollar enterprise, anybody can access the computing capacity they need on the cloud.
Cloud makes it possible for businesses to:
- Experiment
- Fail
- Learn Faster than ever before with low risk.
- Businesses today have greater freedom to change course than to live with the consequences of expensive decisions taken in the past.
- To remain, competitive, businesses need to be able to respond quickly to marketplace changes.
- Product lifecycles have shortened, and barriers to entry have become lower.
- The power, scalability, flexibility, and pay-as-you-go economics of cloud has made it underpinning foundation for digital transformation.
Emerging Technologies Accelerated by Cloud
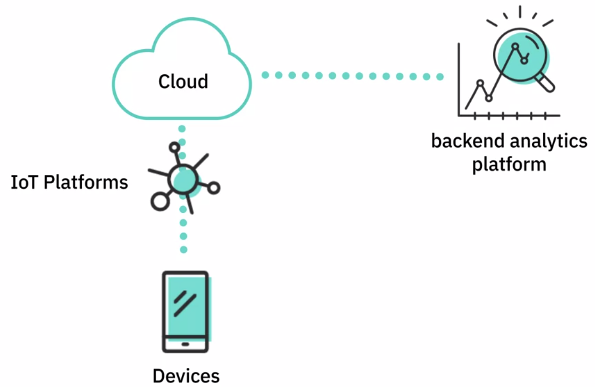
Internet of Things in the Cloud
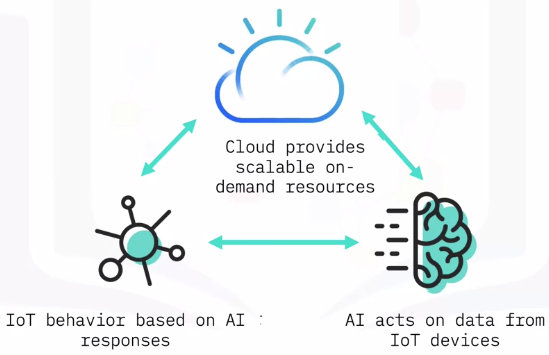
Artificial Intelligence on the Cloud
AI, IoT, and the Cloud
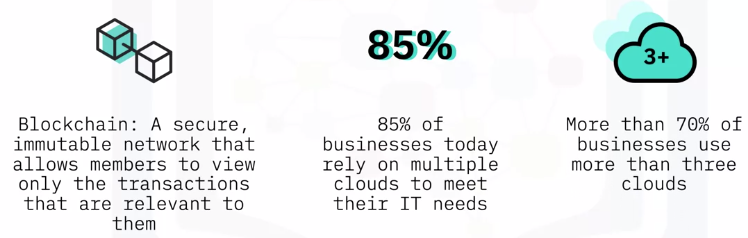
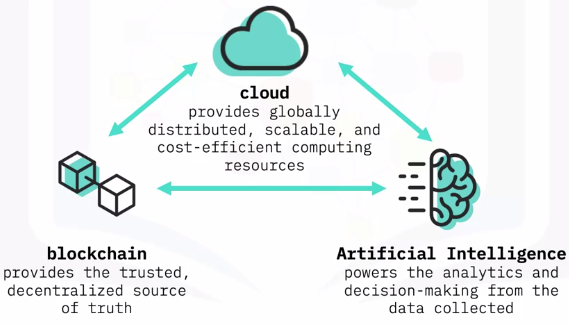
BlockChain and Analytics in the Cloud
Blockchain & Cloud
A 3-Way Relationship
Analytics on the Cloud
How can analytics technology leverage the cloud?
- Track trends on social media to predict future events
- Analyze data to build machine learning models in cognitive applications
- Data analytics and predictions maintenance solutions for city infrastructure
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.